Abstract
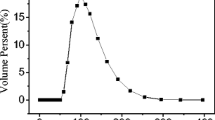
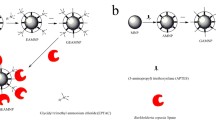
In this paper, the free Phospholipase A1 (PLA1) was immobilized on a magnetic carrier. The average particle diameter of the magnetic carrier was 97 ± 1.3 nm, and the average particle diameter of the magnetically immobilized PLA1 was 105 nm ± 1.3 nm. The enzyme activity was 1940.5 U/g. The magnetic enzyme was chemically modified with formaldehyde, dextran-aldehyde, and dextran-aldehyde-glycine. The proportions of primary amino groups in the modified magnetic immobilized enzyme PLA1 were 0, 53.5% and 47.3%, respectively. The optimum pH of the enzyme after chemical modification was 6.5. When the system temperature was 60 °C, the magnetically immobilized PLA1 modified with dextran-aldehyde-glycine had the optimal activity and stability. This chemically modified magnetic immobilized PLA1 was applied to soybean oil degumming at 60 °C, 6.5 h (reaction time), and 0.10 mg/kg (enzyme dosage). The phosphorus content in the degummed oil was 9.2 mg/kg. The relative enzyme activity was 77.6% after 7 reuses which would be potentially advantageous for industrial applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not Applicable.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
AOCS, 1997. Official methods and recommended practices of the American Oil Chemist’s Society. Ca 12–55 Campaign, IL, USA
Aoki J, Inoue A, Makide K, Saiki N, Arai H (2007) Structure and function of extracellular phospholipase A1 belonging to the pancreatic lipase gene family. Biochimie 89:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2006.09.021
Ariaeenejad S, Motamedi E, Salekdeh GH (2020) Application of the immobilized enzyme on magnetic graphene oxide nano-carrier as a versatile bi-functional tool for efficient removal of dye from water. Bioresour Technol 319:124228
Bhatti HN, Rashid MH, Asgher M, Nawaz R, Khalid AM, Perveen R (2007) Chemical modification results in hyperactivation and thermostabilization of Fusarium solani glucoamylase. Can J Microbiol 53(2):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1095-6433(98)00034-8
Bi Y, Yu M, Zhou H, Zhou H, Wei P (2016) Biosynthesis of oleyl oleate in solvent-free system by Candida rugosa Lipase (CRL) immobilized in macroporous resin with cross-linking of aldehyde-dextran. J Mol Catal B Enzym 133:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2016.05.002
Chahardahcherik M, Ashrafi M, Ghasemi Y, Aminlari M (2020) Effect of chemical modification with carboxymethyl dextran on kinetic and structural properties of L-asparaginase. Anal Biochem 591:113537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2019.113537
De Simone A, Naldi M, Bartolini M, Davani L, Andrisano V (2018) Immobilized enzyme reactors: an overview of applications in drug discovery from 2008 to 2018. Chromatographia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3663-5
Fang X, Wang X, Li G, Zeng J, Li J, Liu J (2018) SS-mPEG chemical modification of recombinant phospholipase C for enhanced thermal stability and catalytic efficiency. Int J Biol Macromol 111:1032–1039
Fuentes M, Mateo C, García L, Tercero JC, Guisán JM, Fernández-Lafuente R (2004) Directed covalent immobilization of aminated DNA probes on aminated plates. Biomacromol 5:883–888. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm0343949
Garcia-Galan C, Barbosa O, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2013) Stabilization of the hexameric glutamate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli by cations and polyethyleneimine. Enzyme Microb Technol 52:211–217
Hassani L, Nourozi R (2014) Modification of lysine residues of horseradish peroxidase and its effect on stability and structure of the enzyme. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:3558–3569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0756-y
Hu F, Deng C, Zhang X (2008) Development of high-performance liquid chromatography with immobilized enzyme onto magnetic nanospheres for screening enzyme inhibitor. J chromatogr B 871:67–71
Hu Y, Yang J, Jia R, Ding Y, Li S, Huang H (2014) Chemical modification with functionalized ionic liquids: a novel method to improve the enzymatic properties of Candida rugosa lipase. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 37(8):1617–1626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1134-4
Jia R, Hu Y, Liu L, Jiang L, Huang H (2013) Chemical modification for improving activity and stability of lipase B from Candida antarctica with imidazolium-functional ionic liquids. Org Biomol Chem 11:7192–7198. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ob41076e
Jiang X, Chang M, Wang X, Jin Q, Wang X (2014) A comparative study of phospholipase A1 and phospholipase C on soybean oil degumming. J Am Oil Chem Soc 91:2125–2134
Kajiwara S, Yamada R, Mori H, Hara M, Ogino H (2017) Development of sucrose-complexed lipase to improve its transesterification activity and stability in organic solvents. Biochem Eng J 121:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2017.02.002
Kajiwara S, Komatsu K, Yamada R, Matsumoto T, Yasuda M, Ogino H (2019) Modification of lipase from Candida cylindracea with dextran using the borane-pyridine complex to improve organic solvent stability. J Biotechnol 296:1–6
Lei L, Liu X, Li Y, Cui Y, Yang Y, Qin G (2011) Study on synthesis of poly (GMA)-grafted Fe3O4/SiOX magnetic nanoparticles using atom transfer radical polymerization and their application for lipase immobilization. Mater Chem Phys 125:866–871
Liang H, Russell SJ, Wood DJ, Tronci G (2018) A hydroxamic acid–methacrylated collagen conjugate for the modulation of inflammation-related MMP upregulation. J Mater Chem B 6:3703–3715. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB03035E
Manjula S, Jose A, Divakar S, Subramanian R (2011) Degumming rice bran oil using phospholipase-A1. Euro J Lipid Sci Technol 113(5):658–664. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201000376
Orrego AH, Ghobadi R, Moreno-Perez S, Mendoza AJ, Fernandez-Lorente G, Guisan JM, Rocha-Martin J (2018) Stabilization of immobilized lipases by intense intramolecular cross-linking of their surfaces by using Aldehyde-Dextran polymers. Int J Mol Sci 19:553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020553
Qu Y, Sun L, Li X, Zhou S, Zhang Q, Sun L, Yu D, Jiang L, Tian B (2016) Enzymatic degumming of soybean oil with magnetic immobilized phospholipase A2. LWT - Food Sci Technol 73:290–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.06.026
Real-Guerra R, Carlini CR, Stanisçuaski F (2013) Role of lysine and acidic amino acid residues on the insecticidal activity of Jackbean urease. Toxicon 71:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.05.008
Rodrigues RC, Bolivar JM, Volpato G, Filice M, Godoy C, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Guisan JM (2009) Improved reactivation of immobilized-stabilized lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus by its coating with highly hydrophilic polymers. J Biotechnol 144:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.09.002
Rodrigues R, Berenguer-Murcia A, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2011) Coupling chemical modification and immobilization to improve the catalytic performance of enzymes. Adv Synth Catal 353:2216–2238. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201100163
Rueda N, dos Santos JC, Ortiz C, Torres R, Barbosa O, Rodrigues RC, Berenguer-Murcia Á, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2016) Chemical modification in the design of immobilized enzyme biocatalysts: drawbacks and opportunities. Chem rec 16:1436–1455. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.201600007
Sampaio KA, Zyaykina N, Uitterhaegen E, De Greyt W, Verhé R, de Almeida Meirelles AJ, Stevens CV (2019) Enzymatic degumming of corn oil using phospholipase C from a selected strain of Pichia pastoris. Lebensm Wiss Technol 107:145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.03.003
Sheldon RA, van Pelt S (2013) Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: why, what and how. Chem Soc rev 42:6223–6235. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60075k
Siar EH, Arana-Peña S, Barbosa O, Zidoune MN, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2018) Solid phase chemical modification of agarose glyoxyl-ficin: Improving activity and stability properties by amination and modification with glutaraldehyde. Process Biochem 73:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.07.013
Sun X, Zhang L, Tian S, Yang K, Xie J (2019) Phospholipid composition and emulsifying properties of rice bran lecithin from enzymatic degumming. LWT - Food Sci Technol 117:108588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108588
Wang X, Liu X, Lei L, Zhu H, Yang Y, Li Y (2014) Preparation and characterization of magnetic microspheres with an epoxy group coating and their applications for lipase immobilization. J Macromol Sci B 53:1348–1363. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2014.928156
Wang H, Lin P, Zhao S, Li S, Lu X, Liang H (2017) Preparation of magnetic microsphere-gold nanoparticle-immobilized enzyme batch reactor and its application to enzyme inhibitor screening in natural extracts by capillary electrophoresis. Chin J Chem 35:943–948
Xiang M, Wang L, Ya Q, Jian Z, Yang S (2020) High-level expression and characterization of a novel phospholipase C from Thielavia terrestris suitable for oil degumming. Int J Biol Macromol 156:740–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.104
Xie W, Huang M (2020) Fabrication of immobilized Candida rugosa lipase on magnetic Fe3O4-poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) composite as an efficient and recyclable biocatalyst for enzymatic production of biodiesel. Renew Energ 158:474–486
Yang X, Wang Y, Bai R, Ma H, Wang W, Sun H, Dong Y, Qu F, Tang Q, Guo T, Binks BP (2019) Pickering emulsion-enhanced interfacial biocatalysis: tailored alginate microparticles act as particulate emulsifier and enzyme carrier. Green Chem 21:2229–2233. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03573C
Yu D, Jiang L, Li Z, Shi J, Xue J, Kakuda Y (2012) Immobilization of phospholipase A1 and its application in soybean oil degumming. J Am Oil Chem Soc 89:649–656
Yu D, Ma Y, Jiang L, Elfalleh W, Shi M, Hu L (2013a) Optimization of magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 degumming process for soybean oil using response surface methodology. Eur Food Res Technol 237:811–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-013-2057-z
Yu D, Ma Y, Xue SJ, Jiang L, Shi J (2013b) Characterization of immobilized phospholipase A1 on magnetic nanoparticles for oil degumming application. LWT - Food Sci Technol 50:519–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.08.014
Yu D, Zhang X, Zou D, Wang T, Liu T, Wang L, Elfalleh W, Jiang L (2018) Immobilized CALB catalyzed transesterification of soybean oil and phytosterol. Food Biophys 13(2):208–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9526-7
Zi-Jian WA, Jing-Bo Y, Li GP, Ning-Ning S, Wan-Chun SU, Qi-Sheng PE, Ning LI (2016) Chemical modifications of peptides and proteins with low concentration formaldehyde studied by mass spectrometry. Chin J Anal Chem 44:1193–1199
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a grant from rice bran high-value steady-state processing technology and intelligent equipment research and demonstration (2018YFD0401101). This work was also supported by a grant from the Province Natural Science Foundation of Heilong Jang: Mechanism of enzymatic degumming process of soybean oil characterized by electrochemical biosensor (LH2020C061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Authors have no competing interest to declare.
Consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Ethics approval
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weining, W., Tang, H., Chen, Y. et al. Chemically modified magnetic immobilized phospholipase A1 and its application for soybean oil degumming. J Food Sci Technol 59, 317–326 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05017-4
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05017-4