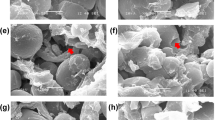
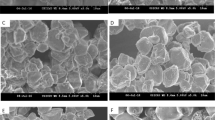
Abstract
The global consumption of a large quantity of banana generates a huge quantity of banana peels which creates the problem of its disposal and proper management. The utilization of banana peels for the extraction of resistant starch can be a valuable strategy of waste valorization with economic viability at the industrial level. Green techniques like ultrasound can be efficacious in terms of increasing the extraction efficiency and yield of resistant starch. In this study, ultrasound assisted enzymatic extraction of resistant starch was optimized using response surface methodology. The optimum yield (60.6%) of resistant starch was obtained at 35 °C temperature, 30:1 liquid to solid ratio after a treatment time of 9 min. The results showed that a combination of ultrasound treatment with enzymatic extraction of resistant starch can be an efficient approach for the valorization of banana peels. Resistant starch holds application as a valuable supplement in functional food development in the fields of dairy, bakery, beverages, etc.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- RSM :
-
Response Surface Methodology.
- BBD :
-
Box-Behnken design.
- XRD :
-
X-ray diffraction.
- FTIR :
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.
- WAC :
-
Water holding capacity.
- OAC :
-
Oil holding capacity.
References
AACC (2000) Approved methods of the AACC international, Methods 44–17, 76–13, 08–16, 32 40 and 35–05, 10th ed. The Association AACC, St. Paul, MN
Ahmad M, Gani A, Masoodi FA, Rizvi SH (2020) Influence of ball milling on the production of starch nanoparticles and its effect on structural, thermal and functional properties. Int J Biol Macromol 151:85–91
Aijun H, Jing L, Jie Z, Junyan S, Lin Y, Xiaoqinq Z, Ying Z, Qiuqian L (2013) Ultrasonically aided enzymatical effects on the properties and structure of mung bean starch. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 20:146–151
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC
Aparicio-Saguilán A, Gutiérrez-Meraz F, García-Suárez FJ, Tovar J, Bello-Péreza LA (2008) Physicochemical and functional properties of cross-linked banana resistant starch. Effect of pressure cooking. Starch – Stärke 60:286–291
Bernardo CO, Ascheri JLR, Chávez DWH, Carvalho CWP (2018) Ultrasound assisted extraction of yam (Dioscorea bulbífera) starch: effect on morphology and functional properties. Starch – Stärke. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201700185
Bi Y, Zhang Y, Jiang H, Hong Y, Gu Z, Cheng L, Li Z, Li C (2017) Molecular structure and digestibility of banana flour and starch. Food Hydrocoll 72:219–227
Chang Y, Yan X, Wang Q, Ren L, Tong J, Zhou J (2017) High efficiency and low-cost preparation of size-controlled starch nanoparticles through ultrasonic treatment and precipitation. Food Chem 227:369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.111
Correa M, Bombardelli MCM, Fontana PD, Bovo F, Messias-Reason IJ, Maurer JBB, Corazza ML (2016) Bioactivity of extracts of Musa paradisiaca L. obtained with compressed propane and supercritical CO2. J Supercrit Fluids 122:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2016.12.004
Ding Y, Xiao Y, Ouyang Q, Luo F, Lin Q (2021) Modulating the in vitro digestibility of chemically modified starch ingredient by a non-thermal processing technology of ultrasonic treatment. Ultrason Sonochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105350
Dundar AN, Gocmen D (2013) Effects of autoclaving temperature and storing time on resistant starch formation and its functional and physicochemical properties. Carbohydr Polym 97:764–771
FAO (2021) Banana market review – Preliminary results 2020. Rome
Fontes SDM, Cavalcanti MT, Candeia RA, Almeida EL (2017) Characterization and study of functional properties of banana starch green variety of Mysore (Musa AAB-Mysore). Food Sci Technol 37:224–231
Gani A, Ashwar BA, Akhter G, Gani A, Shah A, Masoodi FA, Wani IA (2020) Resistant starch from five Himalayan rice cultivars and Horse chestnut: extraction method optimization and characterization. Sci Rep 10:4097. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60770-4
Hodge JE, Hofreiter BT (1962) Carbohydrates. In: Whistler RL, Miller JNB (eds) Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry. Academic Press, New York, NY, pp 17–22
Izidoro DR, Sierakowski MR, Haminiuk CWI, de Souza CF, Scheer ADP (2011) Physical and chemical properties of ultrasonically, spray-dried green banana (Musa cavendish) starch. J Food Eng 4(104):639–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.02.002
Khawas P, Deka SC (2016) Comparative nutritional, functional, morphological, and diffractogram study on culinary banana (Musa ABB) peel at various stages of development. Int J Food Prop 19(12):2832–2853.https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1141296
Kuang Q, Xu J, Wang K, Zhou S, Liu X (2016) Structure and digestion of hybrid indica rice starch and its biosynthesis. Int J Biol Macromol 93:402–407
Lee SK, Mun SH, Shin MS (1997) Effect of heating conditions on the resistant starch formation. Korean Agric Chem Biotechnol 40:220–224
Liang Q, Chen X, Ren X, Yang X, Raza H, Ma H (2021) Effects of ultrasound-assisted enzymolysis on the physicochemical properties and structure of arrowhead-derived resistant starch. LWT- Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111616
Noor F, Rahman MJ, Mahomud MS, Akter MS, Talukder MA, Ahmed M (2014) Physicochemical properties of flour and extraction of starch from Jackfruit seed. Int J Nutr Food Sci. https://doi.org/10.11648/J.IJNFS.20140304.27
Noor N, Gani A, Jhan F, Jenno JLH, Dar MA (2021) Resistant starch type 2 from lotus stem: ultrasonic effect on physical and nutraceutical properties. Ultrason Sonochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105655
Ouyang Q, Wang X, Xiao Y, Luo F, Lin Q, Ding Y(2021) Structural changes of A-, B-and C-type starches of corn, potato and pea as influenced by sonication temperature and their relationships with digestibility.Food Chemistry,358
Ramli S, Ismail N, Alkarkhi AF, Easa AM (2010) The use of principal component and cluster analysis to differentiate banana peel flours based on their starch and dietary fibre components. Trop life Sci Res 21(1):91–100
Scheerer L, Pemsl DE, Dita M, Perez Vicente L, Staver C (2018) A quantified approach to projecting losses caused by Fusarium wilt tropical race 4. Acta Hortic 1196:211–218
Singh R, Sharanagat VS (2020) Physico-functional and structural characterization of ultrasonic-assisted chemically modified elephant foot yam starch. Int J Biol Macromol 164:1061–1069
Sujka M, Jamroz J (2013) Ultrasound-treated starch: SEM and TEM imaging, and functional behaviour. Food Hydrocoll 31(2):413–419
Tribess TB, Hernández-Uribe JP, Méndez-Montealvo MGC, Menezes EW, Bello-Perez LA, Tadini CC (2009) Thermal properties and resistant starch content of green banana flour (Musa cavendishii) produced at different drying conditions. LWT-Food Sci Technol 42(5):1022–1025
Vu HT, Scarlett CJ, Vuong QV (2018) Phenolic compounds within banana peel and their potential uses: a review. J Funct Foods 40:238–248
Wang L, Bai X (2017) The producing technology of resistant starch (RS) from buckwheat using microwave treatment. Sustain Environ 2(3):301–308
Wang D, Ma X, Yana L, Chantapakul T, Wang W, Ding T, Ye X, Liu D (2017a) Ultrasound assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of starch catalyzed by glucoamylase: investigation on starch properties and degradation kinetics. Carbohydr Polym 175:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.093
Wang J, Huang HH, Chen PS (2017b) Structural and physicochemical properties of banana resistant starch from four cultivars. Int J Food Prop 20(6):1338–1347
Wang H, Xu K, Ma Y, Liang Y, Zhang H, Chen L (2020) Impact of ultrasonication on the aggregation structure and physicochemical characteristics of sweet potato starch. Ultrason Sonochem 63:104868
You Q, Zhang X, Fang X, Yin X, Luo C, Wan M (2019) Ultrasonic-assisted preparation and characterization of RS3 from Pea starch. Food Bioprocess Technol 12:1244–1249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02277-z
Zhang B, Dhital S, Flanagan BM, Luckman P, Halley PJ, Gidley MJ (2015) Extrusion induced low-order starch matrices: enzymic hydrolysis and structure. Carbohydr Polym 134:485–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.07.095
Zhou D, Ma Z, Xu J, Li X (2019) Resistant starch isolated from enzymatic, physical, and acid treated pea starch: preparation, structural characteristics, and in vitro bile acid capacity. LWT-Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LWT.2019.108541
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by ASEAN India Science & Technology Development Fund (AISTDF), by Science & Engineering Research Board, Department of Science & Technology (SERB-DST) under Grant No. IMRC/AISTDF/CRD/2019/000141.
Funding
The research project was funded by ASEAN India Science & Technology Development Fund (AISTDF), Science & Engineering Research Board- Department of Science & Technology (SERB-DST) under Grant No. IMRC/AISTDF/CRD/2019/000141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Brahmeet Kaur: Investigation, Methodology, Writing - original draft. Kamble B. Venkatrao: Formal analysis. Parmjit S. Panesar: Conceptualization, Writing - review & editing, Supervision, Project administration. Harish K. Chopra: Supervision, Guidance. Anil K. Anal: Conceptualization, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, B., Venkatrao, K.B., Panesar, P.S. et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction of resistant starch from green banana peels and its structural characterization. J Food Sci Technol 59, 4663–4672 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05546-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05546-6