Abstract
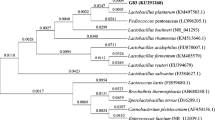
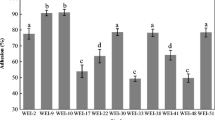
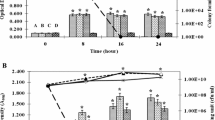
Probiotics are important bacteria due to their benefit on human health. In this study, four strains of lactic acid bacteria from chicken bile were isolated and the strain with the best antimicrobial activity was selected for further identification and evaluation on its probiotic traits and safety. The strain was identified as Enterococcus faecium by biochemical characterization and 16S rDNA gene sequencing. The strain, named E. faecium MK-SQ-1, was tolerant to acid (pH 3.0), bile salts (up to 0.3%) or trypsin (up to 0.4%) for 3 h and it was able to survive from high temperature (up to 60 °C) for 15 min. This strain inhibited the growth of Salmonella enteritidis and Staphylococcus aureus intermediately. The genes responsible for virulence including asa1, cylA, efaA, esp, gelE and hyl were absent and the mice administrated orally with a very high dose (2 × 109 CFU) of the strain daily for 35 days were not found abnormal. The strain enhanced the serum IgG level and phagocytic index of mice significantly by daily oral administration at a high dose (2 × 108 CFU) for 21 days (p < 0.05). The strain did not have multi-antibiotic resistance and vancomycin resistance. Comprehensive evaluation showed E. faecium MK-SQ-1 could be a candidate as a probiotic strain used in human or animals.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam S, Mushtaq M (2009) Antibiotic associated diarrhea in children. Indian Pediatr 46:491–496
Ambadoyiannis G, Hatzikamari M, Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E, Tzanetakis N (2004) Probiotic and technological properties of enterococci isolates from infants and cheese. Food Biotechnol 18:307–325
Ayyash M, Abushelaibi A, Al-Mahadin S et al (2018) In-vitro investigation into probiotic characterization of Streptococcus and Enterococcus isolated from camel milk. LWT Food Sci Technol 87:478–487
Bauer AW, Kirby WM, Sherris JC, Turck M (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol 45:493–496
Broom LJ, Miller HM, Kerr KG, Knapp JS (2006) Effects of zinc oxide and Enterococcus faecium SF68 dietary supplementation on the performance, intestinal microbiota and immune status of weaned piglets. Res Vet Sci 80:45–54
Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (1984) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. Science Press, Beijing, pp 347–395
Bustos AY, de Valdez GF, Fadda S, Taranto MP (2018) New insights into bacterial bile resistance mechanisms: the role of bile salt hydrolase and its impact on human health. Food Res Int 112:250–262
Canani RB, Cirillo P, Terrin G et al (2007) Probiotics for treatment of acute diarrhoea in children: randomised clinical trial of five different preparations. BMJ 335(7615):340
Coleman R, Lowe PJ, Billington D (1980) Membrane lipid composition and susceptibility to bile salt damage. BBA Biomembranes 599:294–300
Collado MC, Gueimonde M, Herna’ndez M, Sanz Y, Salminen S (2005) Adhesion of selected bifidobacterium strains to human intestinal mucus and the role of adhesion in enteropathogen exclusion. J Food Prot 68:2672–2678
Cross ML (2002) Microbes versus microbes: immune signals generated by probiotic lactobacilli and their role in protection against microbial pathogens. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 34:245–253
Dong X, Cai M (2001) Manual of system determinative common bacteriology. Science Press, Beijing, pp 370–398
FAO/WHO (2006) Probiotics in food. Health and nutritional properties and guidelines for evaluation. FAO Food and Nutritional paper No. 85 (ISBN 92-5-105513-0)
Feng Y, Qiao L, Liu R et al (2017) Potential probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from the intestinal mucosa of healthy piglets. Ann Microbiol 67:239–253
Fernandez MF, Boris S, Barbes C (2003) Probiotic properties of human lactobacilli strains to be used in the gastrointestinal tract. J Appl Microbiol 94:449–455
Floch MH (2010) Probiotic therapy for ulcerative colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 44:237–238
Fuller R (1989) Probiotics in man and animals. J Appl Bacteriol 66:365–378
Gaglio R, Couto N, Marques C et al (2016) Evaluation of antimicrobial resistance and virulence of enterococci from equipment surfaces, raw materials, and traditional cheeses. Int J Food Microbiol 236:107–114
George A, Chinnappan S, Choudhary Y, Bommu P, Sridhar M (2014) Immunomodulatory activity of an aqueous extract of Polygonum minus Huds on Swiss albino mice using carbon clearance assay. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 4:398–400
Hlivak P, Odraska J, Ferencik M et al (2005) One-year application of probiotic strain Enterococcus faecium M-74 decreases serum cholesterol levels. Bratisl Lek Listy 106:67–72
Juturu V, Wu J (2018) Microbial production of bacteriocins: latest research development and applications. Biotechnol Adv 36:2187–2200
Khalkhali S, Mojganic N (2018) In vitro and in vivo safety analysis of Enterococcus faecium 2C isolated from human breast milk. Microb Pathog 116:73–77
Kos B, Suskovic J, Vukovic S et al (2003) Adhesion and aggregation ability of probiotic strain Lactobacillus acidophilus M92. J Appl Microbiol 94:981–987
Krammer HJ, Schlieger F, Harder H et al (2005) Probiotics as therapeutic agents in irritable bowel syndrome. Z Gastroenterol 43:467–471
Li G (2012) Intestinal probiotics: interactions with bile salts and reduction of cholesterol. Procedia Environ Sci 12(Part B):1180–1186
Lins RX, Oliveira-Andrade A, Hirata JR et al (2013) Antimicrobial resistance and virulence traits of Enterococcus faecalis from primary endodontic infections. J Dent 41:779–786
Liu Y, Tang H, Lin Z, Xu P (2015) Mechanisms of acid tolerance in bacteria and prospects in biotechnology and bioremediation. Biotechnol Adv 33:1484–1492
Lye HS, Kuan CY, Ewe JA et al (2009) The improvement of hypertension by probiotics: effects on cholesterol, diabetes, renin, and phytoestrogens. Int J Mol Sci 109:3755–3775
Martin L, Pieper R, Kroger S et al (2012) Influence of age and Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 10415 on development of small intestinal digestive physiology in piglets. Anim Feed Sci Technol 175:65–75
Messi P, Guerrieri E, de Niederhäusern S, Sabia C, Bondi M (2006) Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) in meat and environmental samples. Int J Food Microbiol 107:218–222
Osterlund P, Ruotsalainen T, Korpela R et al (2007) Lactobacillus supplementation for diarrhoea related to chemotherapy of colorectal cancer: a randomised study. Br J Cancer 97:1028–1034
Paéz R, Lavari L, Vinderola G et al (2012) Effect of heat treatment and spray drying on lactobacilli viability and resistance to simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Res Int 48:748–754
Palmer KL, Godfrey P, Griggs A et al (2012) Comparative genomics of enterococci: variation in Enterococcus faecalis, clade structure in E. faecium, and defining characteristics of E. gallinarum and E. casseliflavus. MBio 3(1):e00318-11
Pellegrino MS, Frola ID, Natanael B et al (2019) In vitro characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from bovine milk as potential probiotic strains to prevent bovine mastitis. Probiotics Antimicro Proteins 11:74–84
Pollmann M, Nordhoff M, Pospischil A, Tedin K, Wieler LH (2005) Effects of a probiotic strain of Enterococcus faecium on the rate of natural chlamydia infection in swine. Infect Immun 73:4346–4353
Prasad J, Gill H, Smart J, Gopal PK (1998) Selection and characterisation of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains for use as probiotics. Int Dairy J 8:993–1002
Rehaiem A, Belgacem ZB, Edalatian MR, Martínez B, Guerra NP (2014) Assessment of potential probiotic properties and multiple bacteriocin encoding-genes of the technological performing strain Enterococcus faecium MMRA. Food Control 37:343–350
Reik R, Tenover F, Klein E, McDonald C (2008) The burden of vancomycin-resistant enterococcal infections in US hospitals, 2003 to 2004. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 62:81–85
Reyes K, Bardossy AC, Zervos M (2016) Vancomycin-resistant enterococci: epidemiology, infection prevention, and control. Infect Dis Clin N Am 30:953–965
Samtiya M, Bhat MI, Gupta T et al (2019) Safety assessment of potential probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum MTCC-5898 in murine model after repetitive dose for 28 days (sub-acute exposure). Probiotics Antimicrob Prot. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-09529-6
Scharek L, Guth J, Reiter K et al (2005) Influence of a probiotic Enterococcus faecium strain on development of the immune system of sows and piglets. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 105:151–161
Servin AL, Coconnier MH (2003) Adhesion of probiotic strains to the intestinal mucosa and interaction with pathogens. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17:741–754
Singh TP, Kaur G, Malik RK, Schillinger U, Guigas C, Kapila S (2012) Characterization of intestinal Lactobacillus reuteri strains as potential probiotics. Probiotics Antimicrob Prot 4:47–58
Solieri L, Bianchi A, Mottolese G, Lemmetti F, Giudici P (2014) Tailoring the probiotic potential of non-starter Lactobacillus strains from ripened Parmigiano Reggiano cheese by in vitro screening and principal component analysis. Food Microbiol 38:240–249
Sun P, Wang J, Jiang Y (2010) Effects of Enterococcus faecium (SF68) on immune function in mice. Food Chem 123:63–68
Tinrat S, Khuntayaporn P, Thirapanmethee K, Chomnawang MT (2018) In vitro assessment of Enterococcus faecalis MTC 1032 as the potential probiotic in food supplements. J Food Sci Technol 55:2384–2394
Yoon MY, Kim YJ, Hwang H (2008) Properties and safety aspects of Enterococcus faecium strains isolated from Chungkukjang, a fermented soy product. LWT Food Sci Technol 41:925–933
Zhang ZF, Rolando AV, Kim IH (2016) Effects of benzoic acid, essential oils and Enterococcus faecium SF68 on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, blood profiles, faecal microbiota and faecal noxious gas emission in weanling pigs. J Appl Anim Res 44:173–179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Zhai, M., Li, J. et al. Evaluation of safety and probiotic properties of a strain of Enterococcus faecium isolated from chicken bile. J Food Sci Technol 57, 578–587 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04089-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04089-7