Abstract
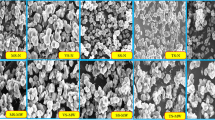
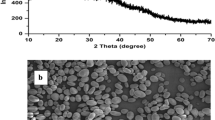
Starch was extracted from the rice bean which is largely underutilized and modified by physical (i.e. heat moisture treatment and retrogradation) and chemical (i.e. esterification and acid alcohol modification) methods. Both, physical and chemical modifications significantly (p < 0.05) affected the physicochemical, pasting, particle size and morphological properties of rice bean starch. Both amylose content and swelling power reduced after physical and chemical modifications. Among modified starches, retrograded starch showed higher solubility (8.56%) at 90 °C. Retrogradation also resulted in higher values of water (251%) and oil absorption (106%) capacities in comparison to other modified starches. Physical modifications greatly influenced the pasting properties in comparison to chemical modifications. The particle size distribution followed the order: native starch (659.8 nm) > heat moisture treated (434.3 nm) > retrograded (355.4 nm) > esterified (218 nm) > acid alcohol treated starch (234.5 nm). The study revealed that the particle size of rice bean starch was reduced by both physical and chemical modifications. FE-Scanning electron microscopy was used to study the morphological characteristics of starches and it was observed that retrogradation had a pronounced effect on the starch granules morphology.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akubor P (2007) Chemical and functional properties of modified and unmodified cassava and sweet potato starches. J Food SciTechnol 44(3):260–263
Anderson AK, Guraya HS (2006) Effects of microwave heat-moisture treatment on properties of waxy and non-waxy rice starches. Food Chem 97(2):318–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.04.025
Arns B, Bartz J, Radunz M, Evangelho JA, Pinto VZ, Zavareze ER, Dias ARG (2015) Impact of heat-moisture treatment on rice starch, applied directly in grain paddy rice or in isolated starch. LWT- Food SciTechnol 60:708–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.10.059
Bajaj R, Singh N, Kaur A (2019) Properties of octenyl succinic anhydride (OSA) modified starches and their application in low fat mayonnaise. Int J BiolMacromol 131:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.054
Bhagyawant SS, Bhadkaria A, Narvekar DT, Srivastava N (2019) Multivariate biochemical characterization of rice bean (Vigna umbellate) seeds for nutritional enhancement. BiocatalAgricBiotechnol 20:101193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101193
Dutta H, Paul SK, Kalita D, Mahanta CL (2011) Effect of acid concentration and treatment time on acid–alcohol modified jackfruit seed starch properties. Food Chem 128(2):284–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.016
Fang JM, Fowler PA, Tomkinson J, Hill CAS (2002) The preparation and characterization of a series of chemically modified potato starches. CarbohydrPolym 47:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(01)00187-4
Franco CM, Ciacco CF, Tavares DQ (1995) Effect of the heat-moisture treatment on the enzymatic susceptibility of corn starch granules. Starke 47(6):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.19950470607
John JK, Raja KC, Rani S, Moorthy SN, Eliasson A (2002) Properties of arrowroot starch treated with aqueous HCl at ambient temperature. J Food Sci 67(1):10–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002tb11350.x
Kaur B, Ariffin F, Bhat R, Karim AA (2012) Progress in starch modification in the last decade. Food Hydrocoll 26(2):398–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.02.016
Kaur A, Kaur P, Singh N, Virdi AS, Singh P, Rana JC (2013) Grains, starch and protein characteristics of rice bean (Vigna umbellata) grown in Indian Himalaya regions. Food Res Int 54(1):102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.05.019
Lan H, Hoover R, Jayakody L, Liu Q, Donner E, Baga M, Asare EK, Hucl P, Chibbar RN (2008) Impact of annealing on the molecular structure and physicochemical properties of normal, waxy and high amylose bread wheat starches. Food Chem 111:663–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.04.055
Lawal OS (2004) Composition, physicochemical properties and retrogradation characteristics of native, oxidised, acetylated and acid-thinned new cocoyam (Xanthosoma sagittifolium) starch. Food Chem 87:205–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.11.013
Lawal OS (2005) Studies on the hydrothermal modification of new cocoyam (Xanthosona saggittifolium) starch. Int J BiolMacromol 37:268–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2005.12.016
Li MN, Xie Y, Chen HQ, Zhang B (2019) Effects of heat-moisture treatment after citric acid esterification on structural properties and digestibility of wheat starch, A-and B-type starch granules. Food Chem 272:523–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.079
Lin JH, Lee SY, Chang YH (2003) Effect of acid–alcohol treatment on the molecular structure and physicochemical properties of maize and potato starches. CarbohydrPolym 53(4):475–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(03)00145-0
Patel H, Royall PG, Gaisford S, Williams GR, Edwards CH, Warren FJ, Flanagan BM, Ellis PR, Butterworth PJ (2017) Structural and enzyme kinetic studies of retrograded starch: Inhibition of α-amylase and consequences for intestinal digestion of starch. CarbohydrPolym 164:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.01.040
Raman S, Chopra AR (2012) In-vitro plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in rice-bean Vigna umbellata (Thunb) Ohwi and Ohashi: an underutilized and recalcitrant grain legume. J Environ Res Dev 6(3):452–457
Rondán-Sanabria GG, Finardi-Filho F (2009) Physical–chemical and functional properties of maca root starch (Lepidium meyenii Walpers). Food Chem 114(2):492–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.076
Sadeghi R, Daniella Z, Uzun S, Kokini J (2017) Effects of starch composition and type of non-solvent on the formation of starch nanoparticles and improvement of curcumin stability in aqueous media. J Cereal Sci 76:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2017.05.020
Sandhu KS, Singh N, Malhi NS (2005) Physicochemical and thermal properties of starches separated from corn produced from crosses of two germ pools. Food Chem 89(4):541–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.03.007
Schoch TJ (1964) Non-carbohydrate substance in cereal starches. J Am ChemSoc 64(12):2954–2957. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01264a064
Shah U, Naqash F, Gani A, Masoodi FA (2016) Art and science behind modified starch edible films and coatings: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 15:568–580. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12197
Sharma M, Yadav DN, Singh AK, Tomar SK (2015) Effect of heat-moisture treatment on resistant starch content as well as heat and shear stability of pearl millet starch. Agric Res 4:411–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-015-0177-3
Singh N, Kaur S, Isono N, Ichihashi Y, Noda T, Kaur A, Rana JC (2012) Diversity in characteristics of starch amongst rice bean (Vigna umbellate)germplasm: amylopectin structure, granule size distribution, thermal and rheology. Food Res Int 46:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.11.015
Sodhi NS, Chang YH, Kaur N, Kohyama K (2009) Effect of acid–methanol treatment on the molecular structure and physicochemical properties of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik) starch. Food Hydrocoll 23(8):2219–2225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2009.05.004
Sosulki FW (1976) Functional properties of barley starch. Food SciTechnol 52:142–177
Tang L, Huang B, Lu Q, Wang S, Ou W, Lin W, Chen X (2013) Ultrasonication-assisted manufacture of cellulose nanocrystals esterified with acetic acid. BioresourTechnol 27:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.09.133
Thory R, Sandhu KS (2017) A Comparison of mango kernel starch with a novel starch from litchi (Litchi chinensis) kernel: physicochemical, morphological, pasting, and rheological properties. Int J Food Prop 20(4):911–921. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1188403
Tian Y, Zhan J, Zhao J, Xie Z, Xu X, Jin Z (2013) Preparation of products rich in slowly digestible starch (SDS) from rice starch by a dual-retrogradation treatment. Food Hydrocoll 31(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.09.005
Wadikar DD, Bepary RH (2020) Ricebean. In: Manickavasagan A, Thirunathan P (eds) Pulses: processing and product development. Springer Nature, Cham, pp 297–331. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41376-7
Wang W, Zhou H, Yang H, Zhao S, Liu Y, Liu R (2017) Effects of salts on the gelatinization and retrogradation properties of maize starch and waxy maize starch. Food Chem 214:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.040
Wang T, Wu C, Fan G, Li T, Gong H, Cao F (2018) Ginkgo biloba extracts-loaded starch nano-spheres: preparation, characterization, and in vitro release kinetics. Int J BiolMacromol 106:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.012
Watcharatewinkul Y, Uttapap D, Puttanlek C, Rungsardthong V (2010) Enzyme digestibility and acid/shear stability of heat–moisture treated canna starch. Starke 62(3–4):205–216. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.200900221
Williams PC, Kuzina FD, Hlynka I (1970) Rapid colorimetric procedure for estimating the amylose content of starches and flours. Cereal Chem 47:411–420
Zavareze ER, Dias ARG (2011) Impact of heat–moisture treatment and annealing in starches: a review. CarbohydrPolym 83:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.064
Zhou Y, Meng S, Chen D, Zhu X, Yuan H (2014) Structure characterization and hypoglycemic effects of dual modified resistant starch from indica rice starch. CarbohydrPolym 103:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.12.020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YT Laboratory experimentation, Data collection; RT Experimental design, Manuscript writing, Validation, Supervision; KSS Validation, Supervision; MK Conceptualization, Formal analysis; AS Conceptualization, Resources, Investigation; AKP Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, Y., Thory, R., Sandhu, K.S. et al. Effect of selected physical and chemical modifications on physicochemical, pasting, and morphological properties of underutilized starch from rice bean (Vigna umbellata). J Food Sci Technol 58, 4785–4794 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-04974-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-04974-0