Abstract
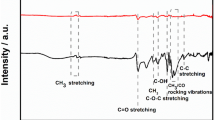
A carbon quantum dot (CQD)/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was developed as a novel system for electrochemical detection of cadmium ion (Cd). The characterization of the synthesized CQD/rGO nanocomposite was done by Fourier transform infrared, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, Raman, ultraviolet–visible, and X-ray diffraction analyses. The blending of CQD and rGO provides the sensor with a large surface area, high selectivity, sensitivity, stability, and excellent electrochemical compatibility. The modified CQD/rGO/GCE gives a linear response for Cd ion from 0.5 to 9 nM with a recognition limit of 0.3 nM. Over the studied scan rate, the composite exhibited a diffusion-controlled behavior. The modified electrode showed a good selectivity against interfering species (e.g., Zn2+, Ba2+, Bi2+, Hg2+, Cr3+, Pb2+, Ca2+, Ni2+, Mg2+, and Cu2+) with good reproducibility. This proposed detection system was proved to be cost-effective, precise, and easy to apply for environment monitoring such as groundwater, river water, and industrial effluents.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L.W. Ling, S.A. Ghani, Poly (4-vinylpyridine-co-aniline)-modified electrode synthesis, characterization, and application as cadmium (II) ion sensor. J. Solid State Electrochem. 17, 681–690 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1910-5
L. Nejdl, J. Kynicky, M. Brtnicky, M. Vaculovicova, V. Adam, Amalgam electrode-based electrochemical detector for on-site direct determination of cadmium (II) and lead (II) from soils. Sensor 17, 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17081835
G. Bhanjana, N. Dilbaghi, R. Kumar, A. Umar, S. Kumar, SnO2 quantum dots as novel platform for electrochemical sensing of cadmium. Electrochim. Acta. 169, 97–102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.045
Y. Si, J. Liu, Y. Chen, X. Miao, F. Ye, Z. Liu, J. Li, RGO/AuNPs/tetraphenyl porphyrin nanoconjugates-based electrochemical sensor for high-sensitive detection of cadmium ions. Anal. Methods. 10, 3631–3636 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY01020J
R. Manjumeena, D. Duraibabu, T. Rajamuthuramalingam, R. Venkatesan, P.T. Kalaichelvan, Highly responsive glutathione functionalized green AuNP probe for precise colorimetric detection of Cd2+ contamination in the environment. RSC Adv. 5, 69124–69133 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA12427A
S. Wu, K. Li, X. Dai, Z. Zhang, An ultrasensitive electrochemical platform based on imprinted chitosan/gold nanoparticles/graphenenanocomposite for sensing cadmium (II) ions. Microchem. J. 155, 104710–104718 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/.microc.2020.104710
Y. Guo, Y. Zhang, H. Shao, Z. Wang, X. Wang, X. Jiang, Label-free colorimetric detection of cadmium ions in rice samples using gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 86(17), 8530–8534 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac502461r
V.N. Mehta, H. Basu, R.K. Singhal, S.K. Kailasa, Simple and sensitive colorimetric sensing of Cd2+ ion using chitosandithiocarbamate functionalized gold nanoparticles as a probe. Sens. Actuators B 220, 850–858 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.05.105
P. Huang, S. Li, N. Gao, F. Wu, Toward selective, sensitive, and discriminative detection of Hg2+ and Cd2+ via pH-modulated surface chemistry of glutathione-capped gold nanoclusters. Analyst 140, 7313–7321 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AN01356A
H.R.L.Z. Zhad, Y.M. Rodriguez, R.Y. Lai, A reagentless and reusable electrochemical aptamer-based sensor for rapid detection of Cd (II). J Electroanal. Chem. 803, 89–94 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.09.022
Y. Noh, E.-J. Jo, H. Mun, Ahn Y–D, Kim M–G, Homogeneous and selective detection of cadmium ions by forming fluorescent cadmium-protein nanoclusters. Chemosphere 174, 524–530 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.025
Y. Zhang, X. Chen, J. Liu, G. Gao, X. Zhang, S. Hou, H. Wang, A highly selective and sensitive fluorescent chemosensor for distinguishing cadmium(II) from zinc(II) based on amide tautomerization. New J Chem. 42, 19245–19251 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nj03465f
S. Thatai, P. Khurana, S. Prasad, D. Kumar, A.M. Asiri, Plasmonic detection of Cd2+ ions using surface-enhanced Raman scattering active core–shell nanocomposites. Talanta 134, 568–575 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.11.024
D. Martín-Yerga, I. Álvarez-Martos, M.C. Blanco-López, C.S. Henry, M.T. Fernández-Abedul, Point-of-need simultaneous electrochemical detection of lead and cadmium using low-cost stencil-printed transparency electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta. 981, 24–33 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.05.027
J. Zhou, Q. Wang, F. Liu, S. Xiong, Electroanalysis of Cd2+ and Pb2+ based on Bi/Fe3O4/RTIL electrode. Electrocatalysis 12, 381–389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00661-y
V.N. Mehta, J.V. Rohit, S.K. Kailasa, Functionalization of silver nanoparticles with 5-sulfoanthranilic acid dithiocarbamate for selective colorimetric detection of Mn2+ and Cd2+ ions. New J Chem. 40, 4566–4574 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ03454J
R. Golbedaghi, S. Jafari, M.R. Yaftian, R. Azadbakht, S. Salehzadeh, B. Jaleh, Determination of cadmium (II) ion by atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. J Iran Chem. Soc. 9, 251–256 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-011-0018-7
O.V. Lundovskaya, A.R. Tsygankova, N.I. Petrova, A.I. Saprykin, Analysis of cadmium and cadmium oxide by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. J Anal. Chem. 73, 877–883 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934818090058
M. Musa, A. Kikuchi, N.E. Ismail, J. Jaafar, Z.A. Majid, M.R. Salim, K. Tanaka, Application of ion chromatography for the assessment of cadmium adsorption in simulated wastewater by activated carbon. Desalin Water Treat. 52, 3616–3622 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.854099
Z.-X. Wang, Y.-X. Guo, S.-N. Ding, Fluorometric determination of cadmium (II) and mercury (II) using nanoclusters consisting of a gold-nickel alloy. Microchim. Acta. 182, 2223–2231 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1563-z
W. Jin, P. Huang, F. Wu, L.-H. Ma, Ultrasensitive colorimetric assay of cadmium ion based on silver nanoparticles functionalized with 5-sulfosalicylic acid for wide practical applications. Analyst 140, 3507–3513 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an00230c
Y. Dong, L. Ding, X. Jin, N. Zhu, Silver nanoparticles capped with chalcon carboxylic acid as a probe for colorimetric determination of cadmium (II). Microchim. Acta. 184, 3357–3362 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2358-1
Z. Koudelkova, T. Syrovy, P. Ambrozova, Z. Moravec, L. Kubac, D. Hynek, L. Richtera, V. Adam, Determination of zinc, cadmium, lead, copper and silver using a carbon paste electrode and a screen printed electrode modified with chromium(III) oxide. Sensors 17, 1–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17081832
X. Chai, L. Zhang, Y. Tian, Ratiometric electrochemical sensor for selective monitoring of cadmium ions using biomolecular recognition. Anal. Chem. 86, 10668–10673 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac502521f
J. Meng, D. Li, L. Zhang, W. Gao, K. Huang, C. Geng, Y. Guan, H. Ming, W. Jiang, J. Liang, Degradation of norfloxacin by electrochemical oxidation using Ti/Sno2-Sb electrode doped with Ni or Mo. Electrocatalysis 12, 436–446 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00663-w
A.N. Jijana, N. Mphuthi P. Shumbula, S. Vilakazi, L. Sikhwivhilu, The ultra-sensitive electrochemical detection of As (III) in ground water using disposable L-cysteine/lipoic acid functionalised gold nanoparticle modified screen-printed electrodes. Electrocatalysis 12, 310–325 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00658-7
K. Mielech-Łukasiewicz, M. Domalewska, Electrochemical determination of ciclopirox olamine by using boron-doped diamond electrode modified with overoxidized polypyrrole film. Electrocatalysis 12, 283–294 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00651-0
Y.H. Chang, P.M. Woi, Y.B. Alias, Electrochemical characterization of melamine electropolymerized in deep eutectic solvents for selective detection of dopamine. Electrocatalysis 12, 238–250 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00648-9
Y. Wang, L. Wanga, W. Huang, T. Zhang, X. Hu, J.A. Perman, S. Ma, Metal-organic framework and conducting polymer based electrochemical sensor for high performance cadmium ions Detection. J Mater. Chem. A 5, 8385–8393 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA01066D
X. Lia, H. Wen, Q. Fu, D. Peng, J. Yua, Q. Zhang, X. Huang, Morphology-dependent NiO modified glassy carbon electrode surfacefor lead (II) and cadmium (II) detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 363, 7–12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.011
A.K. Wanekaya, Applications of nanoscale carbon-based materials in heavy metal sensing and detection. Analyst 136, 4383–4391 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1an15574a
S.K. Ponnaiah, P. Periakaruppan, B. Vellaichamy, T. Paulmony, R. Selvanathan, Picomolar-level electrochemical detection of thiocyanate in the saliva samples of smokers and non-smokers of tobacco using carbon dots doped Fe3O4 nanocomposite embedded on g-C3N4 nanosheets. Electrochim. Acta 283, 914–921 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.07.012
J. Li, J.–J Zhu, Quantum dots for fluorescent biosensing and bio-imaging applications. Analyst 138, 2506–2515 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an36705c
M.J. Molaei, Carbon quantum dots and their biomedical and therapeutic applications: a review. RSC Adv 9, 6460–6481 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra08088g
D. Yoo, Y. Park, B. Cheon, M.-H. Park, 2019 Carbon dots as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for metal ion detection. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 14, 272-285. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-019-3088-6
P. Devi, P. Rajput, A. Thakur, K.-H. Kim, P. Kumar, Recent advances in carbon quantum dot-based sensing of heavy metals in water. Trends Anal. Chem. 114, 171–195 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.03.003
B.B.R. Khan, P. Periakaruppan, S.K. Ponnaiah, G. Venkatachalam, B. Jeyaprabha, A new nanocomposite electrode of carbon quantum dots doped functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for lethal mercury sensing. J Cluster Sci. 32, 135–144 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01770-2
T. Kokulnathan, S. Sakthinathan, S.-M. Chen, R. Karthik, T.-W. Chiu, Hexammine cobalt(iii) coordination complex grafted reduced graphene oxide composite for sensitive and selective electrochemical determination of morin in fruit samples. Inorg. Chem. Front. 1145-1155 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8QI00055G
R. Karthik, J.V. Kumar, S.-M. Chen, T. Kokulnathan, T.-W. Chen, S. Sakthinathan, T.-W. Chiu, V. Muthuraj, Development of novel 3D flower-like praseodymium molybdate decorated reduced graphene oxide: an efficient and selective electrocatalyst for the detection of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor methyl parathion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 270, 353–361 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.054
M.G. Ashritha, S.R. Rondiya, R.W. Cross, N.Y. Dzade, S.D. Dhole, K. Hareesh, D.V. Sunitha, Experimental and computational studies of sonochemical assisted anchoring of carbon quantum dots on reduced graphene oxide sheets towards the photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 545, 148962-148972 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.148962
E. Aawani, N. Memarian, H.R. Dizaji, Synthesis and characterization of reduced graphene oxide–V2O5 nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic activity under different types of irradiation. J Phys. Chem. Solids 125, 8–15 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.09.028
T.F. Emiru, D.W. Ayele, Controlled synthesis, characterization and reduction of graphene oxide: a convenient method for large scale production. Egypt J Basic. Appl Sci. 4, 74–79 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbas.2016.11.002
M.F. Zainuddin, N.H.N. Raikhan, N.H. Othman, W.F.H. Abdullah, Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) using different treatments of graphene oxide (GO). Mater. Sci. Eng. 358, 1–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/358/1/012046
X. Jia, J. Lia, E. Wang, One-pot green synthesis of optically pH-sensitive carbon dots with upconversion luminescence. Nanoscale 4, 5572–5575 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr31319g
Y, Dong. N, Zhou. X, Lin. J, Lin. Y, Chi. G, Chen. Extraction of electrochemiluminescent oxidized carbon quantum dots from activated carbon. Chem Mater. 22, 5895-5899 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm1018844
A.K. Roy, S.-M. Kim, P. Paoprasert, S.-Y. Park, I. In, Preparation of biocompatible and antibacterial carbon quantum dots derived from resorcinol and formaldehyde spheres. RSC Adv. 5, 31677–31682 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra01506e
S. Cai, H. Pan, Á. González-Vila, T. Guo, D.C. Gillan, R. Wattiez, C. Caucheteur, Selective detection of cadmium ions using plasmonic optical fiber gratings functionalized with bacteria. Opt. Express 28(13), 19740–19749 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.397505
H. Jin, F. Rui, J. Chongyue, L. Zhilin, W. Min, Y. Ping, X. Yuanhua, Highly sensitive detection of trace Hg2+ via PdNPs/g-C3N4 nanosheet-modified electrodes using DPV. Microchem. J 152, 104356–104367 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104356
W. Huang, Y. Liu, N. Wang, G. Song, X. Yin, L. Zhang, X. Ni, W. Xu, A Sensitive electrochemical sensor based on ion imprinted polymers with gold nanoparticles for high selective detecting Cd (II) ions in real samples. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. 31, 2043–2053 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-01892-8
Z. Dahaghin, P.A. Kilmartin, H. Z. Mousavi, Novel ion imprinted polymer electrochemical sensor for the selective, detection of lead(II), Food Chem. 303, 125374–125381. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125374
M.B. Gumpu, M. Veerapandianc, U.M. Krishnand, J.B.B. Rayappan, Simultaneous electrochemical detection of Cd (II), Pb (II), As (III) and Hg (II) ions using ruthenium(II)-textured graphene oxide nanocomposites. Talanta 162, 574–582 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.10.076
M.Y. Pudza, Z.Z. Abidin, S. Abdul-Rashid, F.M. Yasin, A.S.M. Noor, J. Abdullah, Selective and simultaneous detection of cadmium, lead and copper by tapioca-derived carbon dot–modified electrode. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27, 1–10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07695-7
J.-H. Yoon, J. Yang, J.P. Kim, J.S. Bae, Y.-B. Shim, M.-S. Won, Simultaneous detection of Cd (II), Pb (II), Cu (II), and Hg (II) ions in dye waste water using a boron doped diamond electrode with DPASV. Bull Korean Chem. Soc. 31, 141–145 (2010). https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2010.31.01.140
A.E. Beltagi, E.M. Ghoneim, M.M. Ghoneim, Controlled synthesis, simultaneous determination of cadmium (II), lead (II), copper (II) and mercury (II) by square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry at a montmorillonite-calcium modified carbon paste electrode. Intern. J Environ. Anal. Chem. 91, 17–32 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/03067310902962577
A. Aravind, B. Mathew, Tailoring of nanostructured material as an electrochemical sensor and sorbent for toxic Cd (II) ions from various real samples. J Anal. Sci. Technol. 9, 1–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-018-0153-1
W. Wu, M. Jia, Z. Wang, W. Zhang, Q. Zhang, G. Liu, Z. Zhang, P. Li, Simultaneous voltammetric determination of cadmium (II), lead (II), mercury (II), zinc (II), and copper (II) using a glassy carbon electrode modified with magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles and fluorinated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Microchim. Acta. 186, 1–10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3216-5
Y. Wang, Z. Nie, X. Li, Y. Zhao, H. Wang, Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on porous graphitic carbon nitride/CoMn2O4 nanocomposite toward heavy metal ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 346, 130539–130548 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130539
X.-Z. Yao, Z. Guo, Q.H. Yuan, Z.G. Liu, J.H. Liu, X.J. Huang, Exploiting differential electrochemical stripping behaviors of Fe3O4 nanocrystals toward heavy metal ions by crystal cutting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(15), 12203–12213 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am501617a
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RasulKhan, B., Ponnaiah, S.K., Balasubramanian, J. et al. Novel Carbon Quantum Dotted Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheets for Nano-molar Range Cadmium Quantification. Electrocatalysis 13, 435–446 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-022-00732-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-022-00732-8