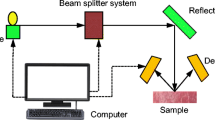
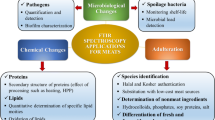
Abstract
The muscles derived from livestock are highly perishable. Rapid and nondestructive methods are essential for quality assurance of such products. Potential nondestructive methods, which can supplement or replace many of traditional time consuming destructive methods, include colour and computer image analysis, NIR spectroscopy, NMRI, electronic nose, ultrasound, X-ray imaging and biosensors. These methods are briefly described and the research work involving them for products derived from livestock is reviewed. These methods will be helpful in rapid screening of large number of samples, monitoring distribution networks, quick product recall and enhance traceability in the value chain of livestock products. With new developments in the areas of basic science related to these methods, colour, image processing, NIR spectroscopy, biosensors and ultrasonic analysis are expected to be widespread and cost effective for large scale meat quality evaluation in near future.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrés S, Murray I, Navajas EA, Fisher AV, Lambe NR, Bünger L (2007) Prediction of sensory characteristics of lamb meat samples by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Meat Sci 76:509–516
Ballerini L, Hogberg A, Borgefors G, Bylund AC, Lindgard A, Lundstrom K, Rakotonirainy O, Soussi B (2002) A segmentation technique to determine fat content in NMR images of beef meat. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 49:195–199
Benedito J, Carcel J, Rosselló C, Mulet A (2001) Composition assessment of raw meat mixtures using ultrasonics. Meat Sci 57:365–370
Bertram HC, Jorgensen HS, Karlsson AH, Adersen HJ (2002) Post mortem energy metabolism and meat quality of porcine M. longissimus dorsi as influenced by stunning method—A 31P NMR spectroscopic study. Meat Sci 62:113–119
Bertram HC, Straadt IK, Jensen JA, Aaslyng MD (2007) Relationship between water mobility and distribution and sensory attributes in pork slaughtered at an age between 90 and 180 days. Meat Sci 77:190–195
Bosch ME, Sánchez AJR, Rojas FS, Ojeda CB (2007) Recent development in optical fiber biosensors. Sensors 7:797–859
Braggins TJ, Frost DA, Agnew MP, Farouk MM (1999) Application of an electronic nose in the meat industry. In: Hurst WJ (ed) Electronic noses and sensor array based systems design and applications. Technomic Publishing Company, Lancaster, pp 51–82
Brienne JP, Denoyelle C, Baussart H, Daudin JD (2001) Assessment of meat fat content using dual energy X-ray absorption. Meat Sci 57:235–244
Brosnan T, Sun DW (2004) Improving quality inspection of food products by computer vision—a review. J Food Eng 61:3–16
Chao K, Chen YR, Hruschka WR, Park B (2001) Chicken heart disease characterization by multi-spectral imaging. Appl Eng Agric 17:99–106
Chen Z, Tao Y, Chen X (2001) Multiresolution local contrast enhancement of x-ray images for poultry meat inspection. Appl Opt 40:1195–1200
Collewet G, Bogner P, Allen P, Busk H, Dobrowolski A, Olsen E, Davenel A (2005) Determination of the lean meat percentage of pig carcasses using magnetic resonance imaging. Meat Sci 70:563–572
Coupland J, McClements DJ (2001) Ultrasonics. In: Gunasekaran S (ed) Nondestructive food evaluation. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 217–242
Demarco DR, Lim DV (2002) Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in 10- and 25-gramground beef samples with an evanescent-wave biosensor with silica and polystyrene Waveguides. J Food Prot 65:596–602
Descalzo AM, Rossetti L, Grigioni G, Irurueta M, Sancho AM, Carrete J, Pensel NA (2007) Antioxidant status and odour profile in fresh beef from pasture or grain-fed cattle. Meat Sci 75:299–307
Dey BP, Chen YR, Hsieh C, Chan DE (2003) Detection of septicemia in chicken livers by spectroscopy. Poult Sci 82:199–206
Du C, Sun DW (2004) Recent developments in the applications of image processing techniques for food quality evaluation. Trends Food Sci Technol 15:230–249
Faucitano L, Huff P, Teuscher F, Gariepy C, Wegner J (2005) Application of computer image analysis to measure pork marbling characteristics. Meat Sci 69:537–543
Fillit C, Jaffrezic-renault N, Bessueille F, Leonard D, Mitsubayashi K, Ttardy J (2008) Development of a microconductometric biosniffer for detection of trimethylamine. Mater Sci Eng, C 28:781–786
Frébort I, Skoupá L, Peč P (2000) Amine oxidase-based flow biosensor for the assessment of fish freshness. Food Control 11:13–18
Gaitán-Jurado AJ, Ortiz-somovilla V, España-españa F, Pérez-aparicio J, Pedro-sanz EJD (2008) Quantitative analysis of pork dry-cured sausages to quality control by NIR spectroscopy. Meat Sci 78:391–399
Geng T, Uknalis J, Tu S, Bhunia AK (2006) Fiber-Optic Biosensor employing alexa-fluor conjugated antibody for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from ground beef in four hours. Sensors 6:796–807
Geng T, Morgan MT, Bhunia AK (2004) Detection of low levels of Listeria monocytogenes cells by using a fiber-optic immunosensor. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6138–6146
Ghaedian R, Decker EA, McClements DJ (1997) Use of ultrasound to determine cod fillet composition. J Food Sci 62:500–504
Ghosh HS, Sarker D, Misra TN (1998) Development of an amperometric enzyme electrode biosensor for fish freshness detection. Sens Actuators, B 53:58–62
Grimes LM, Naganathan GK, Subbiah J, Calkins CR (2008) Predicting aged beef tenderness with a hyperspectral imaging system. Nebraska Beef Report. 138–139. (http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/animalscinbcr/53 accessed on 3rd August 2010)
Hoving-Bolink AH, Vedder HW, Merks JWM, De Klein WJH, Reimert HGM, Frankhuizen R, Van den Broek WHAM, En Lambooij E (2005) Perspective of NIRS measurements early post mortem for prediction of pork quality. Meat Sci 69:417–423
Hsieh C, Chen YR, Dey BP, Chan DE (2002) Separating septicemic and normal chicken livers by visible/near-infrared spectroscopy and back-propagation neural networks. Trans ASAE 45:459–469
Karamichou E, Merrell BG, Murray WA, Simm G, Bishop SC (2007) Selection for carcass quality in hill sheep measured by X-ray computer tomography. Animal 1:3–11
Kim G, Morgan M, Hahm B, Kothapalli A, Bhunia AK (2007) An automated fiber optic biosensor based binding inhibition assay for the detection of Listeria Monocytogenes. Food Sci Biotechnol 16:337–342
King RC (2004) Ultrasound sorting of weanlings and identification of tenderness indicators. US Patent No. 6,830,773
Koke JP, Steele CB (2002) Apparatus and method for use in packing meat cuts. Sealed Air(NZ) Ltd. PCT Patent No. WO 2002/016210
Liu Y, Ye J, Li Y (2001) Detection of E. Coli O157:H7 in poultry and meat samples using chemluminscence fiber optic biosensor in combination with immunomagnetic separation, Paper number 017033, ASAE Annual Meeting
Lu J, Tan J, Shatdal P, Gerrard DE (2000) Evaluation of pork color by using computer vision. Meat Sci 56:57–60
Mancini RA, Hunt MC (2005) Current research in meat color. Meat Sci 71:100–121
Mancini RA, Hunt MC, Hachmeister KA, Kropf DH, Johnson DE (2005) Exclusion of oxygen from modified atmosphere packages limits beef rib and lumbar vertebrae marrow discoloration during display and storage. Meat Sci 69:493–500
Meeusen CA, Alocilja EC, Osburn W (2001) Evaluation of a surface plasmon resonance biosensor in the detection of Salmonella spp. Paper number 016035, 2001 ASAE Annual Meeting
Mercier J, Pomar C, Marcoux M, Goulet F, Thériault M, Castonguay FW (2006) The use of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry to estimate the dissected composition of lamb carcasses. Meat Sci 73:249–257
Mitchell AD (2006) Meat Quality. In: Chaughule RS, Rande SS (eds) Looking into living things through magnetic resonance imaging. Prism Publications, Mumbai, pp 127–139
Mitchell AD, Scholz AM, Pursel VG (2003) Prediction of pork carcass composition based on cross-sectional region analysis of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans. Meat Sci 63:265–271
Mitsubayashi K, Kubotera Y, Yano K, Hashimoto Y, Kon T, Nakakura S, Nishi Y, Endo H (2004) Trimethylamine biosensor with flavin-containing monooxygenase type 3 (FMO3) for fish-freshness analysis. Sens Actuators, B 103:463–467
Monziols M, Collewet G, Bonneau M, Mariette F, Davenel A, Kouba M (2006) Quantification of muscle, subcutaneous fat and intermuscular fat in pig carcasses and cuts by magnetic resonance imaging. Meat Sci 72:146–154
Morgan MT, Kim G, Ess D, Kothapalli A, Hahm B, Bhunia AK (2006) Binding inhibition assay using fiber optic based biosensor for the detection of foodborne pathogens. Key Eng Mater 321–323:1145–1150
Mörlein D, Rosner F, Brand S, Jenderka K-V, Wicke M (2005) Non-destructive estimation of the intramuscular fat content of the longissimus muscle of pigs by means of spectral analysis of ultrasound echo signals. Meat Sci 69:187–199
Müller WD, Dederer I, Linn SJ (2005) Use of X-ray technology for the determination of fat content by meat sorting. Fleischwirtschaft 85:128–131
Nanduri V, Kim G, Morgan MT, Ess D, Hahm B, Kothapalli A, Valadez A, Geng T, Bhunia AK (2006) Antibody immobilization on waveguides using a flow–through system shows improved Listeria monocytogenes detection in an automated fiber optic biosensor: RAPTOR™. Sensors 6:808–822
Nanduri V, Bhunia AK, Tu S, Paoli GC, Brewster JD (2007) SPR biosensor for the detection of L. monocytogenes using phage-displayed antibody. Biosens Bioelectron 23:248–252
O’sullivan MG, Byrne DV, Jensen MT, Andersen HJ, Vestergaard J (2003) A comparison of warmed-over flavour in pork by sensory analysis, GC/MS and the electronic nose. Meat Sci 65:1125–1138
Olsen EV, Otokar MC, Oksama M, Kien S, Lisiak D, Busk H (2007) On-line measurements in pig carcass classification: repeatability and variation caused by the operator and the copy of instrument. Meat Sci 75:29–38
rPanigrahi S, Balasubramanian S, Gu H, Logue CM, Marchello M (2006) Neural-network-integrated electronic nose system for identification of spoiled beef. LWT Food Sci Technol 39:135–145
Park B, Whittaker AD, Miller RK, DS HALE (1994) Ultrasonic spectral analysis for beef sensory attributes. J Food Sci 59:697–701
Passaro VMN, Dell’olio F, Casamassima B, de Lleonardis F (2007) Guided-wave optical biosensors. Sensors 7:508–536
Prieto N, Andrés S, Giráldez FJ, Mantecón AR, Lavín P (2006) Potential use of near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS) for the estimation of chemical composition of oxen meat samples. Meat Sci 74:487–496
Prieto N, Andrés S, Giráldez FJ, Mantecón AR, Lavín P (2008) Discrimination of adult steers (oxen) and young cattle ground meat samples by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS). Meat Sci 79:198–201
Prieto N, Roehe R, Lavín P, Batten G, Andrés S (2009) Application of of near infrared reflectance spectroscopy to predict meat and meat products quality: a review. Meat Sci 83:175–186
Rosenvold K, Andersen HJ (2003) The significance of preslaughter stress and diet on colour and colour stability of pork. Meat Sci 63:199–209
Ruan RR, Chen PL (2001) Nuclear magnetic resonance techniques and their application in food quality analysis. In: Gunasekaran S (ed) Nondestructive food evaluation. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 165–216
Scholz AM, Mitchell AD, Forster M, Pursel VG (2007) Two-site evaluation of the relation between in vivo and carcass dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) in pigs. Livest Prod Sci 110:1–11
Straadt IK, Rasmussen M, Andersen HJ, Bertram HC (2007) Aging-induced changes in microstructure and water distribution in fresh and cooked pork in relation to water-holding capacity and cooking loss—A combined confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and low-field nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation study. Meat Sci 75:687–695
Vestergaard JS, Haugen J, Byrne DV (2006) Application of an electronic nose for measurements of boar taint in entire male pigs. Meat Sci 74:564–577
Watanabe E, Tamada Y, Hamada-Sato N (2005) Development of quality evaluation sensor for fish freshness control based on KI value. Biosens Bioelectron 21:534–538
Williams RE, Bertrand JK, Williams SE, Benyshek LL (1997) Biceps femoris and rump fat as additional ultrasound measurements for predicting retail product and trimmable fat in beef carcasses. J Anim Sci 75:7–13
Yano Y, Miyaguchi N, Watanabe M, Nkamura T, Youdou T, Miyai J, Numata M, Aasano Y (1995) Monitoring of beef aging using a two-line flow injection analysis biosensor consisting of putrescine and xanthine electrodes. Food Res Int 28:611–618
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narsaiah, K., Jha, S.N. Nondestructive methods for quality evaluation of livestock products. J Food Sci Technol 49, 342–348 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0286-3
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0286-3