Abstract
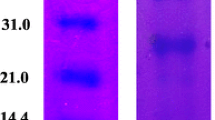
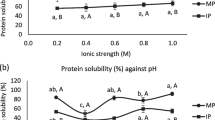
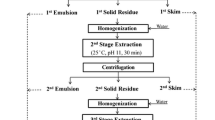
Wild almond (Amygdalus scoparia) is a drought-resistant, non-cultivated plant rich in protein. The extraction of protein isolates from wild almond was carried out using NaOH, buffered saline borate (BSB), and Tris–HCl and the isolates were characterized by their physico-chemical, thermal and emulsifying attributes. Use of BSB solution resulted in the maximum recovery of protein (56%, w/w) from wild almond. The amino acid compositions of wild almond protein isolates (WAPIs) were identified by high-performance liquid chromatography after acid hydrolysis. Aspartic and glutamic acids were the most abundant amino acids found in the WAPIs. Differential scanning calorimeter showed that WAPI is denatured above 80 °C. It was also found that the surface hydrophobicity values of the NaOH- and BSB-extracted proteins were 375 ± 6 and 359 ± 5, respectively. Water absorption capacities of isolates extracted by NaOH and BSB were 2.3 ± 0.4 and 2.6 ± 0.3 g water/g protein, respectively. In addition, oil absorption capacities for the isolates extracted using NaOH and BSB were 3.5 ± 0.7 and 3.1 ± 0.4 g oil/g protein, respectively. Moreover, the solubility levels of the extracted isolates increased up to 85.3% under alkaline conditions. The emulsion-activity indices of isolates increased at pH <4 and also at pH >4.5. In addition, the highest foaming capacity was obtained at pH 2 for the extracted isolates. In conclusion, the study has shown that WAPIs can enhance the oil absorption capacity, emulsifying and foaming properties. Thus, they could be considered for application as an ingredient for functional foods processed in alkaline conditions at temperatures below 80 °C.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Berghout, R. Boom, A. van der Goot, The potential of aqueous fractionation of lupin seeds for high-protein foods. Food Chem. 159, 64–70 (2014)
R. Horax, N. Hettiarachchy, A. Kannan, P. Chen, Protein extraction optimisation, characterisation, and functionalities of protein isolate from bitter melon (Momordica charantia) seed. Food Chem. 124, 545–550 (2011)
A. Mohamed, G. Biresaw, J. Xu, M.P. Hojilla-Evangelista, P. Rayas-Duarte, Oats protein isolate: thermal, rheological, surface and functional properties. Food Res. Int. 42, 107–114 (2009)
S.O. Ogunwolu, F.O. Henshaw, H.P. Mock, A. Santros, S.O. Awonorin, Functional properties of protein concentrates and isolates produced from cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) nut. Food Chem. 115, 852–858 (2009)
A. Cano-Medina, H. Jiménez-Islas, L. Dendooven, R.P. Herrera, G. González-Alatorre, E.M. Escamilla-Silva, Emulsifying and foaming capacity and emulsion and foam stability of sesame protein concentrates. Food Res. Int. 44, 684–692 (2011)
M. Aider, D. Djenane, W.B. Ounis, Amino acid composition, foaming, emulsifying properties and surface hydrophobicity of mustard protein isolate as affected by pH and NaCl. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 47, 1028–1036 (2012)
K. Sze-Tao, S. Sathe, Functional properties and in vitro digestibility of almond (Prunus dulcis L.) protein isolate. Food Chem. 69, 153–160 (2000)
S. Ahrens, M. Venkatachalam, A.M. Mistry, K. Lapsley, S.K. Sathe, Almond (Prunus dulcis L.) protein quality. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 60, 123–128 (2005)
S. Yada, K. Lapsley, G. Huang, A review of composition studies of cultivated almonds: Macronutrients and micronutrients. J. Food Compos. Anal. 24, 469–480 (2011)
K. Sorkheh, B. Shiran, V. Rouhi, E. Asadi, H. Jahanbazi, H. Moradi, T. Gradziel, P. Martínez-Gómez, Phenotypic diversity within native Iranian almond (Prunus spp.) species and their breeding potential. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 56, 947–961 (2009)
A. Moayedi, K. Rezaei, S. Moini, B. Keshavarz, Chemical compositions of oils from several wild almond species. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 88, 503–508 (2011)
M. Balvardi, J.A. Mendiola, P. Castro-Gómez, J. Fontecha, K. Rezaei, E. Ibáñez, Development of pressurized extraction processes for oil recovery from wild almond (Amygdalus scoparia). J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 92, 1503–1511 (2015)
M. Balvardi, K. Rezaei, J.A. Mendiola, E. Ibáñez, Optimization of the aqueous enzymatic extraction of oil from Iranian wild almond. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc 92, 985–992 (2015)
M. Mirzapour, K. Rezaei, M.A. Sentandreu, A.A. Moosavi-Movahedi, In vitro antioxidant activities of hydrolysates obtained from Iranian wild almond (Amygdalus scoparia) protein by several enzymes. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 51, 609–619 (2016)
D. Firestone, Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists. (Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, 1990)
S.K. Sathe, M. Venkatachalam, G.M. Sharma, H.H. Kshirsagar, S.S. Teuber, K.H. Roux, Solubilization and electrophoretic characterization of select edible nut seed proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 7846–7856 (2009)
C. Zhong, R. Wang, Z. Zhou, S.-R. Jia, Z.-L. Tan, P.-P. Han, Functional properties of protein isolates from Caragana korshinskii Kom. Extracted by three different methods. J. Agric. Food Chem 60, 10337–10342 (2012)
K.N. Pearce, J.E. Kinsella, Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 26, 716–723 (1978)
A.J. Sfahlan, A. Mahmoodzadeh, A. Hasanzadeh, R. Heidari, R. Jamei, Antioxidants and antiradicals in almond hull and shell (Amygdalus communis L.) as a function of genotype. Food Chem. 115, 529–533 (2009)
Y.W. Sari, M.E. Bruins, J.P. Sanders, Enzyme assisted protein extraction from rapeseed, soybean, and microalgae meals. Ind. Crops Prod. 43, 78–83 (2013)
F.A.O/W.H.O. Protein and amino acid requirements in human nutrition. Report of a Joint WHO/FAO/UNU Expert Consultation, WHO technical report series 935. (Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2007)
K.S. Kumar, K. Ganesan, K. Selvaraj, P.S. Rao, Studies on the functional properties of protein concentrate of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Doty) Doty–An edible seaweed. Food Chem. 153, 353–360 (2014)
K. Shevkani, N. Singh, A. Kaur, J.C. Rana, Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 43, 679–689 (2015)
H. Zuber, Temperature adaptation of lactate dehydrogenase structural, functional and genetic aspects. Biophys. Chem. 29, 171–179 (1988)
Q. Deng, L. Wang, F. Wei, B. Xie, F. Huang, W. Huang, J. Shi, Q. Huang, B. Tian, S. Xue, Functional properties of protein isolates, globulin and albumin extracted from Ginkgo biloba seeds. Food Chem. 124, 1458–1465 (2011)
A. Moure, J. Sineiro, H. Domínguez, J.C. Parajó, Functionality of oilseed protein products: a review. Food Res. Int. 39, 945–963 (2006)
E. Pastor-Cavada, R. Juan, J.E. Pastor, M. Alaiz, J. Vioque, Protein isolates from two Mediterranean legumes: Lathyrus clymenum and Lathyrus annuus. Chemical composition, functional properties and protein characterisation. Food Chem. 122, 533–538 (2010)
G.M. Sharma, M. Su, A.U. Joshi, K.H. Roux, S.K. Sathe, Functional properties of select edible oilseed proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58, 5457–5464 (2010)
S.A. Malomo, R.E. Aluko, A comparative study of the structural and functional properties of isolated hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) albumin and globulin fractions. Food Hydrocoll. 43, 743–752 (2015)
E. Akintayo, E. Adebayo, L. Arogundade, Chemical composition, physicochemical and functional properties of akee (Bilphia sapida) pulp and seed flours. Food Chem. 77, 333–336 (2002)
M. Majzoobi, E. Abedi, A. Farahnaky, M. Aminlari, Functional properties of acetylated glutenin and gliadin at varying pH values. Food Chem. 133, 1402–1407 (2012)
M.A. Mwasaru, K. Muhammad, J. Bakar, Y.B.C. Man, Influence of altered solvent environment on the functionality of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan) and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) protein isolates. Food Chem. 71, 157–165 (2000)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support provided by “Ministry of Science, Research and Technology,” “Center of Excellence for Application of Modern Technologies for Producing Functional Foods and Drinks” and “Research Council of University of Tehran” (Tehran, Iran) and also “the Research Council of College of Agriculture and Natural Resources of University of Tehran” (Karaj, Iran).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amirshaghaghi, Z., Rezaei, K. & Habibi Rezaei, M. Characterization and functional properties of protein isolates from wild almond. Food Measure 11, 1725–1733 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9553-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9553-y