Abstract
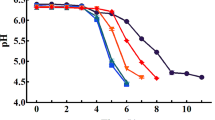
The fish oil (FO), and fish oil powder (FOP) at 10 % of recommended daily intake (RDI) were used to make two types of fortified feta cheeses. The physicochemical, rheological and sensory properties of ripened samples at 0, 30, and 60th days of cold store (5 °C) showed that the FO samples had a faster pH reduction, higher MSNF (milk solid non-fat) increase (p < 0.05) and more pores formation. Storage (G’) and loss (G”) moduli for both samples decreased until the 30th day of cold storage and then increased until the end of the storage time but both of them were higher for FOP samples. The index of secondary lipid oxidation or thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) of FO was lower than FOP samples. Although the polyunsaturated fatty acids of both samples were much higher than common feta cheese, their degradation in FO was less than FOP samples after storage. The sensory scores of FO were significantly higher than FOP sample (P < 0.05), and it obtained up to 70 % of overall acceptability after 30 and 60 days storage for its better hardness, texture and flavor.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AFFSA (2003) Acides Gras de la Famille Oméga 3 et Système Cardiovasculaire: Intérêtnutritionnel et allegations. AgenceFrancaise de Sécurité Sanitaire des Aliments. http://www.anses.fr/Documents/NUT-Ra-omega3.pdf (accessed 17 September 2012)
AHA (2006) Diet and lifestyle recommendations revision: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Nutrition Committee. Circulation 114:82–96
Aminifar M, Hamedi M, Emam-Djomeh Z, Mehdinia A (2010) Microstructural, compositional and textural properties during ripening of Lighvan cheese, A traditional raw sheep cheese. J Texture Stud 41:579–593
AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists) (1997) Official methods of analysis (16th ed., 3rd rev. method 920.123), Arlington, VA, USA
AOCS (American Oil Chemists Society) (2009) 2- Thiobarbituric acid value, direct method, official method Cd 19–90, 2710 S. Boulder, Urbana, IL 61802–6996 USA
Aryana KJ (2007) Cheddar cheese manufactured with oil high in omega-3 fatty acids. Milchwissenschaft 62:167–170
Baik MY, Suhendro EL, Nawar WW, McClements DJ, Decker EA, Chinachoti P (2004) Effect of antioxidants and humidity on the oxidative stability of microencapsulated fish oil. JAOCS 81(4):355–360
Barrow CJ, Nolan C, Holub BJ (2009) Bioequivalence of encapsulated and microencapsulated fish-oil supplementation. J Funct Foods I: 38–43
Bennett T, Desmond A, Harrington M (2000) The effect of high intakes of casein and casein phosphopeptide on calcium absorption in the rat. Br J Nutr 83:673–680
Bermudez-Aguirre D, Barbosa-Canovas GV (2011) Quality of selected cheeses fortified with vegetable and animal sources of omega-3. LWT-Food Sci Technol 44(7):1577–1584
Brennan JG (1980) Food texture measurements. In: King RD (ed) Developments in food analysis techniques. Applied Science Publisher, London, pp 41–45
Bylund G (1995) Dairy processing handbook. Tetra Pak processing systems AB, S-221 86 Lund, Sweden, pp 326–328
Choe E, Min DB (2006) Mechanisms and factors for edible oil oxidation. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Safety 5:169–186
Curtis JM, Berrigan N, Dauphinee P (2008) The determination of n-3 fatty acid levels in Food Products containing microencapsulated fish oil using the one-step extraction method. J Am Oil Chem Soc 85:297–305
Drake MA, Herrett W, Boylston TD, Swanson BG (1996) Lecithin improves texture of reduced fat cheeses. J Food Sci 61:639–642
Drusch S, Serfert Y, Scampicchio M, Schmidt-Hansberg B, Schwaz K (2007) Impact of physicochemical characteristics on the oxidative stability of fish oil microencapsulated by spray-drying. J Agric Food Chem 55(26):11044–11051
Faraji H, McClements DJ, Decker EA (2004) Role of continuous phase protein on the oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions. J Agric Food Chem 52:4558–4564
Fox PF, McSweeney PLH, Cogan TM, Guinee TP (1993) Biochemistry of cheese ripening. In: Fox PF (ed) Cheese: chemistry. Physics and Microbiology, Chapman, pp 389–438
Fox PF, McSweeney PLH, Cogan TM, Guinee TP (2000) Fundamentals of cheese science. Aspen Publishers Inc, Maryland
Fredrick IA, Atson JW, Nottingham SM, Dulley J (1986) The effect of neutral fungal protease in cheddar cheese ripening. N Z J Dairy Sci Technol 43:35–39
Gibbs BF, Kermasha S, Alli I, Mullingan CN (1999) Encapsulation in the food industry: a review. Int J Food Sci Nutr 50:213–224
Gunasekaran S, Mehmet Ak M (2003) Cheese rheology and texture. CRC press, Florida
Health Council of the Netherlands (2006) Guidelines for a Healthy Diet. Health Council of the Netherlands Publication No. 2006/21E, The Hague, Netherlands
Hibbeln JR, Nieminen LRG, Blasbalg TL, Riggs JA, Lands WEM (2006) Healthy intakes of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids: Estimations considering worldwide diversity. Am J Clin Nutr 83:1483s–1493s
Hooper L, Harrison RA, Summerbell CD, Moore H, Worthington HV, Ness A, Capps N, Davey Smith G, Riemersma R, Ebrahim S (2004) Omega 3 fatty acids for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD 003177
IDF (International Dairy Federation) (1991) Anhydrous milk fat, Determination of peroxide value. In: International IDF Standards Sect. 74A:1991, Square Vergot 41, Brussels, Belgium
Jalali-Heravi M, Zekavat B, Sereshti H (2007) Use of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry combined with resolution methods to characterize the essential oil components of Iranian cumin and caraway. J Chromatogr A 1143(1–2):215–226
James CS (1995) Analytical chemistry of foods. Blackie Academic and professional, Glasgow
Karami M, Ehsani MR, Mousavi SM, Rezaei K, Safari M (2009) Changes in the rheological properties of Iranian UF-feta cheese during ripening. Food Chem 112(3):539–544
Karoui R, Dufour E (2003) Dynamic testing rheology and fluorescence spectroscopy investigations of surface to centre differences in ripened soft cheeses. Int Dairy J 13:973–985
Kinsella JE (1984) Milk proteins: Physicochemical and functional properties. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 21:197–262
Kolanowski W, Laufenberg G (2006) Enrichment of food products with polyunsaturated fatty acids by fish oil addition. Eur Food Res Technol 222:472–477
Kolanowski W, Laufenberg G, Kunz B (2004) Fish oil stabilisation by microencapsulation with modified cellulose. Int J Food Sci Nutr 55:333–343
Kolanowski W, Jaworska D, Weißbrodt J (2007) Importance of instrumental and sensory analysis in the assessment of oxidative deterioration of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid-rich foods. J Sci Food Agric 87(2):181–191
Kris-Etherton PM (1999) Monounsaturated fatty acids and risk of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 100:1253–1258
Lobato-Calleros C, Rodriguez E, Sandoval-Castilla O, Vernon-Carter EJ, Alvarez-Ramirez J (2006) Reduced-fat white fresh cheese-like products obtained from W1/o/W2 multiple emulsions: Viscoelastic and high-resolution image analyses. Food Res Int 39:678–685
Lopez C, Dufour E (2001) The composition of the milk fat globule surface alters the structural characteristics of the coagulum. J Colloid Interface Sci 233:241–249
Lopez-Huertas E (2010) Health effects of oleic acid and long chain omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) enriched milks: A review of intervention studies. Pharmacol Res 61:200–207
Madadlou A, Khosrowshahi-Asl A, Mousavi ME, Farmani J (2007) The influence of brine concentration on chemical composition and texture of Iranian white cheese. J Food Eng 81:330–335
Martinez-Cuesta MC, De Palencia PF, Requena T, Pelaez C (2001) Enzymatic ability of Lactobacillus caseisubsp. caseiIFPL 731 for flavor development in cheese. Int Dairy J 11:577–585
Martini S, Thurgood JE, Brothersen C, Ward R, McMahon DJ (2009) Fortification of reduced-fat Cheddar cheese with n-3 fatty acids: Effect on off-flavor generation. J Dairy Sci 92(5):1876–1884
Mensink RP, Katan MB (1992) Effects of dietary fatty acids on serum lipids and lipoproteins: A meta-analysis of 27 trials. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 12:911–919
Mortensen G, Sorensen J, Stapelfeldt H (2002) Comparison of peroxide value methods used for semihard cheeses. J Agric Food Chem 50:5007–5011
Robinson RK, Tamime AY (1991) Feta and related cheeses. Ellis Horwood Limited, Market Cross House, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 1EB, England
Ruxton CHS, Reed SC, Simpson MJA, Millington KJ (2004) The health benefits of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: A review of the evidence. J Hum Nutr Diet 17(5):449–459
Sepahioglu O, Alvarez V, Solano-Lopez C (1999) Structure, physico-chemical and sensory properties of Feta cheese made with tapioca starch and lecithin as fat mimetics. Int Dairy J 9:783–789
Serfert Y, Drusch S, Schwarz K (2009) Chemical stabilisation of oils rich in long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids during homogenisation, microencapsulation and storage. Food Chem 113(4):1106–1112
Simopoulos AP (1999) Essential fatty acids in health and chronic disease. Am J Clin Nutr 70:560–569
Singh H, Zhu X-Q, Ye A (2009) Lipid encapsulation. US patent 20090029017
Steffe JF (1996) Rheological methods in food process engineering. Freeman press, East lansing, USA
Thautwein EA (2001) N-3 fatty acids–physiological and technical aspects for their use in food. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 103:45–55
Tunick MH (2000) Rheology of dairy foods. J Dairy Sci 83:1892–1898
Waagner-Nielsen E (1993) North European varieties of cheese. In: Fox PF (ed) Cheese: chemistry. Physics and Microbiology, London, pp 389–438
Walstra P, Smulders I (1997) Making emulsions and foams: an overview. In: Dickinson E, Bergenstahl B (eds) Food colloids: proteins, lipids and polysaccharides. The Royal Society of Chemistry, London, pp 367–381
Walstra P, Geurts TJ, Noomen A, Jellema A, Van Boekel MAJS (1999) Dairy technology. Principles of milk properties and processes. Marcel Decker Inc, 270 Madison Avenue
WHO (2002) Diet nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases: Report of a WHO/FAO joint expert consultation, technical report 916. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wium H, Qvist KB (1998) Rheological properties of Uf-Feta cheese determined by uniaxial compression and dynamic testing. J Texture Stud 28:435–454
Wium H, Gross M, Qvist K (1997) Uniaxial compression of UF-Feta cheese related to sensory texture analysis. J Texture Stud 28:455–476
Ye A, Cui J, Taneja A, Zhu X, Singh H (2009) Evaluation of processed cheese fortified with fish oil emulsion. Food Res Int 42(8):1093–1098
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate The University of Tehran and Iran Dairy Industries Co. especially Pegah-e-Khorasan, for their financial support and technical assistance (physicochemical analysis). They also express their thanks to Akbarieh Co. and Mr. Dolatkhah-Nezhad for supplying the fish oil and fish oil powder and also Testa Laboratory (Dr. Beheshti) for performing the analytical tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farbod, F., Kalbasi, A., Moini, S. et al. Effects of storage time on compositional, micro-structural, rheological and sensory properties of low fat Iranian UF-Feta cheese fortified with fish oil or fish oil powder. J Food Sci Technol 52, 1372–1382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1163-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1163-z