Abstract
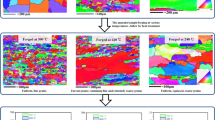
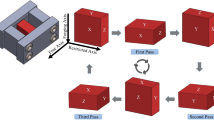
Multi directional forging is an important process for producing fine grains in bulk materials by means of severe plastic deformation. Zn-Al alloy is used for making sleeves of plain bearings, but the presence of porosity degrades its usage in industrial application. In the present investigation, multi directional forging of Zn-24Al-2Cu alloy was carried out at 100 and 200 °C up to total strain of 0.6 and 1.2 respectively. Mechanical properties and microstructural characterization were carried out on the processed material. It was inferred that processing at 100 °C up to three passes increased ultimate tensile strength from 185 to 267 MPa with ductility of 14 %. The average grain size was reduced from 30 to 2 µm. In the case of samples processed at 200 °C up to six passes, the average grain size was reduced to 1 µm. The ultimate tensile strength increased to 276 MPa and ductility significantly improved to 21 %. The strength of the processed material increased due to strain hardening and grain refinement. Uniform distribution of various dispersed phases contributed to the enhancement of ductility during multi directional forging at 200 °C. Analysis of the fractured surface of the tensile samples revealed highly ductile nature of the fracture.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Estrin Y, and Vinogradov A, Acta Mater 61 (2013) 782.
Valiev R Z, Islamgaliev R K, and Alexandrov I V, Prog Mater Sci 45 (2000) 103.
Salishchev G, Zaripova R, Galeev R, and Valiakhmetov O, Nanostruct Mater 6 (1995) 913.
Kaibyshev O A, J Mater Process Technol 117 (2001) 300.
Sakai T, Belyakov A, Kaibyshev R, Miura H, and Jonas J J, Prog Mater Sci 60 (2014) 130.
Prasad B K, Mater Sci Eng A 245 (1998) 257.
Babic M, Mitrovic S, and Jeremic B, Tribol Int 43 (2010) 16.
Babic M, Ninkovic R, Mitrovic S, and Bobic I, Tribol Ind 29 (2007) 23.
Al-Maharbi M, Karaman I, and Purcek G, Mater Sci Eng A 527 (2010) 518.
Chou C Y, Lee S L, Lin J C, and Hsu C M, Scripta Mater 57 (2007) 972.
Furukawa M, Ma Y, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Valiev R Z, and Langdon T G, Mater Sci Eng A 241 (1998) 122.
Kawasaki M, and Langdon T G, Mater Sci Eng A 503 (2009) 48.
Kawasaki M, Ahn B, and Langdon T G, Acta Mater 58 (2010) 919.
Purcek G, J Mater Process Technol 169 (2005) 242.
Liu Y, Li H, Jiang H, and Lu X, T Nonferr Metals Soc 23 (2013) 642.
Zhu Y H, Mater Trans 45 (2004) 3083.
Dorantes Rosales H J, Lopez Hirata V M, and Zhu Y H, Mater Sci Eng A 271 (1999) 366.
Preetham Kumar G V, and Uday Chakkingal, Mater Sci Forum 667 (2011) 867.
Zehetbauer M J, and Zhu Y T, Bulk Nanostructured Materials, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (2009), p 430.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharath, P.C., Udupa, K.R. & Kumar, G.V.P. Effect of Multi Directional Forging on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Zn-24 wt% Al-2 wt% Cu Alloy. Trans Indian Inst Met 70, 89–96 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0863-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0863-2