Abstract
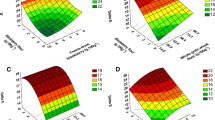
Red ginseng marc (RGM), a by-product from ginseng industry, still contains bioactive compounds such as ginsenosides and dietary fibers. The objective of this study was to investigate effects of baking conditions and formulations on physicochemical and sensory characteristics of crackers in which RGM was incorporated. The sum of ginsenoside Rb1, Rg1 and Rg3 (58.69 ± 2.93 mg/100 g, dry basis) and dietary fibers (7.52 ± 1.22 g/100 g) were the highest in the crackers baked at 120 °C for 60 min. The crackers with 5% replacement of wheat flour with RGM scored the highest in taste and overall acceptability. The baked crackers still contained relatively high amounts of ginsenoside Rb1 (7.62 ± 0.34 mg/100 g), Rg3(R) (7.51 ± 0.99 mg/100 g) and Rg3(S) (8.65 ± 0.77 mg/100 g) and dietary fiber (2.59 ± 0.17 g/100 g). The results suggest that low temperature-long time may be a suitable baking condition to retain bioactive ginsenosides in RGM and using proper amount of RGM in bakery products may improve not only nutritional quality but also sensory properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The codes used in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- RGM:
-
Red ginseng marc
References
Ahmed ZS, Abozed SS (2015) Functional and antioxidant properties of novel snack crackers incorporated with Hibiscus sabdariffa by-product. J Adv Res 6:79–87
AOAC (2000) Official methods of analysis of AOAC International, 17th edn. AOAC International, Gaithersburg, MD
Chang YH, Ng PKW (2009) Extraction of ginsenosides from a blend of wheat flour and ginseng powder. Food Chem 115:1512–1518
Hwang CR, Lee SH, Jang GY, Hwang IG, Kim HY, Woo KS, Lee J, Jeong HS (2014) Changes in ginsenoside compositions and antioxidant activities of hydroponic-cultured ginseng roots and leaves with heating temperature. J Ginseng Res 38:180–186
Hwang IG, Kim HY, Joung EM, Woo KS, Jeong JH, Yu KW, Lee J (2010) Changes in ginsenosides and antioxidant activity of Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) with heating temperature and pressure. Food Sci Biotechnol 19:941–949
Hyun JS, Kim MA (2005) The effect of addition of level of red ginseng powder on Yackwa quality and during storage. J Korean Soc Food Cult 20:352–359
Jung YM, Oh H, Kang ST (2015) Quality characteristics of muffins added with red ginseng marc powder. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 44:1050–1057
Kim H, Yang HJ, Lee KY, Baek SE, Song KB (2017) Characterization of red ginseng residue protein films incorporated with hibiscus extract. Food Sci Biotechnol 26:369–374
Kohajdová Z, Karovičová J, Magala M (2013) Rheological and qualitative characteristics of pea flour incorporated cracker biscuits. Croat J Food Sci Technol 5:11–17
Lafaga T, Gallagher E, Bademunt A, Bobo G, Echeverria G, Viñas I, Aguiló-Aguayo I (2019) Physicochemical and nutritional characteristics, bioaccessibility and sensory acceptance of baked crackers containing broccoli co-products. Int J Food Sci Technol 54:634–640
Lee NR, Han JS, Kim JS, Choi JE (2011) Effects of extraction temperature and time on ginsenoside content and quality in ginseng (Panax ginseng) flower water extract. Korean J Med Crop Sci 19:271–275
Lee SM, Bae BS, Park HW, Ahn NG, Cho BG, Cho YL, Kwak YS (2015) Characterization of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer): History preparation method, and chemical composition. J Ginseng Res 39:384–391
Li X, Yao F, Fan H, Li K, Sun L, Liu Y (2018) Intraconversion of polar ginsenosides, their transformation into less-polar ginsenosides, and ginsenoside acetylation in ginseng flowers upon baking and steaming. Molecules 23:759
Liljeberg H, Åkerberg A, Björck I (1996) Resistant starch formation in bread as influenced by choice of ingredients or baking conditions. Food Chem 56:389–394
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (2018) Health functional food code, Osong, Korea, pp 48–50
Millar KA, Barry-Ryan C, Burke R, Hussey K, McCarthy S, Gallagher E (2017) Effect of pulse flours on the physicochemical characteristics and sensory acceptance of baked crackers. Int J Food Sci Technol 52:1152–1163
Park K, Cho AE (2017) Using reverse docking to identify potential targets for ginsenosides. J Ginseng Res 41:534–539
Park YR, Han IJ, Kim MY, Choi SH, Shin DW, Chun SS (2008) Quality characteristics of sponge cake prepared with red ginseng marc powder. Korean J Cook Sci 24:236–242
Patel AS, Kar A, Pradhan RC, Mohapatra D, Nayak B (2019) Effect of baking temperatures on the proximate composition, amino acids and protein quality of de-oiled bottle gourd (Lagenaria siceraria) seed cake fortified biscuit. LWT-Food Sci Technol 106:247–253
Roehrig KL (1988) The physiological effects of dietary fiber—a review. Food Hydrocolloids 2:1–18
Saa DT, Silvestro RD, Dinelli G, Gianotti A (2017) Effect of sourdough fermentation and baking process severity on dietary fibre and phenolic compounds of immature wheat flour bread. LWT-Food Sci Technol 83:26–32
Schimidt C, Geweke I, Struck S, Zahn S, Rohm H (2018) Black currant pomace from juice processing as partial flour substitute in savory crackers: dough characteristics and product properties. Int J Food Sci Technol 53:237–245
Seo WK, Kim YA (1995) Effects of heat treatments on the dietary fibrecontents of rice, brown rice, yellow soybean, and black soybean. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 11:20–25
Slavin M, Lu Y, Kaplan N, Yu L (2013) Effect of baking condition on cyanidin-3-glucoside content and antioxidant properties of black and yellow soybean crackers. Food Chem 141:1166–1174
Xu XF, Cheng XL, Lin QH, Li SS, Jia Z, Han T, Lin RC, Wang D, Wei F, Li XR (2016) Identification of mountain-cultivated ginseng using UPLC/oa-TOF MSE with a multivariate statistical sample-profiling strategy. J Ginseng Res 40:344–350
Yadav BS (2011) Effect of frying, baking and storage conditions on resistant starch content of foods. Br Food J 113:710–719
Yeboah-Awudzi M, Lutterodt HE, Kyereh E, Reyes V, Sathivel S, Manful J, King JM (2018) Effect of bambara groundnut supplementation on the physicochemical properties of rice flour and crackers. J Food Sci Technol 55:3556–3563
Zang OH, Park J, Kim SH, Lee SY, Moon BK (2014) Quality characteristics of yackwa with red ginseng marc powder. Korean J Food Sci Cook Sci 30:800–805
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JY Lee designed the study, conducted all experimental works and wrote the original manuscript. T Lim advised on the overall research outline and edited the manuscript. J Kim assisted extraction of ginsenosides and HPLC-UV analysis. KT Hwang organized the whole research outline and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare any conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
The research protocol was approved by Institutional Review Board (IRB) at Seoul National University (IRB No. 1812/003–001).
Consent to participate
All authors have approved and reviewed the final manuscript.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.Y., Lim, T., Kim, J. et al. Physicochemical characteristics and sensory acceptability of crackers containing red ginseng marc. J Food Sci Technol 59, 212–219 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05002-x
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05002-x