Abstract
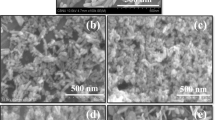
The synthesis of pectin-mediated HAP Nanoparticle (pHAP) and Hydroxyapatite/Pectin Nanocomposite (HAP/P Composite) utilizing carrot pomace pectin as a template to support greener technologies was the focus of this research. To produce a regulated crystallinity, pectin is extracted from carrot pomace. Spectral techniques such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) to find out the chemical behavior of the compound, proton-1 nuclear resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR), and carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (13C NMR) to identify the H and C atoms that were in the extricated pectin. FTIR, SEM, and XRD were used to assess the crystallinity, shape, and purity of the HAP nanoparticles. A protein denaturation assay and a proteinase inhibition assay were used to assess the anti-inflammatory effect of pectin-mediated HAP nanoparticles and Hydroxyapatite/Pectin Nanocomposite. According to the results, the pectin-mediated HAP nanoparticles generated in the presence of an optimal pectin concentration are pure, spherical, low crystalline, and discrete particles with a reduced size. Furthermore, it has antimicrobial properties. According to this study, the HAP nanoparticles incorporated utilizing pectin as a green template can operate as a useful biomaterial for biomedical purposes. MTT Assay and ALP Activity were performed on pHAP and HAP/Pectin Nanocomposites. When compared to pectin-mediated hydroxyapatite, the experimental results demonstrated that HAP/Pectin Nanocomposites have higher cell survival and bone mineralization. As a result, the HAP/Pectin Nanocomposites could be useful in biomedical applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Halim NA, Hussein MZ, Kandar MK (2021) Nanomaterials-upconverted hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering and a platform for drug delivery. Int J Nanomedicine 16:6477–6496. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S298936
Anuj NL, Aifa F, Vincent SGP (2021) In-vitro Evaluation of chitosan hydroxyapatite nanocomposite scaffolds as bone substitutes with antibiofilm properties. J Pure Appl Microbiol 15(3):1455–1471. https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.15.3.39
Cao H, Zhang L, Zheng H, Wang Z (2010) Hydroxyapatite nanocrystals for biomedical applications. J Phys Chem C 114:18352–18357. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp106078b
Chen Y, Tingfei XI, Zheng Y, Wan Y (2009) In vitro cytotoxicity study of the nano-hydroxyapatite/bacterial cellulose nanocomposites. Mater Sci Forum. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.610-613.1011
Christopher II (2020) Progress in polymer nanocomposites for bone regeneration and engineering. Polym Polym Compos. https://doi.org/10.1177/0967391120913658
Devanesan S, AlSalhi MS, Balaji RV, Ranjitsingh AJA, Ahamed A, Alfuraydi AA, AlQahtani FY, Aleanizy FS, Othman AH (2018) Antimicrobial and cytotoxicity effects of synthesized silver nanoparticles from Punica granatum Peel extract. Nanoscale Res Lett 13(1):315. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2731-y
Dhandapani P, Devanesan S, Arulprakash A, AlSalhi MS, Paramasivam S, Rajasekar A (2020) Bio-approach synthesis of nanosilver impregnation on calcium hydroxyapatite by biological activated ammonia from urinary waste. Arab J Chem 13(6):5878–5889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.04.024
Gopi D, Kanimozhi K, Bhuvaneshwari N, Indira J, Kavitha L (2014) Novel banana peel pectin mediated green route for the synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and their spectral characterization. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 118:589–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.09.034
Kohsuke M, Takayoshi H, Tomoo M, Kohki E, Kiyotomi K (2004) Hydroxyapatite-supported palladinum nanoclusters: a highly active heterogeneous catalyst for selective oxidation of alcohols by use of molecular oxygen. J.am Chem Soc 126:10657–10666. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0488683
Leroux J, Langendorff V, Schick G, Vaishnav V, Mazoyeri J (2003) Emulsion stabilizing properties of pectin. Food Hydrocoll 17(4):455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0268-005X(03)00027-4
Liao J, Li Y, Duan X, Zhu L (2015) Nano-hydroxyapatite/polymer composite as bone repair materials. Prog Chem 27(2/3):220–228. https://doi.org/10.7536/pc140810
Mohsen H, Saeid SN (2019) Design and preparation of poly (lactic acid) hydroxyapatite nanocomposites reinforced with phosphorus-based organic additive: thermal, combustion, and mechanical properties studies. Polym Adv Technol. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.4652
Murugan S, Dharman G, Murugaraj J, Arfajj A, Murugan AM, SureshKumar S, Rajan M (2017) Sustainable pectin fascinating hydroxyapatite nanocomposite scaffolds to enhance tissue regeneration. Sustain Chem Pharm 5:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2017.02.001
Nuha A, Mahmoud AH, Yas A, Ahmad U (2022) Cellulose Acetate-hydroxyapatite-Bioglass-Zirconia nanocomposite particles as potential biomaterial: synthesis. Characterization Biol Prop Bone Appl Eng Sci 17:70–82. https://doi.org/10.30919/es8d528
Oliveira TÍ, Rosa MF, Cavalcante FL, Pereira PH, Moates GK, Wellner N, Mazzetto SE, Waldron KW, Azeredo HM (2016) Optimization of pectin extraction from banana peels with citric acid by using response surface methodology. Food Chem 198:113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.080
Paulo H, Pereira F, Oliveira TIS, Rosa MF, Cavalcante LM, Moates GK, Wellner N, Waldron KW, Azeredo HMC (2016) Pectin extraction from pomegranate peels with citric acid. Int J Biol Macromo 88:373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.074
Pedro H, Curry C, Kestur G, Satyanarayanna FW (2009) Nanocomposites, synthesis, structure, properties and new application opportunities. Mat Res. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392009000100002
Poonam Y, Parijat P, Neeta SP (2017) Pectin as natural polymer; an overview. Res J Pharm Tech 10(4):1225–1229. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360X.2017.00219.0
Sarveswaran R, Jayasuriya WJAN, Suresh TS (2017) In vitro assays to investigate the anti-inflammatory activity of herbal extracts: a review. World J Pharm Res 6(17):131–141 (ISSN2277-7105)
Sebastiammal S, Lesly Fathima AS, Devanesan S, AlSalhi MS, Henry J, Govindarajan M, Vaseeharan B (2020) Curcumin-encased hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as novel biomaterials for antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticancer applications: a perspective of nano-based drug delivery. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 57:101752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101752
Shanahan F (2004) Host-flora interactions in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 10:S16–S24. https://doi.org/10.1097/00054725-200402001-00004
Sharma R, Shrinivas Gat Y (2021) Pectin sources, extraction methods and industrial application. Int J All Res Educ Sci Methods 9(3):683–686 ISSN: 2455–6211
Shogren RL, Bagley EB (1999) Natural polymers S advanced materials; some research needs and directions. Chool. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1999-0723
Sriamornsak P (2011) Application of pectin in oral drug delivery. Exp Opin Drug Deliv 8(8):1009–1023. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2011.584867
Suchanek W, Yoshimura M (1998) Processing and properties of hap based biomaterials for use as hard tissue replacement implants. J Mater Res 13:94–117. https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1998.0015
Tian HY, Tang ZH, Zhuang XL, Chen XB, Jing XS, Jing XB (2012) Biodegradable synthetic polymers; preparation, functionalization and biomedical application. Prog Polym Sci 37:237–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.06.004
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Researcher supporting program at King Saud University, Riyadh, for funding this work under Project Number (RSP-2021/328). The authors express their gratitude to GNR Instrumentation Centre, University of Madras, Guindy Campus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vaikundam, M., Shanmugam, S., Aldawood, S. et al. Preparation of biopolymer pectin fascinate hydroxyapatite nanocomposite for biomedical applications. Appl Nanosci 13, 6039–6051 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02578-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02578-4