Abstract
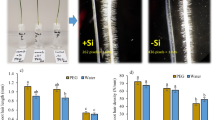
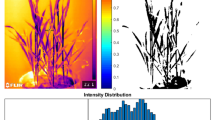
Plant roots are key components of plant growth and development by taking up soil water and inorganic nutrients. Therefore, understanding root characteristics such as root length, root angle, root density, and root diameter is very important for improving crop productivity. Here, we investigate the effects of exogenous application of silicon on root morphological traits in two soybean cultivars (Taeseon and Pungsanaeul). The majority of root morphological traits evaluated show a significant (p < 0.05) effect of Si treatment. The exceptions to this trend were forks (p < 0.8677) and the mean link branching angle (p = 0.0632). In Taeseon cultivars, root morphological traits such as length (21.8%), diameter (19.3%), tips (32.8%), and projected area (34.4%) were significantly increased by Si treatment compared to plants that received no exogenous Si. Pungsanaeul cultivars showed a similar pattern. The length, mean diameter, tips, and projected area increased in soybean plants that received exogenous Si 21.3%, 13.6%, 25.9%, and 33.0%, respectively. In conclusion, exogenous Si application increased root length and root diameter, thereby increasing overall root biomass. Because Si application enhances root growth and development, we anticipate that it will increase soybean productivity by improving water and nutrient uptake. To verify these findings, additional experiments at field conditions are needed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brear EM, Day DA, Smith PMC (2013) Iron: an essential micronutrient for the legume-rhizobium symbiosis. Front Plant Sci 4:359. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00359
Deren CW, Datnoff LE, Snyder GH, Martin FG (1994) Silicon concentration, disease response, and yield components of rice genotypes grown on flooded organic histosols. Crop Sci 34:733–737
Deshmukh RK, Vivancos J, Guérin V, Sonah H, Labbé C, Belzile F, Bélanger RR (2013) Identification and functional characterization of silicon transporters in soybean using comparative genomics of major intrinsic proteins in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol Biol 83:303–315
Gomes D, Agasse A, Thiebaud P, Delrot S, Geros H, Chaumont F (2009) Aquaporins are multifunctional water and solute transporters highly divergent in living organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1788:1213–1228
Gruber BD, Giehl RFH, Friedel S, von Wirén N (2013) Plasticity of the Arabidopsis root system under nutrient deficiencies. Plant Physiol 163:161–179
Henry A, Gowda VRP, Torres RO, McNally KL, Serraj R (2011) Variation in root system architecture and drought response in rice (Oryza sativa L.): phenotyping of the Oryza SNP panel in rainfed low land fields. Field Crops Res 120:205–214
Hove RM, Bhave M (2011) Plant aquaporins with non-aqua functions: deciphering the signature sequences. Plant Mol Biol 75:413–430
Jang SW, Kim Y, Khan AL, Na CI, Lee IJ (2018) Exogenous short-term silicon application regulates macro-nutrients, endogenous phytohormones, and protein expression in Oryza sativa L. BMC Plant Biol 18:4
Kaya C, Tuna AL, Sonmez O, Ince F, Higgs D (2009) Mitigation effects of silicon on maize plants grown at high zinc. J Plant Nutr 32:1788–1798
Kim YH, Khan AL, Kim DH, Lee SY, Kim KM, Waqas M, Jung HY, Shin JH, Kim JG, Lee IJ (2014) Silicon mitigates heavy metal stress by regulating P-type heavy metal ATPases, Oryza sativa low silicon genes, and endogenous phytohormones. BMC Plant Biol 14:13
Liang Y, Si J, Romheld V (2005) Silicon uptake and transport is an active process in Cucumis sativus. New Phytol 167:797–804
Ma JF, Takahashi E (2002) Soil, fertilizer, and plant silicon research in Japan. Elsevier Science B.V, Amsterdam
Ma JF, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Tamai K, Konishi S, Fujiwara T, Katsuhara M, Yano M (2007) An efflux transporter of silicon in rice. Nature 448(7150):209–212
Miao BH, Han XG, Zhang WH (2010) The ameliorative effect of silicon on soybean seedlings grown in potassium-deficient medium. Ann Bot 105:967–973
Mitani N, Chiba Y, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2009) Identification and characterization of maize and barley Lsi2-like silicon efflux transporters reveals a distinct silicon uptake system from that in rice. Plant Cell 21:2133–2142
Mitani N, Yamaji N, Ago Y, Iwasaki K, Ma JF (2011) Isolation and functional characterization of an influx silicon transporter in tow pumpkin cultivars contrasting in silicon accumulation. Plant J 66:4391–4398
Miyake Y, Takahashi E (1985) Effect of Silicon on the growth of soybean plants in a solution culture. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 31:625–636
Ouellette S, Goyette MH, Labbé C, Laur J, Gaudreau L, Gosselin A, Dorais M, Deshmukh RK, Belanger RR (2017) Silicon transporters and effects of silicon amendments in strawberry under high tunnel and field conditions. Front Plant Sci 8:949
Park YG, Park SM, Na CI, Kim Y (2019) Identification of optimal concentration of silicon application and its roles in uptake of essential nutrients in soybean (Glycine max L.). J Crop Sci Biotechnol 22:1–10
Shen X, Zhou Y, Duan L, Li Z, Eneji AE, Li J (2010) Silicon effects on photosynthesis and antioxidant parameters of soybean seedlings under drought and ultraviolet-B radiation. J Plant Physiol 167:1248–1252
Silva ON, Lobato AKS, Ávila FW, Costa RCL, Oliveira Neto CF, Santos Filho BG, Martins Filho AP, Lemos RP, Pinho JM, Medeiros MBCL, Cardoso MS, Andrade IP (2012) Silicon-induced increase in chlorophyll is modulated by the leaf water potential in two water-deficient tomato cultivars. Plant Soil Environ 58:481–486
Wasaya A, Zhang X, Fang Q, Yan Z (2018) Root phenotyping for drought tolerance: a review. Agronomy 8:241
Yamaji N, Chiba Y, Mitani-Ueno N, Ma JF (2012) Functional characterization of a silicon transporter gene implicated in silicon distribution in barley. Plant Physiol 160:1491–1497
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Kyungpook National University Research Fund, 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, Y.S., Kim, SH., Park, C.W. et al. Treatment with silicon fertilizer induces changes in root morphological traits in soybean (Glycine max L.) during early growth. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 23, 445–451 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-020-00052-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-020-00052-7