Abstract
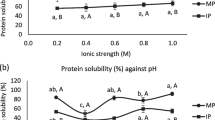
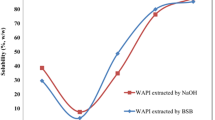
The effect of pH and NaCl on solubility and functional properties of walnut proteins obtained through AOT reverse micelles, enzyme-assisted reverse micelles and aqueous phase extraction methods was investigated and compared. Extraction yield, foaming properties, water holding capacities of protein obtained through enzyme-assisted reverse micelles at pH 2–12 and NaCl concentration 0.1–1 M were significantly higher than those of the AOT reverse micelles and aqueous phase extracted two. The solubility of proteins by AOT reverse micelles and enzyme-assisted reverse micelles at certain pH and NaCl concentration had no significant difference, but was higher that of the aqueous buffer. Oil holding capacity of three proteins was 2.35, 3.96 and 1.08 cm3/g, respectively. At pH 6–12 and NaCl concentration 0.1–1 M, the emulsifying activity of protein from AOT reverse micelles was higher than those of other two methods, while the emulsifying stability of protein from enzyme-assisted reverse micelles was the highest. The functional properties of walnut proteins were affected by extraction methods. It indicated that the walnut protein might be potentially applied in food industry as a food ingredient.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebiyi AP, Aluko RE (2011) Functional properties of protein fractions obtained from commercial yellow field pea (Pisum sativum L.) seed protein isolate. Food Chem 128:902–908
Agboola S, Ng D, Mills D (2005) Characterisation and functional properties of Australian rice protein isolates. J Cereal Sci 41(3):283–290
AOAC (2000) Official methods of analysis of AOAC International (17th ed.). Washington, DS, USA: Association of Official Analytical Chemists (Methods Ba 4e-93)
Belitz HD, Grosch W, Schieberle P (2009) Food Chemistry. Springer, Berlin
Campbell NF, Shih FF, Marshall WE (1992) Enzymic phosphorylation of soy protein isolate for improved functional properties. J Agric Food Chem 40(3):403–406
Chen N, Yang HM, Sun Y, Niu J, Liu SY (2012) Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from walnut (Juglans regia L.) protein hydrolysates. Peptides 38(2):344–349
Chobert JM, Bertrand-Harb C, Nicolas MG, Gaertner HF, Puigserver AJ (1987) Solubility and emulsifying properties of caseins chemically modified by covalent attachment of l-methionine and L-valine. J Agric Food Chem 35(5):638–644
Chove BE, Grandison AS, Lewis MJ (2001) Emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate factions obtained by isoelectric precipitation. J Sci Food Agric 81(8):759–763
Cofrades S, Serrano A, Ayo J, Carballo J, Jiménez-Colmenero F (2008) Characteristics of meat batters with added native and preheated defatted walnut. Food Chem 107(4):1506–1514
Deng QC, Wang L, Wei F, Xie BJ, Huang FH, Huang W, Shi J, Huang QD, Tian BQ, Xue S (2011) Functional properties of protein isolates, globulin and albumin extracted from Ginkgo biloba seeds. Food Chem 124(4):1458–1465
Downs ML, Simpson A, Custovic A, Semic-Jusufagic A, Bartra J, Fernandez-Rivas M, Taylor SL, Baumert JL, Clare Mills EN (2016) Insoluble and soluble roasted walnut proteins retain antibody reactivity. Food Chem 194:1013–1021
Fabian C, Ju YH (2011) A review on rice bran protein: its properties and extraction methods. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 51:816–827
FDA (2011-12-20) Qualified health claims: letter of enforcement discretion-walnuts and coronary heart disease (Docket No.02p-0292). http://www.cfsan.fda.gov/dms/qhcnuts3.html
Gaikaiwari RP, Wagha SA, Kulkarni BD (2012) Extraction and purification of tannase by reverse micelle system. Sep Purif Technol 89:288–296
Gharibzahedi SMT, Mousavi SM, Hamedi M, Rezaei K, Khodaiyan F (2013) Evaluation of physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of Persian walnut oil obtained by several extraction methods. Ind Crops Prod 45:133–140
Ghumman A, Kaur A, Singh N (2016) Functionality and digestibility of albumins and globulins from lentil and horse gram and their effect on starch rheology. Food Hydrocolloid 61:843–850
Guan X, Yao H, Chen Z, Shan L, Zhang M (2007) Some functional properties of oat bran protein concentrate modified by trypsin. Food Chem 101(1):163–170
Hung SC, Zayas JF (1991) Emulsifying capacity and emulsion stability of milkproteins and corn germ protein flour. J Food Sci 56:1216–1223
Kinsella JE, Melachouris N (1976) Functional properties of proteins in foods: a survey. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 7:219–280
Labuckas D, Maestri D, Lamarque A (2014) Effect of different oil extraction methods on proximate composition and protein characteristics of walnut (Juglans regia L.) flour. LWT Food Sci Technol 59:794–799
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lawal OS, Adebowale KO, Ogunsanwo BM, Sosanwo OA, Bankole SA (2005) On the functional properties of globulin and albumin protein fractions and flours of African locust bean (Parkia biglobossa). Food Chem 92:681–691
Lin M, Humbert E, Sosulski F (1974) Certain functional properties of sunflower meal products. J Food Sci 39(2):368–370
Liu Y, Zhao GL, Zhao MM, Ren JY, Yang B (2012) Improvement of functional properties of peanut protein isolate by conjugation with dextran through Maillard reaction. Food Chem 131:901–906
Liu FL, Wang XC, Zhao XY, Hu HF, Chen FL, Sun YL (2014) Surface properties of walnut protein from AOT reverse micelles. Int J Food Sci Technol 49:626–633
Mao X, Hua Y (2012) Composition, structure and functional properties of protein concentrates and isolates produced from walnut (Juglans regia L.). Int J Mol Sci 13:1561–1581
Mundi S, Aluko RE (2012) Physicochemical and functional properties of kidney bean albumin and globulin protein fractions. Food Res Int 48:299–306
Ogunwolu SO, Henshaw FO, Mock HP, Santros A, Awonorin SO (2009) Functional properties of protein concentrates and isolates produced from cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) nut. Food Chem 115(3):852–858
Ragab DM, Babiker EE, Eltinay AH (2004) Fractionation, solubility and functional properties of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) proteins as affected by pH an d/or salt concentration. Food Chem 84:207–212
Shevkani K, Singh N, Kaur A, Rana JC (2015) Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: a comparative study. Food Hydrocolloid 43:679–689
Sze-Tao KWC, Sathe SK (2000) Walnuts (Juglans regia L): proximate composition, protein solubility, protein amino acid composition and protein in vitro digestibility. J Sci Food Agric 80:1393–1401
Vuong HTH, Tran NM, Tran TTT, Ton NMN, Le VVM (2016) Effects of pH and salt concentration on functional properties of rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum L.) seed albumin concentrate. Int J Food Sci Technol 51(5):1212–1219
Wang XS, Tang CH, Li BS, Yang XQ, Li L, Ma CY (2008) Effects of high-pressure treatment on some physicochemical and functional properties of soy protein isolates. Food Hydrocolloid 22:560–567
Withana-Gamage TS, Wanasundara JPD, Pietrasik Z, Shand PJ (2011) Physicochemical, thernal and functional characterisation of protein isolates from kbuli and desi chickpean (Cicer arietinum L): A comparative study with soy (Glycine max) and pea (Pisum sativum L). J Sci Food Agric 91(6):1022–1031
Yin S, Tang C, Wen Q, Yang X, Li L (2008) Functional properties and in vitro trypsin digestibility of red kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein isolate: effect of high-pressure treatment. Food Chem 110(4):938–945
Yuliana M, Truong CT, Huynh LH, Ho QP, Ju YH (2014) Isolation and characterization of protein isolated from defatted cashew nut shell: influence of pH and NaCl on solubility and functional properties. LWT Food Sci Technol 55:621–626
Zhao XY, Chen FS, Xue WT, Lee LT (2008) FTIR spectra studies on the secondary structures of 7S and 11S globulins from soybean proteins using AOT reverse micellar extraction. Food Hydrocolloid 22(4):568–575
Zhao Q, Selomulya C, Xiong H, Chen XD, Ruan X, Wang SQ, Xie JH, Peng HL, Sun WJ, Zhou Q (2012) Comparison of functional and structural properties of native and industrial process-modified proteins from long-grain indica rice. J Cereal Sci 56(3):568–575
Zhao XY, Zhu HT, Chen J (2015) Effects of sodium bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfo succinate(AOT) reverse micelles on physicochemical properties of soy protein. Food Bioprod Process 94:500–506
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21406133), Xinjiang Autonomous Region Forestry Science and Technology Special Fund Finance and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation China (ZR2014BP015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H., Fan, T., Zhao, X. et al. Influence of pH and salt concentration on functional properties of walnut protein from different extraction methods. J Food Sci Technol 54, 2833–2841 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2721-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2721-6