Abstract
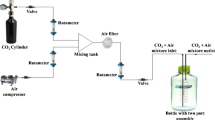
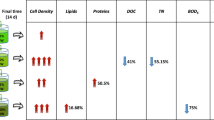
Microalgae have become promising microorganisms for generating high-value commercial products and removing pollutants in aquatic systems. This research evaluated the impact of sunlight intensity on intracellular pigment generation and phosphorus removal from secondary effluents by autoflocculating microalgae consortium BR-UANL-01 in photobioreactor culture. Microalgae were grown in a secondary effluent from a wastewater treatment plant, using a combination of low and high light conditions (photon irradiance; 44 μmol m−2 s−1 and ≈ 1270 μmol m−2 s−1, respectively) and 16:8 h light:dark and 24:0 h light:dark (subdivided into 18:6 LED:sunlight) photoperiods. The autoflocculant rate by consortium BR-UANL-01 was not affected by light intensity and achieved 98% in both treatments. Microalgae produced significantly more lutein, (2.91 mg g−1) under low light conditions. Phosphate removal by microalgae resulted above 85% from the secondary effluent, due to the fact that phosphorus is directly associated with metabolic and replication processes and the highest antioxidant activity was obtained in ABTS•+ assay by the biomass under low light condition (51.71% μmol ET g−1). In conclusion, the results showed that the autoflocculating microalgae consortium BR-UANL-01 is capable of synthesizing intracellular lutein, which presents antioxidant activity, using secondary effluents as a growth medium, without losing its autoflocculating activity and assimilating phosphorus.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this study is publicly accessible and can be found in the REPOSITORIO ACADÉMICO DIGITAL, Data Repository at the following URL: http://eprints.uanl.mx/id/eprint/17880. There are no restrictions on accessing this data, and researchers are encouraged to use it to verify the results presented in this article. For any further inquiries, please contact the main author, EA Fariz-Salinas, at edwin.fariz02@gmail.com.
References
Ahmed SF, Mofijur M, Parisa TA, Islam N, Kusumo F, Inayat A, Ong HC (2022) Progress and challenges of contaminate removal from wastewater using microalgae biomass. Chemosphere 286:131656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131656
Alves-Rodrigues A, Shao A (2004) The science behind lutein. Toxicol Lett 150:57–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.10.031
Amaro HM, Pagels F, Azevedo IC, Azevedo J, Sousa Pinto I, Malcata FX, Guedes A (2020) Light-emitting diodes—a plus on microalgae biomass and high-value metabolite production. J Appl Phycol 32(6):3605–3618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02212-2
Arun J, Avinash U, ArunKrishna B, Pandimadevi M, Gopinath KP (2017) Ultrasound assisted enhanced extraction of lutein (β, ε-carotene-3, 3’-diol) from Mircroalga (Chlorella pyrenoidosa) grown in wastewater: optimization through response surface methodology. Glob Nest J 19(4):574–583. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnj.002415
Beltrán-Rocha JC, Guajardo-Barbosa C, Barceló-Quintal ID, López-Chuken UJ (2017) Biotratamiento de efluentes secundarios municipales utilizando microalgas: efecto del pH, nutrientes (C, N y P) y enriquecimiento con CO2. Rev Viol Mar Oceanogr 52(3):417–427. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-19572017000300001
Beltrán-Rocha JC, Barceló-Quintal ID, García-Martínez M, Osornio-Berthet L, Saavedra-Villarreal N, Villarreal-Chiu J, Javier López-Chuken U (2017b) Polishing of municipal secondary effluent using native microalgae consortia. Water Sci Technol 75:1693–1701. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.046
Beltrán-Rocha JC, Guajardo-Barbosa C, Rodríguez-Fuentes H, Reyna-Martínez GR, Osornio-Berthet L, García-Martínez M, López-Chuken UJ (2021) Some implications of natural increase of pH in microalgae cultivation and harvest by autoflocculation. Latin Am J Aquatic Res 49(5):836–842. https://doi.org/10.3856/vol49-issue5-fulltext-2691
Bohutskyi P, Kligerman DC, Byers N, Nasr LK, Cua C, Chow S, Bouwer EJ (2016) Effects of inoculum size, light intensity, and dose of anaerobic digestion centrate on growth and productivity of Chlorella and Scenedesmus microalgae and their polyculture in primary and secondary wastewater. Algal Res 19:278–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.09.010
Castro-López C, Ventura-Sobrevilla JM, González-Hernández MD, Rojas R, Ascacio-Valdés JA, Aguilar CN, Martínez-Ávila GC (2017) Impact of extraction techniques on antioxidant capacities and phytochemical composition of polyphenol-rich extracts. Food Chem 237:1139–1148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.06.032
Chan M-C, Ho S-H, Lee D-J, Chen C-Y, Huang C-C, Chang J-S (2013) Characterization, extraction and purification of lutein produced by an indigenous microalga Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N. Biochem Eng J 78:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2012.11.017
Chen JH, Chen CY, Chang JS (2017) Lutein production with wild-type and mutant strains of Chlorella sorokiniana MB-1 under mixotrophic growth. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 79:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.04.022
Chen CY, Lu IC, Nagarajan D, Chang CH, Ng IS, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2018) A highly efficient two-stage cultivation strategy for lutein production using heterotrophic culture of Chlorella sorokiniana MB-1-M12. Biores Technol 253:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.027
Chen JH, Chen CY, Hasunuma T, Kondo A, Chang CH, Ng IS, Chang JS (2019) Enhancing lutein production with mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella sorokiniana MB-1-M12 using different bioprocess operation strategies. Biores Technol 278:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.041
Correll DL (1998) The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: a review. J Environ Qual 27(2):261–266. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1998.00472425002700020004x
De Bhowmick G, Sarmah AK, Sen R (2019) Performance evaluation of an outdoor algal biorefinery for sustainable production of biomass, lipid and lutein valorizing flue-gas carbon dioxide and wastewater cocktail. Biores Technol 283:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.075
Del Campo JA, García-González M, Guerrero MG (2007) Outdoor cultivation of microalgae for carotenoid production: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74(6):1163–1174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0844-9
Del Rio-Chanona EA, Ahmed NR, Zhang D, Lu Y, Jing K (2017) Kinetic modeling and process analysis for Desmodesmus sp. lutein photo-production. AIChE J 63(7):2546–2554. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.15667
Devi ND, Mukherjee C, Bhatt G, Rangan L, Goud VV (2022) Co-cultivation of microalgae-cyanobacterium under various nitrogen and phosphorus regimes to concurrently improve biomass, lipid accumulation and easy harvesting. Biochem Eng J 188:108706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2022.108706
Devi ND, Sun X, Hu B, Goud VV (2023) Bioremediation of domestic wastewater with microalgae-cyanobacteria co-culture by nutritional balance approach and its feasibility for biodiesel and animal feed production. Chem Eng J 454:140197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140197
Faraloni C, Torzillo G (2017) Synthesis of antioxidant carotenoids in microalgae in response to physiological stress. Carotenoids. IntechOpen, London, pp 143–157. https://doi.org/10.5772/67843
Fernandes TV, Suárez-Muñoz M, Trebuch LM, Verbraak PJ, Van de Waal DB (2017) Toward an ecologically optimized N: P recovery from wastewater by microalgae. Front Microbiol 8:1742. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01742
Franchino M, Comino E, Bona F, Riggio VA (2013) Growth of three microalgae strains and nutrient removal from an agro-zootechnical digestate. Chemosphere 92(6):738–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04.023
Fu W, Guðmundsson Ó, Paglia G, Herjólfsson G, Andrésson ÓS, Palsson BØ, Brynjólfsson S (2013) Enhancement of carotenoid biosynthesis in the green microalga Dunaliella salina with light-emitting diodes and adaptive laboratory evolution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(6):2395–2403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4502-5
Gatamaneni Loganathan B, Orsat V, Lefsrud M, Wu BS (2020) A comprehensive study on the effect of light quality imparted by light-emitting diodes (LEDs) on the physiological and biochemical properties of the microalgal consortia of Chlorella variabilis and Scenedesmus obliquus cultivated in dairy wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43(8):1445–1455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02338-0
Gayathri S, Rajasree Radhika SR, Suman TY, Aranganathan L (2018) Ultrasound-assisted microextraction of β, ε-carotene-3, 3′-diol (lutein) from marine microalgae Chlorella salina: effect of different extraction parameters. Biomass Conv Bioref 8(4):791–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-018-0331-9
Gayathri S, Rajasree SR, Suman TY, Aranganathan L, Thriuganasambandam R, Narendrakumar G (2021) Induction of β, ε-carotene-3, 3′-diol (lutein) production in green algae Chlorella salina with airlift photobioreactor: interaction of different aeration and light-related strategies. Biomass Conv Bioref 11(5):2003–2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-019-00580-5
Gonçalves AL, Pires JC, Simões M (2017) A review on the use of microalgal consortia for wastewater treatment. Algal Res 24:403–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.11.008
Ho SH, Chan MC, Liu CC, Chen CY, Lee WL, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2014) Enhancing lutein productivity of an indigenous microalga Scenedesmus obliquus FSP-3 using light-related strategies. Biores Technol 152:275–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.11.031
Hu J, Nagarajan D, Zhang Q, Chang JS, Lee DJ (2018) Heterotrophic cultivation of microalgae for pigment production: a review. Biotechnol Adv 36(1):54–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.09.009
Jahns P, Holzwarth AR (2012) The role of the xanthophyll cycle and of lutein in photoprotection of photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Bioenerg 1817(1):182–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.04.012
Kube M, Jefferson B, Fan L, Roddick F (2018) The impact of wastewater characteristics, algal species selection and immobilisation on simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Algal Res 31:478–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.01.009
Lee N, Ko SR, Ahn CY, Oh HM (2018) Optimized co-production of lipids and carotenoids from Ettlia sp. by regulating stress conditions. Biores Technol 258:234–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.006
Liber JA, Bryson AE, Bonito G, Du ZY (2020) Harvesting microalgae for food and energy products. Small Methods 4(10):2000349. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202000349
Lin JH, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2015) Lutein production from biomass: marigold flowers versus microalgae. Biores Technol 184:421–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.099
López-Chuken UJ, Young SD (2010) Modelling sulphate-enhanced cadmium uptake by Zea mays from nutrient solution under conditions of constant free Cd2+ ion activity. J Environ Sci 22(7):1080–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60220-5
Mohsenpour SF, Hennige S, Willoughby N, Adeloye A, Gutierrez T (2021) Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 752:142168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142168
Molino A, Mehariya S, Karatza D, Chianese S, Iovine A, Casella P, Musmarra D (2019) Bench-scale cultivation of microalgae Scenedesmus almeriensis for CO2 capture and lutein production. Energies 12(14):2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12142806
Molino A, Mehariya S, Iovine A, Casella P, Marino T, Karatza D, Musmarra D (2020) Enhancing biomass and Lutein production from Scenedesmus almeriensis: effect of carbon dioxide concentration and culture medium reuse. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00415
Nguyen TDP, Tran TNT, Le TVA, Phan TXN, Show PL, Chia SR (2019) Auto-flocculation through cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris in seafood wastewater discharge: influence of culture conditions on microalgae growth and nutrient removal. J Biosci Bioeng 127(4):492–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.09.004
Nwoba EG, Ogbonna CN, Ishika T, Vadiveloo A (2020) Microalgal pigments: a source of natural food colors. Microalgae biotechnology for food, health and high value products. Springer, Singapore, pp 81–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0169-2_3
Ortiz D, Ferruzzi MG (2019) Identification and quantification of carotenoids and tocochromanols in sorghum grain by high-performance liquid chromatography. Sorghum. Humana Press, New York, pp 141–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9039-9_10
Patil L, Kaliwal BB (2019) Microalga Scenedesmus bajacalifornicus BBKLP-07, a new source of bioactive compounds with in vitro pharmacological applications. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42(6):979–994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02099-5
Pereira S, Otero A (2019) Effect of light quality on carotenogenic and non-carotenogenic species of the genus Dunaliella under nitrogen deficiency. Algal Res 44:101725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2019.101725
Pérez-Gálvez A, Viera I, Roca M (2020) Carotenoids and chlorophylls as antioxidants. Antioxidants 9(6):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060505
Prior RL, Cao G (1999) In vivo total antioxidant capacity: comparison of different analytical methods1. Free Radical Biol Med 27(11–12):1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00203-8
Rashid N, Rehman MSU, Sadiq M, Mahmood T, Han JI (2014) Current status, issues and developments in microalgae derived biodiesel production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 40:760–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.104
Reportlinker (2021) Global Lutein Industry. Global Industry Analysts. https://www.reportlinker.com/p05896164/Global-Lutein-Industry.html Searched on 25 Feb 2021
Safafar H, Van Wagenen J, Møller P, Jacobsen C (2015) Carotenoids, phenolic compounds and tocopherols contribute to the antioxidative properties of some microalgae species grown on industrial wastewater. Mar Drugs 13(12):7339–7356. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13127069
Saha SK, Kazipet N, Murray P (2018) The carotenogenic Dunaliella salina CCAP 19/20 produces enhanced levels of carotenoid under specific nutrients limitation. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7532897
Saini DK, Chakdar H, Pabbi S, Shukla P (2020) Enhancing production of microalgal biopigments through metabolic and genetic engineering. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 60(3):391–405. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1533518
Schipper K, Das P, Al Muraikhi M, AbdulQuadir M, Thaher MI, Al Jabri HMSJ, Wijffels RH, Barbosa MJ (2021) Outdoor scale-up of Leptolyngbya sp.: Effect of light intensity and inoculum volume on photoinhibition and oxidation. Biotechnol Bioeng 118:2368–2379. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.27750
Shahid A, Malik S, Zhu H, Xu J, Nawaz MZ, Nawaz S, Mehmood MA (2020) Cultivating microalgae in wastewater for biomass production, pollutant removal, and atmospheric carbon mitigation; a review. Sci Total Environ 704:135303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135303
Solovchenko AE, Khozin-Goldberg I, Didi-Cohen S, Cohen Z, Merzlyak MN (2008) Effects of light and nitrogen starvation on the content and composition of carotenoids of the green microalga Parietochloris incisa. Russ J Plant Physiol 55(4):455–462. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443708040043
van Lent DM, Leermakers ET, Darweesh SK, Moreira EM, Tielemans MJ, Muka T, Franco OH (2016) The effects of lutein on respiratory health across the life course: a systematic review. Clin Nutr ESPEN 13:e1–e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2016.02.096
Vuolo MM, Lima VS, Junior MRM (2019) Phenolic compounds: structure, classification, and antioxidant power. Bioactive compounds. Woodhead Publishing, pp 33–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814774-0.00002-5
Wan C, Chen BL, Zhao XQ, Bai FW (2019) Stress response of microalgae and its manipulation for development of robust strains. Microalgae biotechnology for development of biofuel and wastewater treatment. Springer, Singapore, pp 95–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2264-8_5
Xie Y, Ho SH, Chen CNN, Chen CY, Ng IS, Jing KJ, Lu Y (2013) Phototrophic cultivation of a thermo-tolerant Desmodesmus sp. for lutein production: effects of nitrate concentration, light intensity and fed-batch operation. Bioresour Technol 144:435–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.064
Xie YP, Ho SH, Chen CY, Chen CNN, Liu CC, Ng IS, Lu YH (2014) Simultaneous enhancement of CO2 fixation and lutein production with thermo-tolerant Desmodesmus sp. F51 using a repeated fed-batch cultivation strategy. Biochem Eng J 86:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.02.015
Xie Y, Li J, Ho SH, Ma R, Shi X, Liu L, Chen J (2020) Pilot-scale cultivation of Chlorella sorokiniana FZU60 with a mixotrophy/photoautotrophy two-stage strategy for efficient lutein production. Biores Technol 314:123767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123767
Xu Y, Ibrahim IM, Harvey PJ (2016) The influence of photoperiod and light intensity on the growth and photosynthesis of Dunaliella salina (chlorophyta) CCAP 19/30. Plant Physiol Biochem 106:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.021
Yang C, Fischer M, Kirby C, Liu R, Zhu H, Zhang H, Tsao R (2018) Bioaccessibility, cellular uptake and transport of luteins and assessment of their antioxidant activities. Food Chem 249:66–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.12.055
Yarkent Ç, Gürlek C, Oncel SS (2020) Potential of microalgal compounds in trending natural cosmetics: a review. Sustain Chem Pharm 17:100304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100304
Yuan H, Zhang X, Jiang Z, Wang X, Wang Y, Cao L, Zhang X (2020) Effect of light spectra on microalgal biofilm: Cell growth, photosynthetic property, and main organic composition. Renew Energy 157:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.109
Zabochnicka-Świątek M, Kamizela T, Kowalczyk M, Kalaji HM, Bąba W (2019) Inexpensive and universal growth media for biomass production of microalgae. Glob Nest J 21(1):82–89. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnj.002558
Zhao X, Ma R, Liu X, Ho SH, Xie Y, Chen J (2019) Strategies related to light quality and temperature to improve lutein production of marine microalga Chlamydomonas sp. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42(3):435–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-2047-4
Zheng H, Wang Y, Li S, Nagarajan D, Varjani S, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2022) Recent advances in lutein production from microalgae. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 153:111795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111795
Acknowledgements
This work received financial support from Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León (UANL), The authors are thankful to the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT) for partially supporting this research under the Sistema Nacional de Investigadores (SNI) program awarded to Ulrico Javier López-Chuken (CVU:37277) and Carlos Castillo-Zacarías (CVU:359310). Special thanks are extended to the Environmental Sciences Laboratory of the Instituto Tecnológico de Nuevo León. Carlos Castillo-Zacarías acknowledges the support of the Red Científica por Nuevo León.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
UJL-C and BL-Ro conceived the presented idea and supervised the project. GCGM-Áa and MEC-C verified the analytical methods. JCB-R, CC-Z, and CG-B supported all the technical details for the experiments performed. EAF-S performed the calculations, culture experiments, and HPLC test and wrote the manuscript. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fariz-Salinas, E.A., Limón-Rodríguez, B., Beltrán-Rocha, J.C. et al. Effect of light stress on lutein production with associated phosphorus removal from a secondary effluent by the autoflocculating microalgae consortium BR-UANL-01. 3 Biotech 14, 23 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03810-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03810-w