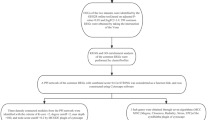
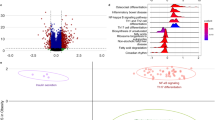
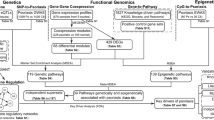
Abstract
Patients with psoriasis often complain of several linked disorders including autoimmune and cardiometabolic diseases. Understanding of molecular link between psoriasis and associated comorbidities would be of great interest at the point of patient care management. Integrative unbiased network approach, indicates significant unidirectional gene overlap between psoriasis and its associated comorbid condition including obesity (31 upregulated and 26 downregulated), ischemic stroke (14 upregulated and 2 downregulated), dyslipidaemia (5 upregulated, 5 downregulated), atherosclerosis (8 upregulated and 1 downregulated) and type II diabetes (5 upregulated, 5 downregulated). The analysis revealed substantial gene sharing among the different psoriasis-associated comorbidities. Molecular comorbidity index determining the strength of the interrelation between psoriasis and its comorbidities indicates prevalence of dyslipidaemia followed by type II diabetes among psoriasis patients. The Jaccard coefficient indices revealed psoriasis shared maximum number of biological pathways with dyslipidaemia followed by type 2 diabetes, ischemic stroke, obesity and atherosclerosis. Moreover, pathway annotation highlighted nearly 45 shared pathways amongst psoriasis and its comorbidities and a substantial number of shared pathways was found among multi-morbidities. Overall, the present study established conceivable link between psoriasis and comorbid diseases. The shared genes and overlapped pathways may be explored as a common productive target for psoriasis and its comorbid conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The relevant data is provided in the manuscript and in case some other data that supports the finding of this study is required, it is accessible from the corresponding authors (Dr. Neeraj Kumar and Dr. Dibyabhaba Pradhan) upon request.
References
Alzamil H (2020) Elevated serum TNF-α is related to obesity in type 2 diabetes mellitus and is associated with glycemic control and insulin resistance. J Obes 2020:e5076858. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5076858
Barabási AL, Gulbahce N, Loscalzo J (2011) Network medicine: a network-based approach to human disease. Nat Rev Genet 12:56–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2918
Bigler J, Rand HA, Kerkof K, Timour M, Russell CB (2013) Cross-study homogeneity of psoriasis gene expression in skin across a large expression range. PLoS ONE 8:e52242
Carow B, Rottenberg ME (2014) SOCS3, a Major Regulator of Infection and Inflammation. Front Immunol 5:58. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00058
Carvalho-Silva D, Pierleoni A, Pignatelli M, Ong C, Fumis L, Karamanis N, Carmona M, Faulconbridge A, Hercules A, McAuley E, Miranda A, Peat G, Spitzer M, Barrett J, Hulcoop DG, Papa E, Koscielny G, Dunham I (2019) Open Targets Platform: new developments and updates two years on. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D1056–D1065. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1133
Choudhary S, Pradhan D, Pandey A, Khan MK, Lall R, Ramesh V, Puri P, Jain AK, Thomas G (2019) The association of metabolic syndrome and psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational study. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 20:703–717. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530319666191008170409
Choudhary S, Patel R, Pradhan D, Deval R, Singh H, Thomas G, Jain AK (2020) Psoriasis and cardiovascular disorders: association or epiphenomenon? Meta-analysis of observational studies. 3 Biotech 10:104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2089-6
Egeberg A (2017) Getting tired of psoriasis? Br J Dermatol 177:899–900. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.15741
El-Boghdady NA, Ismail MF, Abd-Alhameed MF, Ahmed AS, Ahmed HH (2017) Bidirectional association between psoriasis and obesity: benefits and risks. J Interferon Cytokine Res 38:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2017.0105
Forrester HB, Temple-Smith P, Ham S, de Kretser D, Southwick G, Sprung CN (2013) Genome-wide analysis using exon arrays demonstrates an important role for expression of extra-cellular matrix, fibrotic control and tissue remodelling genes in Dupuytren’s disease. PLoS ONE 8:e59056. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059056
Furlong LI (2013) Human diseases through the lens of network biology. Trends Genet 29:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2012.11.004
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) Affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20:307–315. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg405
Gonzalez-Cantero A, Gonzalez-Cantero J, Sanchez-Moya AI, Perez-Hortet C, Arias-Santiago S, Schoendorff-Ortega C, Gonzalez-Calvin JL (2019) Subclinical atherosclerosis in psoriasis. Usefulness of femoral artery ultrasound for the diagnosis, and analysis of its relationship with insulin resistance. PLoS ONE 14:e0211808. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211808
Gruzdeva OV, Akbasheva OE, Dyleva YuA, Antonova LV, Matveeva VG, Uchasova EG, Fanaskova EV, Karetnikova VN, Ivanov SV, Barbarash OL (2017) Adipokine and cytokine profiles of epicardial and subcutaneous adipose tissue in patients with coronary heart disease. Bull Exp Biol Med 163:608–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3860-5
Holm JG, Thomsen SF (2019) Type 2 diabetes and psoriasis: links and risks. Psoriasis (auckl) 9:1–6. https://doi.org/10.2147/PTT.S159163
Krug T, Gabriel JP, Taipa R, Fonseca BV, Domingues-Montanari S, Fernandez-Cadenas I, Manso H, Gouveia LO, Sobral J, Albergaria I, Gaspar G, Jiménez-Conde J, Rabionet R, Ferro JM, Montaner J, Vicente AM, Silva MR, Matos I, Lopes G, Oliveira SA (2012) TTC7B emerges as a novel risk factor for ischemic stroke through the convergence of several genome-wide approaches. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1061–1072. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2012.24
Meephansan J, Subpayasarn U, Ohtsuki MK (2017) Pathogenic role of cytokines and effect of their inhibition in psoriasis. In: Chiriac A (ed) An interdisciplinary approach to psoriasis, vol 41. IntechOpen, Rijeka. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.68421
Miao C, Li J, Li Y, Zhang X (2019) Obesity and dyslipidemia in patients with psoriasis: a case-control study. Medicine (baltimore) 98:e16323. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000016323
Misu H, Takamura T, Takayama H, Hayashi H, Matsuzawa-Nagata N, Kurita S, Ishikura K, Ando H, Takeshita Y, Ota T, Sakurai M, Yamashita T, Mizukoshi E, Yamashita T, Honda M, Miyamoto K, Kubota T, Kubota N, Kadowaki T, Kim H-J, Lee I, Minokoshi Y, Saito Y, Takahashi K, Yamada Y, Takakura N, Kaneko SA (2010) Liver-derived secretory protein, selenoprotein P, causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab 12:483–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.09.015
Morelli M, Scarponi C, Mercurio L, Facchiano F, Pallotta S, Madonna S, Girolomoni G, Albanesi C (2018) Selective immunomodulation of inflammatory pathways in keratinocytes by the janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib: implications for the employment of JAK-targeting drugs in psoriasis. J Immunol Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7897263
Mosig S, Rennert K, Büttner P, Krause S, Lütjohann D, Soufi M, Heller R, Funke H (2008) Monocytes of patients with familial hypercholesterolemia show alterations in cholesterol metabolism. BMC Med Genomics 1:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8794-1-60
Oñate B, Vilahur G, Camino-López S, Díez-Caballero A, Ballesta-López C, Ybarra J, Moscatiello F, Herrero J, Badimon L (2013) Stem cells isolated from adipose tissue of obese patients show changes in their transcriptomic profile that indicate loss in stemcellness and increased commitment to an adipocyte-like phenotype. BMC Genomics 14:625. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-625
Oughtred R, Stark C, Breitkreutz BJ, Rust J, Boucher L, Chang C, Kolas N, O’Donnell L, Leung G, McAdam R, Zhang F, Dolma S, Willems A, Coulombe-Huntington J, Chatr-Aryamontri A, Dolinski K, Tyers M (2019) The BioGRID interaction database: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D529–D541. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1079
Perez-Llamas C, Lopez-Bigas N (2011) Gitools: analysis and visualisation of genomic data using interactive heat-maps. PLoS ONE 6:e19541. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019541
Piñero J, Bravo À, Queralt-Rosinach N, Gutiérrez-Sacristán A, Deu-Pons J, Centeno E, García-García J, Sanz F, Furlong LI (2017) DisGeNET: a comprehensive platform integrating information on human disease-associated genes and variants. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D833–D839. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw943
Prajapati B, Jena PK, Rajput P, Purandhar K, Seshadri S (2014) Understanding and modulating the toll like receptors (TLRs) and NOD like receptors (NLRs) cross talk in type 2 diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev 10:190–200. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573399810666140515112609
Sepehri Z, Kiani Z, Nasiri AA, Kohan F (2016) Toll-like receptor 2 and type 2 diabetes. Cell Mol Biol Lett 21:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-016-0002-4
Siddiqi HK, Ridker PM (2018) Psoriasis and atherosclerosis. Circ Res 123:1183–1184. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314073
Snekvik I, Nilsen TIL, Romundstad PR, Saunes M (2019) Metabolic syndrome and risk of incident psoriasis: prospective data from the HUNT Study, Norway. Br J Dermatol 180:94–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.16885
Sun C, Yuan Q, Wu D, Meng X, Wang B (2017) Identification of core genes and outcome in gastric cancer using bioinformatics analysis. Oncotarget 8:70271–70280. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20082
Sundarrajan S, Arumugam M (2016) Comorbidities of psoriasis—exploring the links by network approach. PLoS ONE 11:e0149175. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149175
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M, Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, Jensen LJ, von Mering C (2017) The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein–protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D362–D368. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw937
Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, Mehta NN, Ogdie A, Van Voorhees AS, Gelfand JM (2017) Psoriasis and comorbid diseases: epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol 76:377–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.07.064
Tan X, Zhang X, Pan L, Tian X, Dong P (2017) Identification of key pathways and genes in advanced coronary atherosclerosis using bioinformatics analysis. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4323496
Tantiwong P, Shanmugasundaram K, Monroy A, Ghosh S, Li M, DeFronzo RA, Cersosimo E, Sriwijitkamol A, Mohan S, Musi N (2010) NF-ΚB activity in muscle from obese and type 2 diabetic subjects under basal and exercise-stimulated conditions. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299:E794–E801. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00776.2009
Wang Y, Zheng T (2014) Screening of hub genes and pathways in colorectal cancer with microarray technology. Pathol Oncol Res 20:611–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9739-5
Wang C, Gong B, Bushel PR, Thierry-Mieg J, Thierry-Mieg D, Xu J, Fang H, Hong H, Shen J, Su Z, Meehan J, Li X, Yang L, Li H, Łabaj PP, Kreil DP, Megherbi D, Gaj S, Caiment F, van Delft J, Kleinjans J, Scherer A, Devanarayan V, Wang J, Yang Y, Qian HR, Lancashire LJ, Bessarabova M, Nikolsky Y, Furlanello C, Chierici M, Albanese D, Jurman G, Riccadonna S, Filosi M, Visintainer R, Zhang KK, Li J, Hsieh JH, Svoboda DL, Fuscoe JC, Deng Y, Shi L, Paules RS, Auerbach SS, Tong W (2014) The concordance between RNA-Seq and microarray data depends on chemical treatment and transcript abundance. Nat Biotechnol 32:926–932. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3001
Wolk K, Sabat R (2016) Adipokines in psoriasis: an important link between skin inflammation and metabolic alterations. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 17:305–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-016-9381-0
Xiao L, Ming H, Tao C, Yuliang W (2011) The expression of SOCS is altered in atherosclerosis. Heart 97:A51–A51. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2011-300867.146
Zhang S, Gang X, Yang S, Cui M, Sun L, Li Z, Wang G (2021) The alterations in and the role of the Th17/Treg balance in metabolic diseases. Front Immunol 12:678355. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.678355
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support from the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi [grant number: ISRM/12(117)/2020 (ID No. 2020-4900)] for conducting the study. We also acknowledge financial and administrative support from ICMR-National Institute of Pathology, New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC is credited with designing, data acquisition, analysis, interpretation, drafting and revision of the script. NSK and RV is credited with critical inputs, interpretation, data acquisition and analysis. PS is credited with analysis and revision of the script. HS and AKJ contributed in analysis, interpretation and revision of the script. GT aided in data acquisition, drafting and revision of the script. DBP and NK aided with supervision, conceptualization, interpretation and analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, S., Khan, N.S., Verma, R. et al. Exploring the molecular underpinning of psoriasis and its associated comorbidities through network approach: cross talks of genes and pathways. 3 Biotech 13, 130 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03533-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03533-y