Abstract
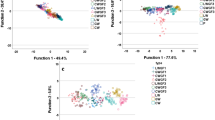
The particle size distribution, protein profile, pasting and dough rheological properties of meal from forty-two Indian durum wheat accessions were evaluated. Meal from accessions with higher grain hardness index (GHI) showed a high proportion of large size particles with higher protein content and lower paste viscosities. Elastic and viscous modulii (G′ and G″) of dough were negatively correlated with paste viscosities, which was associated with the presence/absence of LMW-GS and HMW-GS. Wheat accessions with allelic combinations of (13 + 16) with 97 + 91 kDa polypeptides (PPs) had higher G′ and G″. The accession with 35 kDa PP showed higher while those with 35 and 62 kDa PPs showed lower paste viscosity. Among all accessions, 25 accessions possess 7 + 8 (97 and 88 kDa) type HMW-GS allelic combination. Durum accessions with diverse GHI, particle size distribution, protein profile, paste and dough rheology indicates their variation in milling and processing behaviour.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GHI:
-
Grain hardness index
- TGW:
-
Thousand grain weight
- GD:
-
Grain diameter
- PT:
-
Pasting temperature
- PV:
-
Peak viscosity
- BDV:
-
Breakdown viscosity
- FV:
-
Final viscosity
- SBV:
-
Setback viscosity
- WS:
-
Weakening slope
- LPV:
-
Left peak value
- RPV:
-
Right peak value
- LPW:
-
Left peak width
- RPW:
-
Right peak width
- MPW:
-
Mixograph peak width
- MPT:
-
Mixograph peak time
- G′:
-
Elastic modulus
- G″:
-
Viscous modulus
- LMW-GS:
-
Low molecular weight glutenin subunits
- HMW-GS:
-
High molecular weight glutenin subunits
- MPV:
-
Mixograph peak value
References
AACC International (2000) Approved methods of American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th edn. AACC International Press, St. Paul
Aalami M, Rao UJS, Leelavathi K (2007) Physicochemical and biochemical characteristics of Indian durum wheat varieties: relationship to semolina milling and spaghetti making quality. Food Chem 102:993–1005
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis, 15th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
Baasandroj T, Ohm JB, Manthey F, Simsek S (2015) Effect of kernal size and mill type on protein, milling yield and baking quality of hard red spring wheat. Cereal Chem 92:81–87
Boggini G, Pogna NE (1989) The bread making quality and storage protein composition of Italian durum wheat. J Cereal Sci 9:131–138
Dick JW, Youngs VL (1988) Evaluation of durum wheat, semolina, and pasta in the United States. In: Fabriani G, Lintas C (eds) Durum wheat: chemistry and technology. AACC, St. Paul, pp 237–248
Du Cros DL (1987) Glutenin proteins and gluten strength in durum wheat. J Cereal Sci 5:3–12
Edwards NM, Gianibelli MC, McCaig TN, Clarke JM, Ames NP, Larroque OR, Dexter JE (2007) Relationships between dough strength, polymeric protein quantity and composition for diverse durum wheat genotypes. J Cereal Sci 45:140–149
Ewart JAD (1972) A modified hypothesis for the structure and rheology of glutenins. J Sci Food Agric 23:687–699
Galliard T, Gallagher DM (1988) The effects of wheat bran particle size and storage period on bran flavor and baking quality of bran/flour blends. J Cereal Sci 8:147–154
Gazza L, Sgrulletta D, Cammerata A, Gazzelloni G, Perenzin M, Pogna NE (2011) Pasta making and bread making quality of soft textured durum wheat lines. J Cereal Sci 54:481–487
Haraszi R, Sissons M, Juhasz A, Kadkol G, Tamas L, Anderssen RS (2016) Using rheological phenotype phases to predict rheological features of wheat hardness and milling potential of durum wheat. Cereal Chem 93:369–376
Katyal M, Virdi AS, Kaur A, Singh N, Kaur S, Ahlawat AK, Singh AM (2016) Diversity in quality traits amongst Indian wheat cultivars I: flour and protein characteristics. Food Chem 194:337–344
Kaur A, Singh N, Ahlawat AK, Kaur S, Singh AM, Chauhan H, Singh GP (2013) Diversity in grain, flour, dough and gluten properties amongst Indian wheat cultivars varying in high molecular weight subunits (HMW-GS). Food Res Int 53:63–72
Kaur A, Singh N, Kaur S, Ahlawat AK, Singh AM (2014) Relationships of flour retention capacity, secondary structure and rheological properties with the cookie making characteristics of wheat cultivars. Food Chem 158:48–55
Kaur A, Singh N, Kaur S, Katyal M, Virdi AS, Kaur D, Ahlawat AK, Singh AM (2015) Relationship of various flour properties with noodle making characteristics amongst durum wheat varieties. Food Chem 188:517–526
Li Y, Mao X, Wang Q, Zhang J, Li X, Ma F, Sun F, Chang J, Chen M, Wang Y, Li K, Yang G, He G (2014) Overexpression of puroindoline a gene in transgenic durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) leads to a medium-hard kernel texture. Mol Breed 33:545–554
Martinant JP, Nicolas Y, Bouguennec A, Popineau Y, Saulnier L, Branlard G (1998) Relationships between mixograph parameters and indices of wheat grain quality. J Cereal Sci 27:179–189
Morris CF (2002) Puroindolines: the molecular genetic basis of wheat grain hardness. Plant Mol Biol 48:633–647
Morris CF, Simeone MC, King GE, Lafi andra D (2011) Transfer of soft kernel texture from Triticum aestivum to durum wheat Triticum turgidum ssp. durum. Crop Sci 51:114–122
Murray JC, Kiszonas AM, Morris CF (2017) Influence of soft kernel texture on the flour, water absorption, rheology, and baking quality of durum wheat. Cereal Chem 94:215–222
Nieto-Taladriz MT, Ruiz M, Martínez MC, Vázquez JF, Carrillo JM (1997) Variation and classification of B low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit alleles in durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 95:1155–1160
Novaro P, D’Egidio MG, Mariani BM, Nardi S (1993) Combined effect of protein content and high-temperature drying systems on pasta cooking quality. Cereal Chem 70:716–719
Oak MD, Sissons M, Egan N, Tamhankar SA, Rao VS, Bhosale SB (2006) Relationship between gluten strength and pasta firmness in Indian durum wheats. J Food Sci Technol 41:538–544
Ohm JB, Manthey F, Elias EM (2017) Variation and correlation of protein molecular weight distribution and semolina quality parameters for durum genotypes grown in North Dakota. Cereal Chem 94:780–788
Raggiri V, Barron C, Abecassis J, Lullien-Pellerin V (2016) In-depth study of durum wheat grain tissue distribution at milling. Cereal Chem 93:219–225
Ram S, Sharma S, Verma A, Tyagi BS, Peña RJ (2011) Comparative analyses of LMW glutenin alleles in bread wheat using allele-specific PCR and SDS-PAGE. J Cereal Sci 54:488–493
Rharrabti Y, Royo C, Villegas D, Aparicio N, del Moral LG (2003) Durum wheat quality in Mediterranean environments: I. Quality expression under different zones, latitudes and water regimes across Spain. Field Crop Res 80:123–131
Saini DP, Gautam PL (1990) Notes on G × E analysis in segregating populations of durum wheat. Indian J Genet 50:199–201
Sasaki T, Yasui T, Kohyama K (2008) Influence of starch and gluten characteristics on rheological properties of wheat flour gels at small and large deformation. Cereal Chem 85:329–334
Singh NK, Shepherd KW (1988) Linkage mapping of the genes controlling endosperm proteins in wheat. 1. Genes on the short arms of group-1 chromosome. Theor Appl Genet 75:628–641
Singh NK, Shepherd KW, Cornish GB (1991) A simplified SDS-PAGE procedure for separating LMW subunits of glutenin. J Cereal Sci 14:203–208
Singh S, Singh N, MacRitchie F (2011) Relationship of polymeric proteins with pasting, gel dynamic- and dough empirical-rheology in different Indian wheat varieties. Food Hydrocoll 25:19–24
Singh N, Kaur A, Katyal M, Singh AM, Ahlawat AK, Bhinder S (2016) Diversity in quality traits amongst Indian wheat varieties II: paste, dough and muffin making properties. Food Chem 197:316–324
Song Y, Zheng Q (2007) Dynamic rheological properties of wheat flour dough and proteins. Trends Food Sci Technol 18:132–138
Troccoli A, Borreli GM, De Vita P, Fares C, Di Fonzo N (2000) Durum wheat quality: a multidisciplinary concept. J Cereal Sci 32:99–113
Acknowledgements
NS acknowledges MOFPI, Govt. of India, for providing funds in the form of a research project. MK acknowledges UGC-BSR for providing financial assistance in the form of Fellowship. The authors are thankful to Dr. Arvind Kumar Ahlawat for measuring the grain hardness index of accessions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katyal, M., Virdi, A.S., Singh, N. et al. Diversity in protein profiling, pasting, empirical and dynamic dough rheological properties of meal from different durum wheat accessions. J Food Sci Technol 55, 1256–1269 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3036-y
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3036-y