Abstract
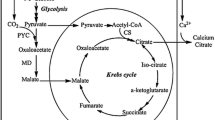
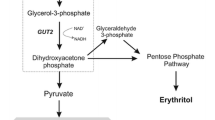
The present study aims to increase pyruvate production by engineering Yarrowia lipolytica through modifying the glycerol metabolic pathway. Results: Wild-type Yarrowia lipolytica (Po1d) was engineered to produce six different strains, namely ZS099 (by over-expressing PYK1), ZS100 (by deleting DGA2), ZS101 (by over-expressing DAK1, DAK2, and GCY1), ZS102 (by over-expressing GUT1 and GUT2), ZS103 (by over-expressing GUT1) and ZSGP (by over-expressing POS5 and deleting GPD2). Production of pyruvate from engineered and control strains was determined using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Subsequently, the fermentation conditions for producing pyruvate were optimized, including the amount of initial inoculation, the addition of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), thiamine and glycerol. Finally, for scaled-up purposes, a 20-L fermentor was used. It was observed that pyruvate production increased by 136% (8.55 g/L) in ZSGP strain compared to control (3.62 g/L). Furthermore, pyruvate production by ZSGP reached up to 110.4 g/L in 96 h in the scaled-up process. We conclude that ZSGP strain of Y. lipolytica can be effectively used for pyruvate production at the industrial level.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAK:
-
Dihydroxyacetone kinases
- GUT1:
-
Glycerol kinase
- GUT2:
-
3-Phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase
- GPD:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GPP:
-
Glycerol-1-phosphatase
- GCY1:
-
Glycerol dehydrogenase
- Gly-3-p:
-
Glycerol-3- phosphate
- DHA:
-
1, 3-Dihydroxyacetone
- PYK1:
-
Pyruvate kinase
- POS5:
-
NADH kinase POS5
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- DGA:
-
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase
- DHAP:
-
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
- MPC:
-
Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier
- GAP:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
References
Aßkamp MR, Klein M, Nevoigt E (2019) Saccharomyces cerevisiae exhibiting a modified route for uptake and catabolism of glycerol forms significant amounts of ethanol from this carbon source considered as “non-fermentable.” Biotechnol Biofuels 12(1):257–257. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-019-1597-2
Babazadeh R, Lahtvee P-J, Adiels CB, Goksör M, Nielsen JB, Hohmann S, Naturvetenskapliga f, Faculty of S, Göteborgs u, Gothenburg U, Department of P, Department of C, Molecular B, Institutionen för kemi och m, Institutionen för f (2017) The yeast osmostress response is carbon source dependent. Sci Rep 7(1):990–911. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01141-4
Beopoulos A, Haddouche R, Kabran P, Dulermo T, Chardot T, Nicaud J-M (2012) Identification and characterization of DGA2, an acyltransferase of the DGAT1 acyl-CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase family in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. New insights into the storage lipid metabolism of oleaginous yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(4):1523–1537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3506-x
Bricker DK, Taylor EB, Schell JC, Orsak T, Boutron A, Chen Y-C, Cox JE, Cardon CM, Van Vranken JG, Dephoure N, Redin C, Boudina S, Gygi SP, Brivet M, Thummel CS, Rutter J (2012) A mitochondrial pyruvate carrier required for pyruvate uptake in yeast, drosophila, and humans. Science (american Association for the Advancement of Science) 337(6090):96–100. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1218099
Burke RL, Tekamp-Olson P, Najarian R (1983) The isolation, characterization, and sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 258(4):2193–2201. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)32907-7
Cybulski K, Tomaszewska-Hetman L, Rakicka M, Juszczyk P, Rywińska A (2019) Production of pyruvic acid from glycerol by Yarrowia lipolytica. Folia Microbiol 64(6):809–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00695-2
Friedlander J, Tsakraklides V, Kamineni A, Greenhagen EH, Consiglio AL, MacEwen K, Crabtree DV, Afshar J, Nugent RL, Hamilton MA, Shaw AJ, South CR, Stephanopoulos G, Brevnova EE (2016) Engineering of a high lipid producing Yarrowia lipolytica strain. Biotechnol Biofuels 9(1):77–77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0492-3
Gao C-H, Cao H, Cai P, Sørensen SJ (2021) The initial inoculation ratio regulates bacterial coculture interactions and metabolic capacity. ISME J 15(1):29–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-00751-7
Han HS, Kang G, Kim JS, Choi BH, Koo SH (2016) Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Exp Mol Med 48:e218. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2015.122
Hohmann S (2002) Osmotic stress signaling and osmoadaptation in yeasts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66(2):300–372. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.66.2.300-372.2002
Hollmann R, Deckwer WD (2004) Pyruvate formation and suppression in recombinant Bacillus megaterium cultivation. J Biotechnol 111(1):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.03.006
Jager R, Metzger J, Lautmann K, Shushakov V, Purpura M, Geiss KR, Maassen N (2008) The effects of creatine pyruvate and creatine citrate on performance during high intensity exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 5:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-5-4
Jeon YH, Kim SG, Hwang I, Kim YH (2010) Effects of initial inoculation density of Paenibacillus polymyxa on colony formation and starch-hydrolytic activity in relation to root rot in ginseng. J Appl Microbiol 109(2):461–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04674.x
Ju KD, Shin EK, Cho EJ, Yoon HB, Kim HS, Kim H, Yang J, Hwang Y-H, Ahn C, Oh K-H (2012) Ethyl pyruvate ameliorates albuminuria and glomerular injury in the animal model of diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol-Renal Physiol 302(5):F606–F613. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00415.2011
Kamzolova SV, Morgunov IG (2016) Biosynthesis of pyruvic acid from glucose by Blastobotrys adeninivorans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(17):7689–7697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7618-1
Krzysztof C, Ludwika T-H, Magdalena R, Wojciech L, Waldemar R, Anita R (2018a) The bioconversion of waste products from rapeseed processing into keto acids by Yarrowia lipolytica. Ind Crops Prod 119:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.04.014
Li Y, Chen J, Lun SY (2001) Biotechnological production of pyruvic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57(4):451–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100804
Liu L-M, Li Y, Du G-C, Chen J (2003) CaCO3 stimulates alpha-ketoglutarate accumulation during pyruvate fermentation by Torulopsis glabrata. Shengwu Gongcheng Xuebao 19(6):745–749
Liu L, Xu Q, Li Y, Shi Z, Zhu Y, Du G, Chen J (2007) Enhancement of pyruvate production by osmotic-tolerant mutant of Torulopsis glabrata. Biotechnol Bioeng 97(4):825–832. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.21290
Luo Z, Liu S, Du G, Xu S, Zhou J, Chen J (2018) Enhanced pyruvate production in Candida glabrata by carrier engineering. Biotechnol Bioeng 115(2):473–482. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26477
Maleki N, Eiteman MA (2017) Recent progress in the microbial production of pyruvic acid. Fermentation (basel) 3(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation3010008
McCommis KS, Finck BN (2015a) Mitochondrial pyruvate transport: a historical perspective and future research directions. Biochem J 466(3):443–454. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20141171
McCommis KS, Finck BN (2015b) Mitochondrial pyruvate transport: a historical perspective and future research directions. Biochem J 466(3):443–454. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20141171
Morgunov IG, Kamzolova SV, Perevoznikova OA, Shishkanova NV, Finogenova TV (2004) Pyruvic acid production by a thiamine auxotroph of Yarrowia lipolytica. Process Biochem 39(11):1469–1474. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00259-0
Nissen TL, Hamann CW, Kielland-Brandt MC, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (2000) Anaerobic and aerobic batch cultivations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants impaired in glycerol synthesis. Yeast (chichester, England) 16(5):463–474. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(20000330)16:5%3c463::AID-YEA535%3e3.0.CO;2-3
Papapetridis I, van Dijk M, van Maris AJA, Pronk JT (2017) Metabolic engineering strategies for optimizing acetate reduction, ethanol yield and osmotolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels 10(1):107–107. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0791-3
Pavlik P, Simon M, Schuster T, Ruis H (1993) The glycerol kinase (GUT1) gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: cloning and characterization. Curr Genet 24(1–2):21–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324660
Pearce AK, Crimmins K, Groussac E, Hewlins MJE, Dickinson JR, Francois J, Booth IR, Brown AJP (2001) Pyruvate kinase (Pyk1) levels influence both the rate and direction of carbon flux in yeast under fermentative conditions. Microbiology (society for General Microbiology) 147(2):391–401. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-147-2-391
Plotnikov E, Losenkov I, Epimakhova E, Bohan N (2019) Protective effects of pyruvic acid salt against lithium toxicity and oxidative damage in human blood mononuclear cells. Adv Pharm Bull 9(2):302–306. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2019.035
Ronnow B, Kiellandbrandt MC (1993) GUT2, a gene for mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast (chichester, England) 9(10):1121–1130. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.320091013
Saito H, Posas F (2012) Response to hyperosmotic stress. Genetics (austin) 192(2):289–318. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.112.140863
Soma Y, Tsuruno K, Wada M, Yokota A, Hanai T (2014) Metabolic flux redirection from a central metabolic pathway toward a synthetic pathway using a metabolic toggle switch. Metab Eng 23:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2014.02.008
Tomar A, Eiteman MA, Altman E (2003) The effect of acetate pathway mutations on the production of pyruvate in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62(1):76–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1234-6
Tomàs-Gamisans M, Andrade CCP, Maresca F, Monforte S, Ferrer P, Albiol J (2020) Redox engineering by ectopic overexpression of NADH Kinase in recombinant Pichia pastoris (Komagataella phaffii): Impact on cell physiology and recombinant production of secreted proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02038-19
van Maris AJ, Geertman JM, Vermeulen A, Groothuizen MK, Winkler AA, Piper MD, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2004) Directed evolution of pyruvate decarboxylase-negative Saccharomyces cerevisiae, yielding a C2-independent, glucose-tolerant, and pyruvate-hyperproducing yeast. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(1):159–166. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.1.159-166.2004
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (2009) Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324(5930):1029–1033. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1160809
Wang Q, He P, Lu D, Shen A, Jiang N (2002) Screening of pyruvate-producing yeast and effect of nutritional conditions on pyruvate production. Lett Appl Microbiol 35(4):338–342. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-765x.2002.01188.x
Yuan W, Lin X, Zhong S, Chen J, Wang Z, Sun J (2020) Enhanced pyruvic acid yield in an osmotic stress-resistant mutant of Yarrowia lipolytica. Electron J Biotechnol 44:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2020.01.002
Zahoor A, Küttner FTF, Blank LM, Ebert BE (2019) Evaluation of pyruvate decarboxylase-negative Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains for the production of succinic acid. Eng Life Sci 19(10):711–720. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201900080
Zelic B, Gostovic S, Vuorilehto K, Vasic-Racki D, Takors R (2004) Process strategies to enhance pyruvate production with recombinant Escherichia coli: from repetitive fed-batch to in situ product recovery with fully integrated electrodialysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 85(6):638–646. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.10820
Zeng W, Zhang H, Xu S, Fang F, Zhou J (2017a) Biosynthesis of keto acids by fed-batch culture of Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06. Biores Technol 243:1037–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.063
Zeng W, Zhang H, Xua S, Fang F, Zhou J (2017b) Biosynthesis of keto acids by fed-batch culture of Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06. Biores Technol 243:1037–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.063
Zhang L, Tang Y, Guo Z, Shi G (2013) Engineering of the glycerol decomposition pathway and cofactor regulation in an industrial yeast improves ethanol production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40(10):1153–1160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1311-5
Zhao X, Shi F, Zhan W (2015) Overexpression of ZWF1 and POS5 improves carotenoid biosynthesis in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Lett Appl Microbiol 61(4):354–360. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12463
Zhu Y, Eiteman MA, Altman R, Altman E (2008) High glycolytic flux improves pyruvate production by a metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(21):6649–6655. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01610-08
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. LQ18C010006 and LY19C010005), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 31900497).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Please check the following as appropriate: (a) all authors have participated in (a) conception and design, or analysis and interpretation of the data; (b) drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; and (c) approval of the final version. (b) This manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is under review at another journal or other publishing venue. (c) The authors have no affiliation with any organization with a direct or indirect financial interest in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript. Moral statement: (a) We have no conflict of interest with the editors, reviewers and other personnel of three biotech journals. (b) The subject of our research is microorganisms, which does not involve any human or animal subjects, and does not violate any ethical standards.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Yang, Y., Yu, K. et al. Engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for producing pyruvate from glycerol. 3 Biotech 12, 98 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03158-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03158-7