Abstract
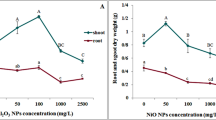
The impact of 100 μg ml−1 alumina (Al2O3) nanoparticles (NPs) on Trigonella foenum (fenugreek) in vitro cultures was studied within 3 weeks (on days 1, 7, 14, and 21) and compared with the control and bulk (macrometer-sized particles) alumina-treated groups. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering were used for the characterization of NPs. The results of TEM analysis represented a nearly spherical shape for the NPs with agglomeration. The zeta potential of alumina NPs was − 25.4 ± 2.5 mV and the averaged diameter was 20 ± 5 nm. Atomic absorption and inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy provided evidence for the release and uptake of aluminum. Treatment of cultures with NPs led to an increase in the formation of lateral roots. Treatment of fenugreek with bulk alumina caused a significant decrease in the number of leaves on day 21 (p < 0.05) and the root length on days 14 and 21 compared with the control group (p < 0.05). Alumina NP has led to a significant increase in the malondialdehyde content on days 7, 14, and 21 (p < 0.001). The glutathione content was decreased significantly in NP and bulk-treated groups on days 1 and 7 (p < 0.05). FRAP assay results showed that NPs and bulk alumina led to a decrease in the antioxidant power on days 7, 14, and 21 (p < 0.001). The increased activity of catalase (p < 0.001) and ascorbate peroxidase (p < 0.001) was observed in the bulk-treated group. Lignin content had a significant increase in response to NPs on days 14 and 21 (p < 0.001). Conclusively, alumina nano/macro particles affected agronomical and physiological properties of T. foenum; however, smaller sized particles do not necessarily imply greater toxicity, while uptake of the aluminum ions should be considered seriously.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NP:
-
Nanoparticles
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- DLS:
-
Dynamic light scattering
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- FRAP:
-
Ferric ion reducing antioxidant power
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- PDI:
-
Polydispersity index
- ENP:
-
Engineered nanoparticles
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- AAS:
-
Atomic absorption spectroscopy
- ICP-OES:
-
Inductive coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy
References
Acharya S, Thomas J, Basu S (2006) Fenugreek: an “old world” crop for the “new world”. Biodiversity 7(3–4):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/14888386.2006.9712808
Ahmed B, Khan MS, Musarrat J (2018) Toxicity assessment of metal oxide nano-pollutants on tomato (Solanum lycopersicon): a study on growth dynamics and plant cell death. Environ Pollut 240:802–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.015
Amako K, Chen GX, Asada K (1994) Separate assays specific for ascorbate peroxidase and guaiacol peroxidase and for the chloroplastic and cytosolic isozymes of ascorbate peroxidase in plants. Plant Cell Physiol 35(3):497–504. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a078621
Amist N, Singh NB, Yadav K, Singh SC, Pandey JK (2017) Comparative studies of Al3+ ions and Al2O3 nanoparticles on growth and metabolism of cabbage seedlings. J Biotechnol 254:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.06.002
Arts JH, Hadi M, Irfan MA, Keene AM, Kreiling R, Lyon D, Maier M, Michel K, Petry T, Sauer UG (2015) A decision-making framework for the grouping and testing of nanomaterials (DF4nanoGrouping). Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 71(2):S1–S27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.03.007
Arts JH, Irfan MA, Keene AM, Kreiling R, Lyon D, Maier M, Michel K, Neubauer N, Petry T, Sauer UG (2016) Case studies putting the decision-making framework for the grouping and testing of nanomaterials (DF4nanoGrouping) into practice. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 76:234–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.11.020
Asztemborska M, Steborowski R, Kowalska J, Bystrzejewska-Piotrowska G (2015) Accumulation of aluminium by plants exposed to nano- and microsized particles of Al2O3. Int J Environ Res 9(1):109–116. https://doi.org/10.22059/ijer.2015.880
Basu SK, Cetzal-IX W, Zandi P (2016) Forage fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) production: a boon for semi-arid agricultural regions. In: VII international scientific agriculture symposium,” Agrosym 2016”, 6–9 Oct 2016, Jahorina, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Proceedings University of East Sarajevo, Faculty of Agriculture
Benzie IF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239(1):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1996.0292
Bhoomika K, Pyngrope S, Dubey R (2013) Differential responses of antioxidant enzymes to aluminum toxicity in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars with marked presence and elevated activity of Fe SOD and enhanced activities of Mn SOD and catalase in aluminum tolerant cultivar. Plant Growth Regul 71(3):235–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-013-9824-5
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Browning BL (1967) Methods of wood chemistry. vol. II. Interscience Publishers, a Division of John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York
de la Rosa G, García-Castañeda C, Vázquez-Núñez E, Alonso-Castro ÁJ, Basurto-Islas G, Mendoza Á, Cruz-Jiménez G, Molina C (2017) Physiological and biochemical response of plants to engineered NMs: implications on future design. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.06.014
Ezaki B, Jayaram K, Higashi A, Takahashi K (2013) A combination of five mechanisms confers a high tolerance for aluminum to a wild species of Poaceae, Andropogon virginicus L. Environ Exp Bot 93:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.05.002
Fathabad AE, Shariatifar N, Moazzen M, Nazmara S, Fakhri Y, Alimohammadi M, Azari A, Khaneghah AM (2018) Determination of heavy metal content of processed fruit products from Tehran’s market using ICP-OES: a risk assessment study. Food Chem Toxicol 115:436–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.03.044
Ghanati F, Morita A, Yokota H (2005) Effects of aluminum on the growth of tea plant and activation of antioxidant system. Plant Soil 276(1–2):133–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-3697-y
Gottschalk F, Sonderer T, Scholz RW, Nowack B (2009) Modeled environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, fullerenes) for different regions. Environ Sci Technol 43(24):9216–9222. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9015553
Goyal S, Gupta N, Chatterjee S (2016) Investigating therapeutic potential of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. as our defense mechanism against several human diseases. J Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1250387
Hatami M, Kariman K, Ghorbanpour M (2016) Engineered nanomaterial-mediated changes in the metabolism of terrestrial plants. Sci Total Environ 571:275–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.184
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125(1):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hemmati S, Schneider B, Schmidt TJ, Federolf K, Alfermann AW, Fuss E (2007) Justicidin B 7-hydroxylase, a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase from cell cultures of Linum perenne Himmelszelt involved in the biosynthesis of diphyllin. Phytochemistry 68(22–24):2736–2743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.10.025
Jin Y, Fan X, Li X, Zhang Z, Sun L, Fu Z, Lavoie M, Pan X, Qian H (2017) Distinct physiological and molecular responses in Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to aluminum oxide nanoparticles and ionic aluminum. Environ Pollut 228:517–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.073
Juhel G, Batisse E, Hugues Q, Daly D, van Pelt FN, O’Halloran J, Jansen MA (2011) Alumina nanoparticles enhance growth of Lemna minor. Aquat Toxicol 105(3):328–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.06.019
Karunakaran G, Suriyaprabha R, Rajendran V, Kannan N (2015) Toxicity evaluation based on particle size, contact angle and zeta potential of SiO2 and Al2O3 on the growth of green algae. Adv Nano Res 3(4):243–255. https://doi.org/10.12989/anr.2015.3.4.243
Karunakaran G, Suriyaprabha R, Rajendran V, Kannan N (2016) Influence of ZrO2, SiO2, Al2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles on maize seed germination under different growth conditions. IET Nanobiotechnol 10(4):171–177. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2015.0007
Krug HF, Bohmer N, Kühnel D, Marquardt C, Nau K, Steinbach C (2018) The DaNa2.0 knowledge base nanomaterials—an important measure accompanying nanomaterials development. Nanomaterials 8(4):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040204
Kumari M, Taylor GJ, Deyholos MK (2008) Transcriptomic responses to aluminum stress in roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Genet Genomics 279(4):339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0316-z
Liu Q, Yang J, He L, Li Y, Zheng S (2008) Effect of aluminum on cell wall, plasma membrane, antioxidants and root elongation in triticale. Biol Plant 52(1):87–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-008-0014-7
Mandegary A, Pournamdari M, Sharififar F, Pournourmohammadi S, Fardiar R, Shooli S (2012) Alkaloid and flavonoid rich fractions of fenugreek seeds (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) with antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects. Food Chem Toxicol 50(7):2503–2507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.04.020
Mirshafa A, Nazari M, Jahani D, Shaki F (2018) Size-dependent neurotoxicity of aluminum oxide particles: a comparison between nano-and micrometer size on the basis of mitochondrial oxidative damage. Biol Trace Elem Res 183(2):261–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1142-8
Mohagheghzadeh A, Hemmati S, Mehregan I, Alfermann AW (2003) Linum persicum: lignans and placement in Linaceae. Phytochem Rev 2(3):363–369. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHYT.0000045501.97438.9c
Mohagheghzadeh A, Dehshahri S, Hemmati S (2009) Accumulation of lignans by in vitro cultures of three Linum species. Z Naturforsch C 64(1–2):73–76. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2009-1-213
Mui J, Ngo J, Kim B (2016) Aggregation and colloidal stability of commercially available Al2O3 nanoparticles in aqueous environments. Nanomaterials 6(5):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6050090
Mustafa G, Komatsu S (2016) Toxicity of heavy metals and metal-containing nanoparticles on plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1864(8):932–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.02.020
Parmar VS, Jha HN, Sanduja SK, Sanduja R (1982) Trigocoumarin—a new coumarin from Trigonella foenum graecum. Z Naturforschung B 37(4):521–523. https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-1982-0423
Petersen M, Hans J, Matern U (2018) Biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids and related compounds. Annual Plant Rev 40:182–257. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119312994.apr0426
Poborilova Z, Opatrilova R, Babula P (2013) Toxicity of aluminium oxide nanoparticles demonstrated using a BY-2 plant cell suspension culture model. Environ Exp Bot 91:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.03.002
Qing-Ru Z, Bo-Han L, Li-Tian Z, Xi-Hong Z, Hong-Xiao T (2006) Short-term alleviation of aluminum phytotoxicity by urea application in acid soils from south China. Chemosphere 63(5):860–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.07.056
Santos C, Silva S, Pinto-Carnide O (2014) Chapter six—Aluminum phytotoxicity: physiological approaches and tolerance. In: Fishbein JC, Heilman JM (eds) Advances in molecular toxicology, vol 8. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 203–236
Shangari N, O’Brien PJ (2006) Catalase activity assays. Curr Protoc Toxicol 27:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471140856.tx0707s27
Smith IK, Vierheller TL, Thorne CA (1988) Assay of glutathione reductase in crude tissue homogenates using 5,5′-dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid). Anal Biochem 175(2):408–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(88)90564-7
Stefaniak AB, Hackley VA, Roebben G, Ehara K, Hankin S, Postek MT, Lynch I, Fu WE, Linsinger TP, Thünemann AF (2013) Nanoscale reference materials for environmental, health and safety measurements: needs, gaps and opportunities. Nanotoxicol 7(8):1325–1337. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2012.739664
Thirunavukkarasu V, Anuradha CV (2007) Gastroprotective effect of fenugreek seeds (Trigonella foenum graecum) on experimental gastric ulcer in rats. J Herbs Spices Med Plants 12(3):13–25. https://doi.org/10.1300/J044v12n03_02
Tripathi DK, Singh S, Singh S, Pandey R, Singh VP, Sharma NC, Prasad SM, Dubey NK, Chauhan DK (2017) An overview on manufactured nanoparticles in plants: uptake, translocation, accumulation and phytotoxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:2–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.07.030
Yanık F, Vardar F (2015) Toxic effects of Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) nanoparticles on root growth and development in Triticum aestivum. Water Air Soil Pollut 226(9):296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2566-4
Yanık F, Vardar F (2018) Oxidative stress response to aluminum oxide (Al2O3) nanoparticles in Triticum aestivum. Biologia 73(2):129–135. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-018-0016-7
Zhou P, Su L, Lv A, Wang S, Huang B, An Y (2016) Gene expression analysis of alfalfa seedlings response to acid-aluminum. Int J Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2095195
Zuverza-Mena N, Martínez-Fernández D, Du W, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Bonilla-Bird N, López-Moreno ML, Komárek M, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2017) Exposure of engineered nanomaterials to plants: insights into the physiological and biochemical responses—a review. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:236–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.037
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, IRAN for Grant Nos. 95-01-05-12926 and 1396-01-05-14613. This work was part of the Pharm D thesis of M. Hakimzadeh and D. Mansouri. Authors would like to thank Dr. S. Abolmaali and Dr. S. Nazmara for DLS and ICP-OES analyses, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SH has conceived and designed the experiments. RH and MH performed the experiments. HO and SH prepared the manuscript. SH has revised the manuscript. All authors proofread the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Dr. Abdolali Mohagheghzadeh on the occasion of his birthday.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
Effect of alumina NPs on the UV absorbance of methanolic extract derived from fenugreek in vitro cultures within 21 days, in comparison with the bulk alumina-treated and control groups. (a) day 1, (b) day 7, (c) day 14, and (d) day 21. (TIFF 11738 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Owji, H., Hemmati, S., Heidari, R. et al. Effect of alumina (Al2O3) nanoparticles and macroparticles on Trigonella foenum-graceum L. in vitro cultures: assessment of growth parameters and oxidative stress-related responses. 3 Biotech 9, 419 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1954-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1954-7