Abstract
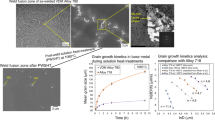
A investigation was done to determine the effect of post-weld heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ERNiCrMo-3 weld metals produced by metal inert gas shielded welding. The microstructure investigation revealed that the elements were irregularly distributed and severely segregated between the interdendritic region and dendrite core. Along the interdendritic region, a sizable number of secondary phases are also observed. The dissolution of Laves phase during the post-weld heat treatment would promote the precipitation of the M23C6 carbide along the grain boundaries. The post-weld heat treatment seemly deteriorated the tensile properties of weld metal and changed the fracture mode from transgranular to a mixed mode of transgranular and intergranular fracture. The M23C6 carbide precipitation at the grain boundaries during the aging heat treatment may be blamed for the decline in mechanical properties.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mithilesh P, Varun D, Reddy A R G, Ramkumar K D, and Narayanan S, Procedia Eng 75 (2014) 66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.11.013
Sun Y, Li Y, Qi Y, Cai X, and Ma C, Mater Lett 328 (2022) 133120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.133120
Ramkumar K D, Singh A, Raghuvanshi S, Bajpai A, and Narayanan S, J Manuf Process 19 (2015) 212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2015.04.005
Li D, Guo Q, Guo S, Peng H, and Wu Z, Mater Des 32 (2011) 696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.07.040
Vishwakarma K R, Richards N L, and Chaturvedi M C, Mater Sci Eng: A 480 (2008) 517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.08.002
Shankar V, Gill T P S, Mannan S L, and Sundaresan S, Sadhana 28 (2003) 359. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706438
Bhatti A A, Barsoum Z, Murakawa H, and Barsoum I, Mater Des 65 (2015) 878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.10.019
Xing X, Di X, and Wang B, J Alloys Compound 593 (2014) 110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.12.224
Yu K, Tang X, Jiang L, Ye X, and Li Z, J Mater Sci 57 (2022) 9415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06769-2
Xu F, Lv Y, Liu Y, Xu B, and He P, Phys Procedia 50 (2013) 48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2013.11.010
Kreitcberg A, Brailovski V, and Turenne S, Mater Sci Eng A 689 (2017) 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.02.038
Davis S H, Theory of solidification, 1st Edition, Cambridge University Press, 8th October 2001, 218 pp, Paperback ISBN: 9781139429634,
Lippold J C, Kiser S D, DuPont J N, Welding metallurgy and weldability of nickel-base alloys, 1st Edition, Wiley, 20th September 2011, 12 pp, Paperback ISBN:9781118210031
Qi H, Azer M, and Ritter A, Metall Mater Trans A 40 (2009) 2410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-9949-3
Mathew M D, Parameswaran P, and Rao K B S, Mater Character 59 (2008) 508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2007.03.007
Lee H S, Kim D H, Kim D S, and Yoo K B, J Alloys Compound 561 (2013) 135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.01.129
Xu F, Lv Y, Liu Y, Shu F, and Xu B, J Mater Sci Technol 29 (2013) 480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.02.010
Floreen S, Fuchs G E, and Yang W J, Superalloys 718 (1994) 13.
Silva C C, De Albuquerque V H C, Miná E M, Moura E P, and Tavares J M R, Metall Mater Trans A 49 (2018) 1653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4526-2
Marchese G, Lorusso M, Parizia S, Bassini E, and Biamino S, Mater Sci Eng A 729 (2018) 64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.05.044
Karmuhilan M and Kumanan S, Vacuum, 207 (2023) 111682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2022.111682
Yangfan W, Xizhang C, and Chuanchu S, Surf Coat Technol 374 (2019) 116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.05.079
Mittra J, Banerjee S, Tewari R, and Dey G K, Mater Sci Eng: A 574 (2013) 86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.03.021
Hu R, Bai G, Li J, Zhang J, and Fu H, Mater Sci Eng A 548 (2012) 83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.03.092
Ramkumar K D, Mulimani S S, Ankit K, Kothari A, Ganguly S, Mater Sci Eng A, 808 (2021) 140926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.140926
Sui S, Tan H, Chen J, Zhong C, and Huang W, Acta Mater 164 (2019) 413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.10.032
Ram G J, Reddy A V, Rao K P, Reddy G M, and Sundar J S, J Mater Process Technol 167 (2005) 73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.09.081
Nitin S, Rahul S M, and Manas M M, Mater Sci Eng A 716 (2018) 179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.01.035
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant Number BK20201036); the Special Talent Introduction for “Double Innovation Plan” in 2020; the Opening Project of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Structural Materials and Application Technology (Grant Number ASMA202007) and the Introduction of Talent Research Fund at Nanjing Institute of Technology (Grant Number YKJ201954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, M., Wan, J., Zhang, X. et al. Effect of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ERNiCrMo-3 Weld Metals. Trans Indian Inst Met 76, 3031–3039 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03085-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03085-y