Abstract
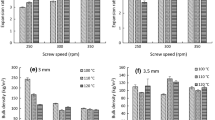
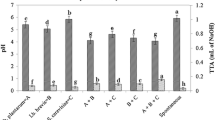
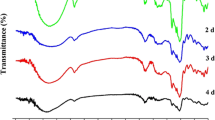
In the current study, effects of fermentation on physicochemical and functional properties of brown rice flour (BRF) were investigated. Fermentation conditions were optimized using response surface methodology to achieve moderate acidity (pH 5–6), specifically pH 5.5 of brown rice batter with time, temperature and yeast concentration as the independent variables. The results indicated that brown rice batter was well fermented to maintain pH 5.5 at optimum conditions of 32 °C for 6.26 h using 1 % yeast concentration. Fermentation at moderate acidity significantly increased the levels of protein, total ash, insoluble fiber, soluble fibre, minerals, phenolics, antioxidants, resistant starch, riboflavin, pyridoxine, nicotinic acid, γ-tocotrienol, and δ-tocotrienol. However, it reduced the contents of γ-oryzanol, γ-tocopherol, α-tocopherol, phytic acid, amylose and total starch. Foaming capacity, foaming stability, oil holding capacity, gelatinization temperatures, enthalpy and whiteness of BRF were increased after fermentation. In contrast, its swelling power, water solubility index, hot paste viscosity, breakdown, and setback significantly decreased. Microstructure of BRF was also influenced, where its starch granules released from its enclosed structure after fermentation. This investigation shows evidence that yeast fermentation modified the functionality of BRF and can be used as a functional food ingredient.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebowale KO, Lawal OS (2004) Comparative study of the functional properties of bambarra groundnut (Voandzeia subterranean), jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis) and mucuna bean (Mucuna pruriens) flours. Food Res Int 37:355–365
Adrian J, Petit L (1970) Vitamins of cereals and their evolution during technologic treatment. Ann Nutr Metab 24:B131–B168
Aguilar-Garcia C, Gavino G, Baragaño-Mosqueda M, Hevia P, Gavino VC (2007) Correlation of tocopherol, tocotrienol, γ-oryzanol and total polyphenol content in rice bran with different antioxidant capacity assays. Food Chem 102:1228–1232
AOAC (2005) Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed, Method 920.87, 934.01, 923.05, 993.19, 985.35, 995.11. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC
AOAC (2005) Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed, Method 953.17. Thiamine (vitamin B1) in grain products. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
Bartolome B, Gómez-Cordovés C (1999) Barley spent grain: release of hydroxycinnamic acids (ferulic and p‐coumaric acids) by commercial enzyme preparations. J Sci Food Agric 79:435–439
Batifoulier F, Verny M, Chanliaud E, Rémésy C, Demigné C (2005) Effect of different breadmaking methods on thiamine, riboflavin and pyridoxine contents of wheat bread. J Cereal Sci 42:101–108
Beta T, Nam S, Dexter JE, Sapirstein HD (2005) Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of pearled wheat and roller-milled fractions. Cereal Chem 82:390–393
Carvalho AV, García NHP, Amaya-Farfán J (2006) Physico-chemical properties of the flour, protein concentrate, and protein isolate of the cupuassu (Theobroma grandiflorum Schum) seed. J Food Sci 71:S573–S578
Chang Y, Lin C, Chen J (2006) Characteristics of mung bean starch isolated by using lactic acid fermentation solution as the steeping liquor. Food Chem 99:794–802
Chiang PY, Yeh AI (2002) Effect of soaking on wet-milling of rice. J Cereal Sci 35:85–94
Chinma CE, Ilowefah M, Shammugasamy B, Ramakrishnan Y, Muhammad K (2014) Chemical, antioxidant, functional and thermal properties of rice bran proteins after yeast and natural fermentations. Int J Food Sci Technol 49:2204–2213
Davis K, Cain R, Peters L, Le Tourneau D, McGinnis J (1981) Evaluation of the nutrient composition of wheat. II. Proximate analysis, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin and pyridoxine. Cereal Chem 58:116–120
Dordević TM, Šiler-Marinković SS, Dimitrijević-Branković SI (2010) Effect of fermentation on antioxidant properties of some cereals and pseudo cereals. Food Chem 119:957–963
Ekinci R (2005) The effect of fermentation and drying on the water-soluble vitamin content of tarhana, a traditional Turkish cereal food. Food Chem 90:127–132
Elkhalifa AEO, Schiffler B, Bernhardt R (2005) Effect of fermentation on the functional properties of sorghum flour. Food Chem 92:1–5
Elkhalifa AEO, Bernhardt R, Bonomi F, Iametti S, Pagani MA, Zardi M (2006) Fermentation modifies protein/protein and protein/starch interactions in sorghum dough. Eur Food Res Technol 222:559–564
Flander L, Suortti T, Katina K, Poutanen K (2011) Effects of wheat sourdough process on the quality of mixed oat-wheat bread. LWT Food Sci Technol 44:656–664
Hagenimana A, Pu P, Ding X (2005) Study on thermal and rheological properties of native rice starches and their corresponding mixtures. Food Res Int 38:257–266
Haros M, Perez OE, Rosell CM (2004) Effect of steeping corn with lactic acid on starch properties. Cereal Chem 81:10–14
Hubert J, Berger M, Nepveu F, Paul F, Daydé J (2008) Effects of fermentation on the phytochemical composition and antioxidant properties of soy germ. Food Chem 109:709–721
AACC International (1995) Approved Methods of Analysis, 9th Ed. Method 61–02.01 Detremination of the pasting properties of rice with Rapid Visco-Analyser. 1995. First Approval 10-26-94. AACC International, St. Paul
AACC International (1999) Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th Ed. Method 86–90.01.B-Vitamin in Vitamin Concentrates by HPLC. Approved November 3. AACC International, St. Paul
AACC International (2001) Approved Methods of Analysis, 10th ed. Methods 61–03.01. Amylograph method for milled rice. AACC International, St. Paul
ISO 2171 (1993) International standard, cereals and milled cereal products- determination of total ash
Jane J, Chen YY, Lee LF, McPherson AE, Wong KS, Radosavljevic M et al (1999) Effects of amylopectin branch chain length and amylose content on the gelatinization and pasting properties of starch. Cereal Chem 76:629–637
Katcher HI, Legro RS, Kunselman AR, Gillies PJ, Demers LM, Bagshaw DM et al (2008) The effects of a whole grain-enriched hypocaloric diet on cardiovascular disease risk factors in men and women with metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 87:79–90
Kati K, Kaisa P, Karin A (2004) Influence and interactions of processing conditions and starter culture on formation of acids, volatile compounds, and amino acids in wheat sourdoughs. Cereal Chem 81:598–610
Katina K, Arendt E, Liukkonen K, Autio K, Flander L, Poutanen K (2005) Potential of sourdough for healthier cereal products. Trends Food Sci Technol 16:104–112
Katina K, Laitila A, Juvonen R, Liukkonen K, Kariluoto S, Piironen V et al (2007) Bran fermentation as a means to enhance technological properties and bioactivity of rye. Food Microbiol 24:175–186
Kaur M, Singh N (2007) Characterization of protein isolatesfrom different Indian chickpea (Cicer arietinum) cultivars. Food Chem 102:366–374
Kwon DY, Kim HJ, Park S (2010) Antidiabetic effects of fermented soybean products on type 2 diabetes. Nutr Res 30:1–13
Lerma-García MJ, Herrero-Martínez JM, Simó-Alfonso EF, Mendonça CRB, Ramis-Ramos G (2009) Composition, industrial processing and applications of rice bran γ-oryzanol. Food Chem 115:389–404
Liang J, Han B, Nout MJR, Hamer RJ (2008) Effects of soaking, germination and fermentation on phytic acid, total and in vitro soluble zinc in brown rice. Food Chem 110:821–828
Lin Q, Xiao H, Fu X, Tian W, Li L, Yu F (2011) Physico-chemical properties of flour, starch, and modified starch of two rice varieties. Agric Sci China 10:960–968
Liu S, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Rexrode KM, Hu FB, Rimm EB et al (2000) Whole grain consumption and risk of ischemic stroke in women: A prospective study. JAMA 284:1534–1540
Lopez HW, Krespine V, Guy G, Messager A, Demigne C, Remesy C (2001) Prolonged fermentation of whole wheat sourdough reduces phytate level and increases soluble magnesium. J Agric Food Chem 49:2657–2662
Lu Z, Li L, Min W, Wang F, Tatsumi E (2005) The effects of natural fermentation on the physical properties of rice flour and the rheological characteristics of rice noodles. Int J Food Sci Technol 40:985–992
Mahgoub SEO, Ahmed BM, Ahmed MMO, Agib EN (1999) Effect of traditional Sudanese processing of kisra bread andhulu-mur drink on their thiamine, riboflavin and mineral contents. Food Chem 67:129–133
Maninder K, Sandhu KS, Singh N (2007) Comparative study of the functional, thermal and pasting properties of flours from different field pea (Pisum sativum L.) and pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan L.) cultivars. Food Chem 104:259–267
Maria PR, Nicula A, Socaciu C (2008) The optimization of extraction and HPLC analysis of vitamins B from yeast products. Bull UASVM Agric 65:324–328
Martínez-Anaya MA (2003) Associations and interactions of micro-organisms in dough fermentations: effects on dough and bread characteristics. In: Kulp K, Lorenz K (eds) Handbook of dough fermentations. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 63.195
Maruatona GN, Duodu KG, Minnaar A (2010) Physicochemical, nutritional and functional properties of marama bean flour. Food Chem 121:400–405
Moore J, Cheng Z, Hao J, Guo G, Liu J, Lin C, Yu L (2007) Effects of solid-state yeast treatment on the antioxidant properties and protein and fiber compositions of common hard wheat bran. J Agric Food Chem 55:10173–10182
Moroni AV, Dal Bello F, Arendt EK (2009) Sourdough in gluten-free bread-making: an ancient technology to solve a novel issue. Food Microbiol 26:676–684
Nakai S (1983) Structure-function relationships of food proteins: with an emphasis on the importance of protein hydrophobicity. J Agric Food Chem 31:676–683
Ndaw S, Bergaentzle M, Aoudea-Werner D, Hasselmann C (2000) Extraction procedures for the liquid chromatographic determination of thiamine, riboflavin and vitamin B6 in foodstuffs. Food Chem 71:129–138
Oyewole OB, Ayo Odunfa S (1989) Effects of fermentation on the carbohydrate, mineral, and protein contents of cassava during “fufu” production. J Food Compos Anal 2:170–176
Sasaki T, Matsuki J (1998) Effect of wheat starch structure on swelling power. Cereal Chem 75:525–529
Shekib LA (1994) Nutritional improvement of lentils, chick pea, rice and wheat by natural fermentation. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 46:201–205
Singh N, Singh J, Kaur L, Sodhi NS, Gill BS (2003) Morphological, thermal and rheological properties of starches from different botanical sources. Food Chem 80:219–231
Singh S, Singh N, Ezekiel R, Kaur A (2010) Effects of gamma-irradiation on the morphological, structural, thermal and rheological properties of potato starches. Carbohydr Polym 83:1521–1528
Sun Q, Spiegelman D, Van Dam RM, Holmes MD, Malik VS, Willett WC et al (2010) White rice, brown rice, and risk of type 2 diabetes in US men and women. Arch Intern Med 170:961–969
Vandeputte GE, Derycke V, Geeroms J, Delcour JA (2003) Rice starch. II Structure aspects provide insight into swelling and pasting properties. J Food Sci 38:53–59
Wang H, Sun D, Zeng Q, Lu Y (2000) Effect of pH, corn starch and phosphates on the pasting properties of rice flour. J Food Eng 46:133–138
Wang B, Wang L, Li D, Wei Q, Adhikari B (2010) The rheological behavior of native and high-pressure homogenized waxy maize starch pastes. Carbohydr Polym 88:481–489
Wu P, Zhao T, Tian JC (2010) Phytic acid contents of wheat flours from different mill streams. Agric Sci China 9:1684–1688
Yang Y, Tao W (2008) Effects of lactic acid fermentation on FT-IR and pasting properties of rice flour. Food Res Int 41:937–940
Ye L, Landen W Jr, Lee J, Eitenmiller R (1998) Vitamin E content of margarine and reduced fat products using a simplified extraction procedure and HPLC determination. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 21:1227–1238
Yousif NE, El Tinay AH (2000) Effect of fermentation on protein fractions and in vitro protein digestibility of maize. Food Chem 70:181–184
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Universiti Putra Malaysia and Padiberas Nasional Berhad (BERNAS) for supporting this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilowefah, M., Bakar, J., Ghazali, H.M. et al. Physicochemical and functional properties of yeast fermented brown rice flour. J Food Sci Technol 52, 5534–5545 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1661-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1661-7