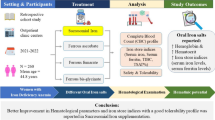
Abstract
Sixty rural women with age varying between 25 and 35 were selected randomly to determine the role of dietary factors on bioavailability of iron in their diets. Food samples of selected subjects were collected for three major meals i.e. breakfast, lunch and dinner for three consecutive days. The samples were analyzed for meal constituents associated with iron absorption as well as for total and dialyzable iron. Based on dietary characteristics, the diets of the farm women were in the class of intermediate diets as per FAO/WHO classification with iron bioavailability of 8.11 %. The statistical analysis revealed that the meal constituents which were found to influence iron absorption positively were ascorbic acid and β-carotene in breakfast and only β-carotene in dinner. The meal constituents which affected iron absorption negatively were zinc and calcium in breakfast as well as lunch and phytates and NDF in dinner, however, polyphenols present in the meals of the subjects did not show any relationship with iron absorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen LH, Ahluwalia N (1997) Improving iron status through diet. The application of knowledge concerning dietary iron bioavailability in human populations. OMNI - Opportunities for Micronutrient Interventions. Washington, DC, John Snow Inc. /OMNI Project, United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
AOAC (1985) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
AOAC (1990) Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis of the AOAC, 15th Edn., Washington, DC
AOAC (1996) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, pp 803–808
Bains K, Mann SK (2000) Physical fitness in relation to energy and iron status of female college students. Food Nutr Bull 21:305–310
Bains K, Aggarwal R, Barakoti L (2006) Development and impact of iron-rich mungbean recipes. Proceedings of Final Workshop of project ‘Improving income and nutrition by incorporating mungbean in cereal fallows in the Indo-Gangetic plains of South Asia’. AVRDC- World Vegetable Center Publication, Shanhua, Taiwan.
Bains K, Kaur H, Kapoor S, Kaur G, Singh A (2012) A study of factors influencing zinc status of women (15–45 years) and children (6–59 months) from Ludhiana district of Punjab, India. Project report, HarvestPlus c/o International Food Policy Research Institute, Washington DC
Carpenter CE, Mahoney AW (1992) Contributions of heme and non-heme iron to human nutrition. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 31:333–367
Chandla H (2006) Nutritional profile of vegetarian and non vegetarian post menopausal women. M.Sc. Thesis. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Chaudhary D (2012) Nutritional and lifestyle factors for the risk assessment of osteoporosis in pre and post menopausal women. M.Sc. Thesis. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Cook JD, Morck TA, Skikne BS, Lynch SR (1981) Biochemical determinants of iron absorption. Prog Clin Biol Res 77:323–331
FAO (1998) Nutrition Country Profiles: India. Rome. Available at: http://www.fao.org/es/ESN/nutrition/ind-e.stm
Fidler MC, Davidsson L, Zeder C, Hurrell RF (2004) Erythorbic acid is a potent enhancer of nonheme-iron absorption. Am J Clin Nutr 79:99–102
FNB (2001) Dietary reference intakes for vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. National Academy Press, Washington
García-Casal MN, Layrisse M, Solano L, Baron MA, Arguello F, Llovera D, Ramiírez J, Leets I, Tropper E (1998) Vitamin A and β-carotene can improve non-heme iron absorption from rice, wheat and corn by humans. J Nutr 128:646–650
Grewal P (1992) Effect of dietary antinutritional factors on mineral availability. Ph.D. dissertation. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Gungeet (2004) Impact of nutritional counselling on the nutritional and health status of perimenopausal women. M.Sc. Thesis. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Hallberg L (1981) Bioavailability of dietary iron in man. Annu Rev Nutr 1:123–147
Hallberg L, Rossander L (1991) Iron requirements in menstruating women. Am J Clin Nutr 54:1047–1058
Hallberg L, Rossander-Hulten L, Brune M, Gleerup A (1992) Calcium and iron absorption: mechanism of action and nutritional importance. Eur J Clin Nutr 46:317–327
Hallberg L, Rossander-Hulthen L, Brune M, Gleerup A (1993) Inhibition of haem-iron absorption in man by calcium. Br J Nutr 69:533–540
Haug W, Lantzsch HT (1983) Sensitive method for rapid determination of phytate in cereals andcereal products. J Sci Food Agric 34:289–295
Hunt RJ (2003) Bioavailability of iron, zinc and other trace minerals from vegetarian diet. Am J Clin Nutr 78:633–639
Hurrell RF (2004) Phytic acid degradation as a means of improving iron absorption. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 74:445–452
ICMR (2010). Nutrient requirements and recommended dietary allowances for Indians.A report of the expert group of the Indian Council of Medical Research. New Delhi
Jain S (2009) Impact of dietary intake and calcium supplement on bone mineral density as an indicator of osteoporosis in menopausal women. Ph.D. dissertation. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Kalaivani K (2009) Prevalence and consequences of anemia in pregnancy. Indian J Med Res 130:627–633
Kaur B (1999) Measurement of energy cost of selected household and form activities performed by rural women. M.Sc. Thesis. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Kaur H (2012) Interrelationship among dietary diversity, socioeconomic factors and food security in rural households. M.Sc. Thesis. Punjab Agricultural University. Ludhiana, India
Kim MH, Choi KC, Sung CJ (2007) Bone mineral density of Korean postmenopausal women is similar between vegetarians and nonvegetarians. Nutr Res 27:212–217
Kochar GK (1981) Effect of dietary fiber on the utilization of various nutrients. Ph.D. Thesis. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Konietzny U, Greiner R (2003) Phytic acid: nutritional impact. In: Caballero B, Trugo L, Finglas P (eds) Encyclopedia of food science and nutrition. Elsevier, London, pp 4555–4563
Kumari N (1979) Effect of dietary fiber and cellulose on the absorption of iron. M.Sc. Thesis. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Kushwaha S (2011) Impact of supplementation of drumstick (Moringa oleifera) and amaranth (Amaranthus tricolor) leaves on the antioxidant status of the post menopausal women. Ph.D. dissertation. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Layrisse M, Martinez-Torres C, Leets I, Taylor P, Ramirez J (1984) Effect of histidine, cysteine, glutathione or beef on iron absorption in humans. J Nutr 114:217–223
Lopez HW, Leenhardt F, Coudray C, Rémésy C (2002) Minerals and phytic acid interactions: Is it a real problem for human nutrition? Int J Food Sci Tech 37:727–739
Miller D, Schricker BR, Rasmussen RR, Campen DV (1981) An in vitro method for estimation of iron availability from meals. Am J Clin Nutr 34:2248–2256
Nagi M, Chawla S, Verma S (1995) A study on work efficiency of anaemic and non anaemic subjects. Ind J Physiol Allied Sci 43:158–164
Nair KM, Lyengar V (2009) Iron content, bioavailability and factors affecting iron status of Indians. Indian J Med Res 130:634–645
Nayak B, Nair M (2003) In vitro bioavailability of iron from wheat flour fortified with ascorbic acid, EDTA and sodium hexametaphosphate, with or without iron. J Food Chem 80:545–550
NFHS (2000) National Family Health Survey 2, India 1998–99; International Institute of Population Sciences, Mumbai, India and ORC Macro, Calverton, Maryland, USA
NIN (1992) Bioavailability of iron and zinc from Indian diets. National Institute of Nutrition, Hyderabad, India, 88–89
NNMB (2006) Diet and nutritional status of population and prevalence of hypertension among adult in rural areas. Technical Report No. 24, Indian Council of Medical Research, Hyderabad, India
Rangana S (1995) Mannual of analysis of fruit and vegetable products. Tata Mcgraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi
Reddy NR (2002) Occurrence, distribution, content, and dietary intake of phytate. In: Reddy NR, Sathe SK (eds) Food phytates. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 25–51
Roughead ZK, Zito CA, Hunt JR (2005) Inhibitory effects of dietary calcium on the initial uptake and subsequent retention of heme and nonheme iron in humans: comparisons using an intestinal lavage method. Am J Clin Nutr 82:589–597
Sandhu N (1998) Impact of counseling on male coronary heart patient belonging to business community. M.Sc. Thesis. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Seshadri S (1993) Bioavailability of microelements with special reference to iron: advantages and limitations of the in vitro method. Proc Nutr Soc India 40:103–112
Seshadri S, Shah A, Bhade S (1985) Haematologic response of anaemic preschool children to ascorbic acid supplementation. Hum Nutr Appl Nutr 39:151–154
Sharma KK (2003) Impoving bioavailability of iron in Indian diet through food based approaches for the control of iron deficiency anaemia. Food Nutr Agric 32:51–61
Sharma DC, Mathur R (1995) Correction of anemia and iron deficiency in vegetarians by administration of ascorbic acid. Ind J Physi Pharm 39:403–406
Shoker RK (2003) A comparative study on nutritional and blood profile of working and non working hypertensive women. M.Sc. Thesis. Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India
Singh P, Aggarwal AR (2001) Nutritional assessment of residents of different types of colonies I Delhi. Ind J Nutr Diet 38:223–230
Song WO, Mann SK, Sehgal S, Devi, PR, Gudaru S, Kakarala M (1992) Nutriguide; Asian Indian Foods. Nutritional Analysis Computer Program. Michigan State University, USA
Storcksdieck BS, Walczyk T, Renggli S, Hurrell RF (2007) Nonheme iron absorption in young women is not influenced by purified sulfated and unsulfated glycosaminoglycans. J Nutr 137:1161–1164
Taylor PG, Martinez-Torres C, Romano EL, Layrisse M (1986) The effect of cysteine-containing peptides released during meat digestion on iron absorption in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 43:68–71
WHO (2004) Micronutrient deficiency anaemia: the challenge. Available from: http://www.who.int/nut/ida.htm, accessed on April 24, 2010
WHO (2011). Haemoglobin concentrations for the diagnosis of anaemia and assessment of severity. Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System, Geneva
Zimmermann MB, Hurrell RF (2007) Nutritional iron deficiency. Lancet 370:511–520
Zimmermann MB, Biebinger R, Rohner F (2006) Vitamin A supplementation in children with poor vitamin A and iron status increases erythropoietin and hemoglobin concentrations without changing total body iron. Am J Clin Nutr 84:580–586
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Bains, K. & Kaur, H. Relationship of dietary factors with dialyzable iron and in vitro iron bioavailability in the meals of farm women. J Food Sci Technol 53, 2001–2008 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2153-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2153-0