Abstract
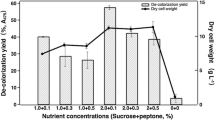
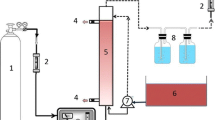
The extracted sugarcane molasses-melanoidins showed the presence of Mn (8.20), Cr (2.97), Zn (16.61), Cu (2.55), Fe (373.95), Pb (2.59), and Ni (4.18 mg L−1) along with mixture of other organic compounds which have endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) properties. A consortium of aerobic bacteria comprising Klebsiella pneumoniae (KU321273), Salmonella enteric (KU726954), Enterobacter aerogenes (KU726955), and Enterobacter cloacae (KU726957) showed the optimum decolourisation of molasses-melanoidins up to 81% through co-metabolism in the presence of glucose (1.0%) and peptone (0.2%) as a carbon and nitrogen source, respectively. The absorption spectrum scanning by UV–visible spectrophotometer between 200 and 700 nm revealed reductions of absorption spectrum of organic compounds present in bacterial degraded sample of melanoidins in range of 200–450 nm compared to control. The degradation and decolourisation of melanoidins by bacterial consortium was noted by induction of manganese peroxidase and laccase activities in sample supernatant. Furthermore, the TLC and HPLC analysis of bacterial decolourised melanoidins also showed degradation and reduction of absorption peak at (295 nm), respectively. Furthermore, FT-IR and GC–MS analysis also showed the change of functional group and disappearance of ion peaks. This indicated the degradation and depolymerisation of melanoidins and cleavage of C=C, C=O and C≡N conjugated bonds which resulted in reduction of colour. The metabolic analysis also showed the disappearance of some organic compounds and generation of new metabolites. Furthermore, the seed germination test using Phaseolus mungo L. showed toxicity reduction in decolourized effluent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (American Public Health Association) (2012) Standard method for examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. APHA, AWWA and WEF, Washington, DC
Arora DS, Chander M, Gill PK (2002) Involvement of lignin peroxidase, manganese peroxidase and laccase in degradation and selective ligninolysis of wheat straw. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 50:115–120
Bharagava R, Chandra R (2010) Effect of bacteria treated and untreated post-methanated distillery effluent (PMDE) on seed germination, seedling growth and amylase activity in Phaseolus mungo L. J Hazard Mater 180:730–734
Bharagava RN, Chandra R, Rai V (2009) Isolation and characterization of aerobic bacteria capable of the degradation of synthetic and natural melanoidins from distillery effluent. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(5):737–744
Billaud C, Maraschin C, Nicolas J (2004) Inhibition of polyphenoloxidase from apple by Maillard reaction products prepared from glucose or fructose with l-cysteine under various conditions of pH and temperature. LWT 37:69–78
Bonugli-Santos RC, Durrant LR, Sette LD (2012) The production of ligninolytic enzymes by marine-derived basidiomycetes and their biotechnological potential in the biodegradation of recalcitrant pollutants and the treatment of textile effluents. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(5):2333–2345
Chandra R, Kumar V (2017a) Detection of Bacillus and Stenotrophomonas species growing in an organic acid and endocrine-disrupting chemicals rich environment of distillery spent wash and its phytotoxicity. Environ Monit Assess 189:26
Chandra R, Kumar V (2017b) Detection of androgenic-mutagenic compounds and potential autochthonous bacterial communities during in situ bioremediation of post methanated distillery sludge. Front Microbiol 8:887
Chandra R, Yadav S, Mohan D (2008) Effect of distillery sludge on seed germination and growth parameters of green gram (Phaseolus mungo L.). J Hazard Mater 152:431–439
Chandra R, Kumar V, Yadav S (2017) Extremophilic ligninolytic enzymes. In: Sani R, Krishnaraj R (eds) Extremophilic enzymatic processing of lignocellulosic feedstocks to bioenergy. Springer, Cham
Chandra R, Kumar V, Tripathi S, Sharma P (2018) Heavy metal phytoextraction potential of native weeds and grasses from endocrine-disrupting chemicals rich complex distillery sludge and their histological observations during in situ phytoremediation. Ecol Eng 111:143–156
Chaudhari PK, Mishra IM, Chand S (2005) Catalytic thermal treatment (catalytic thermolysis) of a biodigester effluent of an alcohol distillery plant. Ind Eng Chem Res 44(15):5518–5525
Chaudhari PK, Mishra IM, Chand S (2007) Decolourization and removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD) with energy recovery: treatment of biodigester effluent of a molasses-based alcohol distillery using inorganic coagulants. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 296(1–3):238–247
Davídek T, Devaud S, Robert F, Blank I (2006) Sugar fragmentation in the Maillard reaction cascade: isotope labeling studies on the formation of acetic acid by a hydrolytic β-dicarbonyl cleavage mechanism. J Agric Food Chem 54(18):6667–6676
de Sousa Andrade LN, De Lima TM, Curi R, de Lauro Castrucci AM (2005) Toxicity of fatty acids on murine and human melanoma cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro 19:553–560
Echavarría AP, Pagán J, Ibarz A (2013a) Antioxidant activity of the melanoidins fraction formed from d-glucose and d-fructose with l-asparagine in the Maillard reaction. Sci Agropecu 4:45–54
Echavarría AP, Pagán J, Ibarz A (2013b) Optimization of Maillard reaction products isolated from sugar-amino acid model system and their antioxidant activity. Afinidad LXX 562:86–92
Echavarría AP, Pagán J, Ibarz A (2014) Kinetics of color development of melanoidins formed from fructose/amino acid model systems. Food Sci Technol Int 20(2):119–126
Ghosh M, Verma SC, Mengoni A, Tripathi AK (2004) Enrichment and identification of bacteria capable of reducing chemical oxygen demand of anaerobically treated molasses spent wash. J Appl Microbiol 96:1278–1286
Gonzalez T, Terron MC, Yague S, Zapico E, Galletti GC, Gonzalez AE (2000) Pyrolysis/gas chromatography/mass spectrometry monitoring of fungal-biotreated distillery wastewater using Trametes sp I-62 (CECT 20197). Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 14:1417–1424
González T, Terrón MC, Yagüe S, Junca H, Carbajo JM, Zapico EJ, Silva R, Arana-Cuenca A, Téllez A, González AE (2008) Melanoidin-containing wastewaters induce selective laccase gene expression in the white-rot fungus Trametes sp. I-62. Res Microbiol 159(2):103–109
Gu FL, Kim J, Abbas S, Zhang XM, Xia SQ, Chen ZX (2010) Structure and antioxidant activity of high molecular weight Maillard reaction products from casein–glucose. Food Chem 120:505–511
Hayase F, Kim SB, Kato H (1984) Decolorization and degradation products of the melanoidins by hydrogen peroxide. Agric Biol Chem 48(11):2711–2717
Jenkins R, Wilson EM, Angus RA, Howell WM, Kirk M (2003) Androstenedione and progesterone in the sediment of a river receiving paper mill effluent. Toxicol Sci 73:53–59
Kalavathi DF, Uma L, Subramanian G (2001) Degradation and metabolization of the pigment—melanoidin in distillery effluent by the marine cyanobacterium Oscillatoria boryana BDU 92181. Enzyme Microb Technol 29:246–251
Kamaya Y, Kurogi Y, Suzuki K (2003) Acute toxicity of fatty acids to the freshwater green alga Selenastrum capricornutum. Environ Toxicol 18:289–294
Kirk TK, Schultz E, Connors WJ, Lorenz LF, Zeikus JG (1978) Influence of culture parameters on lignin metabolism by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Arch Microbiol 117:177–185
Koster IW, Cramert A (1987) Inhibition of methanogenesis from acetate in granular sludge by long-chain fatty acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(2):403–409
Kumar P, Chandra R (2006) Decolourisation and detoxification of synthetic molasses melanoidins by individual and mixed cultures of Bacillus spp. Bioresour Technol 97:2096–2102
Kumar V, Chandra R (2018) Characterisation of manganese peroxidase and laccase producing bacteria capable for degradation of sucrose glutamic acid-Maillard products at different nutritional and environmental conditions. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:82
Liang Z, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Liu H, Wu Z (2009) Variables affecting melanoidins removal from molasses wastewater by coagulation/flocculation. Sep Purif Technol 68:382–389
Liu M, Zhu H, Dong B, Zheng Y, Yu S, Gao C (2013) Submerged nanofiltration of biologically treated molasses fermentation wastewater for the removal of melanoidins. Chem Eng J 223:388–394
Martins S, Van Boekel M (2003) Melanoidins extinction coefficient in the glucose/glycine Maillard reaction. Food Chem 83:135–142
Metcalf, Eddy (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse, 4th edn. McGraw Hill Higher Education, New York
Migo VP, Del Rosario EJ, Matsumura M (1997) Flocculation of melanoidins induced by inorganic ions. J Ferment Bioeng 83:287–291
Miyata N, Iwahori K, Fujita M (1998) Manganese-independent and -dependent decolorization of melanoidin by extracellular hydrogen peroxide and peroxidases from Coriolus hirsutus pellets. J Ferment Bioeng 85(5):550–553
Miyata N, Mori T, Iwahori K, Fujita M (2000) Microbial decolorization of melanoidin-containing wastewaters: combined use of activated sludge and the fungus Coriolus hirsutus. J Biosci Bioeng 89:145–150
Mohana S, Desai C, Madamwar D (2007) Biodegradation and decolorization of anaerobically treated distillery spent wash by a novel bacterial consortium. Bioresour Technol 98(2):333–339
Muhammad F, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Riviere JE (2005) Comparative in vivo toxicity of topical JP-8 jet fuel and its individual hydrocarbon components: identification of tridecane and tetradecane as key constituents responsible for dermal irritation. Toxicol Pathol 33:258–266
OECD (2003) Guideline for testing of chemicals, terrestrial plant tests: 208: seedling emergence and seedling growth test. pp 1–19 (draft)
Onyango M, Kittinya J, Hadebe N, Ojijo V, Ochieng A (2011) Sorption of melanoidin onto surfactant modified zeolite. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 17(4):385–395
Pant D, Adholeya A (2007) Identification, ligninolytic enzyme activity and decolorization potential of two fungi isolated from a distillery effluent contaminated site. Water Air Soil Pollut 183:165–176
Quinn BP, Bernier UR, Geden CJ, Hogsette JA, Carlson DA (2007) Analysis of extracted and volatile components in blackstrap molasses feed as candidate house fly attractants. J Chromatogr 1139:279–284
Ravikumar R, Vasanthi NS, Saravanan K (2011) Single factorial experimental design for decolorizing anaerobically treated distillery spent wash using Cladosporium cladosporioides. J Environ Sci Technol 8:97–106
Santal AR, Singhb NP, Saharan BS (2011) Biodegradation and detoxification of melanoidin from distillery effluent using an aerobic bacterial strain SAG5 of Alcaligenes faecalis. J Hazard Mater 193:319–324
Satyawali Y, Balakrishnan M (2008) Wastewater treatment in molasses-based alcohol distilleries for COD and color removal: a review. J Environ Manag 86(3):481–497
Singh VK, Kavita K, Prabhakaran R, Jha B (2013) Cis-9-octadecenoic acid from the rhizospheric bacterium Stenotrophomonas maltophilia BJ01 shows quorum quenching and anti-biofilm activities. Biofouling 29:855–867
Sirianuntapiboon S, Phothilangka PO (2004) Decolourization of molasses wastewater by a strain no. BP103 of acetogenic bacteria. J Bioresour Technol 92:31–39
Taylor CD, Smith OS, Gagosian R (1981) Use of microbial enrichments for the study of anaerobic degradation of cholesterol. Geochim Coscochim Acta 45:2161–2168
Tiwari S, Gaur R, Singh R (2012) Decolorization of a recalcitrant organic compound (melanoidin) by a novel thermotolerant yeast, Candida tropicalis RG-9. BMC Biotechnol 12:30
Tiwari S, Rai P, Yadav SK, Gaur R (2013) A novel thermotolerant Pediococcus acidilactici B-25 strain for color, COD, and BOD reduction of distillery effluent for end use applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(6):4046–4058
Tiwari S, Gaur R, Singh A (2014) Distillery spent wash decolourisation by a noval consortium of Pedicoccus acidilactici and Candida tropicalis under static condition. Pak J Biol Sci 17(6):780–791
USEPA (2012) US environmental protection agency endocrine disruptor screening program universe of chemicals
Wang H, Qian H, Yao W (2011) Melanoidins produced by the Maillard reaction: structure and biological activity. Food Chem 128(3):573–584
Wedzicha BL, Kaputo MT (1992) Melanoidins from glucose and glycine: composition, characteristics and reactivity towards sulphite ion. Food Chem 43(5):359–367
Wolfrom ML, Kolb DN, Langer AW (1953) Chemical interactions of amino compounds and sugars. VII, pH dependency. J Am Chem Soc 75:3471–3473
Wong DW (2009) Structure and action mechanism of ligninolytic enzymes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 157(2):174–209
Yadav S, Chandra R (2012) Biodegrdation of organic compounds of molasses melanoidins (MM) from biomethanated distillery distillery spent wash (BMDS) during the decolourisation by potential bacterial consortium. Biodegradation 23:609–620
Acknowledgements
Instrumentation facilities for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) from central facilities, CSIR-IITR, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India are gratefully acknowledged. The financial assistance from DBT, New Delhi, India as the Project no. BT/PR13922/BCE/8/1129/2015 to Prof. Ram Chandra. Simultaneously, Rajiv Gandhi National Senior Research Fellowship (RGNSRF) from UGC, New Delhi, to Mr. Vineet Kumar, Ph.D. Scholar is also highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest of any type.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, R., Kumar, V. & Tripathi, S. Evaluation of molasses-melanoidin decolourisation by potential bacterial consortium discharged in distillery effluent. 3 Biotech 8, 187 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1205-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1205-3