Abstract
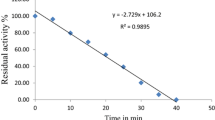
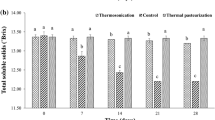
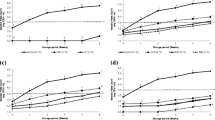
The effects of thermosonication on enzymes (polyphenolase, peroxidase, pectinmethylesterase and lipoxygenase), microorganisms (total plate count, yeast and mold), coloring pigments (carotenoids, lutein and lycopene), ascorbic acid, total phenols, flavonoids, tannins, pH, acidity, °Brix and color of carrot juice in comparison with thermal treatment were investigated. Carrot juice was thermosonicated (20 kHz, 70 % amplitude and 48 W cm−2 of ultrasonic intensity) at 20, 40 and 60 °C for 5 and 10 min using 5 s on/off pulse cycle. The thermal treatment was carried out in a water bath at 80 °C for 1 min. The highest inactivation of enzymes and microorganisms was achieved after thermal and thermosonicated (60 °C) treatments. However, maximum improvement in coloring pigments and more retention of ascorbic acid, total phenols, flavonoids and tannins were observed in thermosonicated (60 °C) treatment compared to thermal treatment. °Brix, pH and acidity remained unchanged irrespective of treatments. The results suggest that thermosonication at 60 °C may be a good alternative to thermal treatment and it may successfully be applied to carrot juice production with reduced enzymes and microbial activity and improved bioactive compounds.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abid M et al (2013) Effect of ultrasound on different quality parameters of apple juice. Ultrason Sonochem 20:1182–1187
Abid M et al (2014a) Thermosonication as a potential quality enhancement technique of apple juice. Ultrason Sonochem 21:984–990
Abid M, Jabbar S, Wu T, Hashim MM, Hu B, Lei S, Zeng X (2014b) Sonication enhances polyphenolic compounds, sugars, carotenoids and mineral elements of apple juice. Ultrason Sonochem 21:93–97
Adekunte A, Tiwari B, Scannell A, Cullen P, O’donnell C (2010) Modelling of yeast inactivation in sonicated tomato juice. Int J Food Microbiol 137:116–120
AOAC International (1999), 16th edn. Gaithersburg
Augustin MA, Ghazali HM, Hashim H (1985) Polyphenoloxidase from guava (Psidium guajava L.). J Sci Food Agric 36:1259–1265
Bermúdez-Aguirre D, Barbosa-Cánovas GV (2012) Inactivation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in pineapple, grape and cranberry juices under pulsed and continuous thermo-sonication treatments. J Food Eng 108:383–392
Broadhurst RB, Jones WT (1978) Analysis of condensed tannins using acidified vanillin. J Sci Food Agric 29:788–794
Butz P, Tauscher B (2002) Emerging technologies: chemical aspects. Food Res Int 35:279–284
Caminiti IM, Noci F, Morgan DJ, Cronin DA, Lyng JG (2012) The effect of pulsed electric fields, ultraviolet light or high intensity light pulses in combination with manothermosonication on selected physico-chemical and sensory attributes of an orange and carrot juice blend. Food Bioprod Process 90:442–448
Chemat F, Zill-e H, Khan MK (2011) Applications of ultrasound in food technology: processing, preservation and extraction. Ultrason Sonochem 18:813–835
Chen CS, Shaw PE, Parish ME (1993) Orange and tangerine juices. Agscience, Auburndale
Cruz RMS, Vieira MC, Silva CLM (2006) Effect of heat and thermosonication treatments on peroxidase inactivation kinetics in watercress (Nasturtium officinale). J Food Eng 72:8–15
de Assis SA, Martins ABG, de Faria Oliveira OMM (2007) Purification and characterization of pectin methylesterase from acerola (Malpighia glabra L.). J Sci Food Agric 87:1845–1849
Ercan SŞ, Soysal Ç (2011) Effect of ultrasound and temperature on tomato peroxidase. Ultrason Sonochem 18:689–695
Espachs-Barroso A, Barbosa-Cánovas GV, Martín-Belloso O (2003) Microbial and enzymatic changes in fruit juice induced by high-intensity pulsed electric fields. Food Rev Int 19:253–273
Fellows P (1994) Tecnología de alimentos procesados: principios y prácticas Zaragoza: Acribia:48
Ganjloo A, Rahman R, Osman A, Bakar J, Bimakr M (2011) Kinetics of crude peroxidase inactivation and color changes of thermally treated seedless guava (Psidium guajava L.). Food Bioprocess Technol 4:1442–1449
Hussein L, el-Tohamy M (1990) Vitamin A potency of carrot and spinach carotenes in human metabolic studies. Int J Vit Nutr Res 60:229–235
Jabbar S et al (2014a) Quality of carrot juice as influenced by blanching and sonication treatments. LWT-Food Sci Technol 55:16–21
Jabbar S et al (2014b) Study on combined effects of blanching and sonication on different quality parameters of carrot juice. Int J Food Sci Nutr 65:28–33
Kiang WS, Bhat R, Rosma A, Cheng LH (2013) Effects of thermosonication on the fate of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Enteritidis in mango juice. Lett ApplMicrobiol 56:251–257
Kim H, Gerber L (1988) Influence of processing on quality of carrot juice. Korean J Food Sci Technol 20:683–690
Kim Y, Park K, Lee C (1987) Purification and thermal inactivation of two lipoxygenase isoenzymes from potato tubers Korean. J Food Sci Technol 19:397–402
Kim YS, Park SJ, Cho YH, Park J (2001) Effects of combined treatment of high hydrostatic pressure and mild heat on the quality of carrot juice. J Food Sci 66:1355–1360
Kwak SS, Kim SK, Lee MS, Jung KH, Park IH, Liu JR (1995) Acidic peroxidases from suspension-cultures of sweet potato. Phytochem 39:981–984
Lee DU, Heinz V, Knorr D (2003) Effects of combination treatments of nisin and high-intensity ultrasound with high pressure on the microbial inactivation in liquid whole egg. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 4:387–393
Lee H, Zhou B, Liang W, Feng H, Martin SE (2009) Inactivation of Escherichia coli cells with sonication, manosonication, thermosonication, and manothermosonication: Microbial responses and kinetics modeling. J Food Eng 93:354–364
Liao H, Sun Y, Ni Y, Liao X, Hu X, Wu J, Chen F (2007) The effect of enzymatic mash treatment, pressing, centrifugation, homogenization, deaeration, sterilization and storage on carrot juice. J Food Process Eng 30:421–435
Lo Scalzo R, Lannoccari T, Summa C, Morelli R, Rapisarda P (2004) Effect of thermal treatments on antioxidant and antiradical activity of blood orange juice. Food Chem 85:41–47
Maturin LJ, Peeler JT (2001) Food and drug administration bacteriological analytical manual, 8th edn. Thomas Hammack, USA
Nagy S, Smoot JM (1977) Temperature and storage effects on percent retention and percent U.S. recommended dietary allowance of vitamin C in canned single-strength orange juice. J Agr Food Chem 25:135–138
Noci F, Walkling-Ribeiro M, Cronin D, Morgan D, Lyng J (2009) Effect of thermosonication, pulsed electric field and their combination on inactivation of Listeria innocua in milk. Int Dairy J 19:30–35
Oms-Oliu G, Odriozola-Serrano I, Soliva-Fortuny R, Martín-Belloso O (2009) Effects of high-intensity pulsed electric field processing conditions on lycopene, vitamin C and antioxidant capacity of watermelon juice. Food Chem 115:1312–1319
Quitão-Teixeira LJ, Aguiló-Aguayo I, Ramos AM, Martín-Belloso O (2008) Inactivation of oxidative enzymes by high-intensity pulsed electric field for retention of color in carrot juice. Food Bioprocess Technol 1:364–373
Raviyan P, Zhang Z, Feng H (2005) Ultrasonication for tomato pectinmethylesterase inactivation: effect of cavitation intensity and temperature on inactivation. J Food Eng 70:189–196
Rawson A, Tiwari BK, Patras A, Brunton N, Brennan C, Cullen PJ, O’Donnell C (2011) Effect of thermosonication on bioactive compounds in watermelon juice. Food Res Int 44:1168–1173
Riener J, Noci F, Cronin DA, Morgan DJ, Lyng JG (2009) The effect of thermosonication of milk on selected physicochemical and microstructural properties of yoghurt gels during fermentation. Food Chem 114:905–911
Rithmanee T, Intipunya P (2012) Effects of high power ultrasonic pretreatment on physicochemical quality and enzymatic activities of dried longan. J Agri Sci 4:299
Sala F, Burgos J, Condon S, Lopez P, Raso J (1995) Effect of heat and ultrasound on microorganisms and enzymes. In: New methods of food preservation. Springer, (pp 176–204)
Sánchez-Moreno C, Plaza L, Elez-Martínez P, De Ancos B, Martín-Belloso O, Cano MP (2005) Impact of high pressure and pulsed electric fields on bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of orange juice in comparison with traditional thermal processing. J Agr Food Chem 53:4403–4409
Saner D, Hami A, Alev B (2007) High hydrostatic pressure treatment and storage of carrot and tomato juices: Antioxidant activity and microbial safety. J Sci Food Agric 87:773–782
Sharma KD, Karki S, Thakur NS, Attri S (2012) Chemical composition, functional properties and processing of carrot-a review. J Food Sci Technol 49:22–32
Shi J, Maguer ML (2000) Lycopene in tomatoes: chemical and physical properties affected by food processing. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 40:1–42
Shivhare US, Gupta M, Basu S, Raghavan GSV (2009) Optimization of blanching process for carrots. J Food Process Eng 32:587–605
Siwach R (2012) Pectin methylesterase inactivation in mosambi juice. J Life Sci 4:81–85
Soria AC, Villamiel M (2010) Effect of ultrasound on the technological properties and bioactivity of food: a review. Trend Food Sci Technol 21:323–331
Talcott ST, Howard LR (1999) Phenolic autoxidation is responsible for color degradation in processed carrot puree. J Agr Food Chem 47:2109–2115
Terefe NS, Gamage M, Vilkhu K, Simons L, Mawson R, Versteeg C (2009) The kinetics of inactivation of pectin methylesterase and polygalacturonase in tomato juice by thermosonication. Food Chem 117:20–27
Tournas VH, Heeres J, Burgess L (2006) Moulds and yeasts in fruit salads and fruit juices. Food Microbiol 23:684–688
Van den Berg H et al (2000) The potential for the improvement of carotenoid levels in foods and the likely systemic effects. J Sci Food Agric 80:880–912
Vercet A, Lopez P, Burgos J (1998) Free radical production by manothermosonication. Ultrason Sonochem 36:615–618
Vercet A, Sánchez C, Burgos J, Montañés L, Lopez Buesa P (2002) The effects of manothermosonication on tomato pectic enzymes and tomato paste rheological properties. J Food Eng 53:273–278
Villamiel M, de Jong P (2000) Influence of high-intensity ultrasound and heat treatment in continuous flow on fat, proteins, and native enzymes of milk. J Agr Food Chem 48:472–478
Walkling-Ribeiro M, Noci F, Riener J, Cronin DA, Lyng JG, Morgan DJ (2009) The impact of thermosonication and pulsed electric fields on Staphylococcus aureus inactivation and selected quality parameters in orange juice. Food Bioprocess Technol 2:422–430
Wong E, Vaillant F, Pérez A (2010) Osmosonication of blackberry juice: impact on selected pathogens, spoilage microorganisms, and main quality parameters. J Food Sci 75:M468–M474
Wu J, Gamage TV, Vilkhu KS, Simons LK, Mawson R (2008) Effect of thermosonication on quality improvement of tomato juice. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 9:186–195
Zhang Q, Tan S, McKay A, Yan G (2005) Carrot browning on simulated market shelf and during cold storage. J Sci Food Agric 85:16–20
Zhou L, Wang Y, Hu X, Wu J, Liao X (2009) Effect of high pressure carbon dioxide on the quality of carrot juice. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 10:321–327
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant-in-aid from a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions. The first two authors would like to express their thanks to the Ministry of Education, China, for financial assistance through Chinese Government Scholarship Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jabbar, S., Abid, M., Hu, B. et al. Exploring the potential of thermosonication in carrot juice processing. J Food Sci Technol 52, 7002–7013 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1847-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1847-7