Abstract
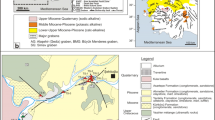
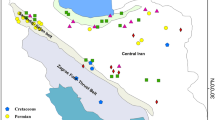
This study investigated the geochemical behavior and aqueous speciation of rare earth elements (REEs) in the geothermal, cold spring, surface waters, and wall rocks in the Havza (Samsun, Turkey) area. The sampled waters have temperatures ranging from 9.8 to 53 °C, pH values between 6.83 and 8.63, and total dissolved solids between 161 and 665 mg/L. The predominant cations and anions of waters are Ca2+, Na+, and HCO3−ions, respectively. The waters in the study area are generally characterized by Na-HCO3 (SH-5) and/or Ca-HCO3 (ILK, KRK, PNK, CEK, BEK, and TAD) types. All waters are saturated with carbonate minerals such as aragonite, calcite, and dolomite. All waters contain low concentrations of Be, (< 1 µg/L), Cr (< 0.5 µg/L), and Cd (< 0.01 µg/L) contents; whereas high concentrations of Li (3–100 µg/L), Al (2–266 µg/L), Mn (0.2–46.2 µg/L), Cu (0.2–6,2 µg/L), As (0.54–25.1 µg/L), Rb (0.35–16.3 µg/L), Sr (243–1070 µg/L), Y (0.01–36.3 µg/L), Ba (54.2–175 µg/L), V (0.47–5.75 µg/L), W (< 0.02–36.3 µg/L), Mo (0.3–1.2 µg/L), Sb (0.11–0.26 µg/L), Cs (0.003–5.30 µg/L), Pb (0.01–0.88 µg/L), and Sn (< 0.1–0.3 µg/L). Besides, the concentrations of Li, Y, W, Mo, Rb, Sb, As, Cu, Cs, Pb, and Sn are higher in Na-HCO3-type geothermal water than in Ca-HCO3-type waters. Higher Rb/Cs value in cold waters than in geothermal waters is an indication that Cs are retained by clay minerals in the host rocks. Concentrations of ∑REE range from 0.004 to 1.799 µg/L and 2.67 to 121.28 mg/kg for waters and wall rock samples, respectively. In all waters, the concentrations of REE are low and negatively correlated with TDS. The chondrite-normalized REE patterns and Eu anomalies of the studied waters indicate the signature of the host rocks. The speciation of REE complexes indicated that Ln(CO3+) is the major speciation in the alkaline waters, whereas Ln3+ and LnSO4+ complexes form in the near-neutral waters. Thus, carbonate (LnCO3+) complexes were one of the reasons for the enrichment of heavy REEs (HREEs) in alkaline waters. The positive Eu anomalies in some water samples may be indicative of the dissolution of Eu-enriched minerals (clays and plagioclase) or the mobilization of Eu2+ during the water–mineral interaction.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are presented and discussed in the tables and figures of this study.
References
Aktimur KT, Tekirli ME, Yurdakul ME, Ateş Ş, Ürgün BM, Teoman MŞ, Keçer M, Turşucu A, Genç S (1989) Niksar-Erbaa ve Destek Dolayının Jeolojisi. Maden Tetkit ve Arama Genel Müdürlüğü Rapor No: 8894, Ankara (in Turkish).
Alakangas LJ, Mathurin FA, Faarinen M, Wallin B, Aström ME (2014) Sampling and characterizing rare earth elements in groundwater in deep-lying fractures in granitoids under in situ high-pressure and low-redox conditions. Aquat Geochem 20:405–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-014-9225-z
Arslan M, Temizel İ, Abdioğlu E, Kolaylı H, Yücel C, Boztuğ D, Şen C (2013) 40Ar-39Ar dating, whole-rock and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope geochemistry of post-collisional Eocene volcanic rocks in the southern part of the Eastern Pontides (NE Turkey): implications for magma evolution in extension-induced origin. Contrib Mineral Petrol 166:113–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-013-0868-3
Banks D, Hall G, Reimann C, Siewers U (1999) Distribution of rare earth elements in crystalline bedrock groundwaters: Oslo and Bergen regions, Norway. Appl Geochem 14(1):27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(98)00037-7
Bau M (1999) Scavenging of dissolved yttrium and rare earths by precipitating iron oxyhydroxides experimental evidence for Ce oxidation, Y-Ho fractionation, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63(1):67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00014-9
Berger G, Schott J, Guy C (1988) Behavior of Li, Rb and Cs during basalt glass and olivine dissolution and chlorite, smectite and zeolite precipitation from seawater, experimental investigations and modelization between 50 °C and 300 °C. Chem Geol 71:297–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(88)90056-3
Bragin IV, Kharitonova NA, Chelnokov GA, Aseeva AV, Chudaev OV (2018) REY geochemistry in groundwater from Paratunka geothermal area (Kamchatka peninsula, Far East of Russia). Environ Earth Sci 77:376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7571-7
Bwire OS, Berry LW, Kathy AW, Robert JP, Karen HJ (2003) Strontium isotopes and rare earth elements as tracers of groundwater-lake water interactions, Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Appl Geochem 18(11):1789–1805. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00104-5
Calmbach L (1997) Aquachem Computer Code-Version 3.7,42. Aqueous GeochemicalAnalyses, Plotting and Modelling, Waterloo Hydrogeologic, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada
De Baar HJW, Shijf J, Byrne RH (1991) Solution chemistry of the rare earth elements in seawater. Eur J Solid State Inorg Chem 28:357–373
De Carlo EH, Wen XY, Irving M (1997) The influence of redox reactions on the uptake of dissolved Ce by suspended Fe and Mn oxide particles. Aquat Geochem 3:357–389. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009664626181
Dobashi R, Shikazono N (2008) Geochemical study of rare earth elements in carbonate minerals in sedimentary rocks around Tono uranium deposit, central Japan: An example of natural analogue study of geological disposal of high-level nuclear waste. Chikyukagaku (geochemistry) 42:79–98 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Fiket Ž, Rožmarić M, Krmpotic M, Petrinec B (2015) Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of Croatian thermal waters. Int J Environ Res 9(2):595–604
Gaillardet J, Viers J, Dupré B (2014) Trace elements in river waters. In: Drever JI (ed) Treatise on geochemistry, 2nd edn. 7. Elsevier, pp 195–235 (ISBN 978-0-08- 098300-4)
Göb S, Loges A, Nolde N, Bau M, Jacob DE, Markl G (2013) Major and trace element compositions (including REE) of mineral, thermal, mine and surface waters in SW Germany and implications for water-rock interaction. Appl Geochem 33:127–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.02.006
Gustafsson JP (2012) Visual MINTEQ ver. 3.1. https://vminteq.lwr.kth.se
Güven İH (1993) Doğu Pontidler’in 1:25000 ölçekli jeolojisi ve kompilasyonu. Maden Tetkik ve Arama Genel Müdürlüğü, Ankara (in Turkish)
Hart SR (1969) K, Rb, Cs contents and K/Rb, K/Cs ratios of fresh and altered submarine basalts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 6:295–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(69)90171-X
HatipoğluTemizel E, Gültekin F, FıratErsoy A (2019) Rare earth elements and yttrium geochemistry of the geothermal fields in the Eastern Black Sea Region (Ordu, Rize, Artvin), NE Turkey. Bull Min Res Exp 160:135–153. https://doi.org/10.19111/bulletinofmre.502835
HatipoğluTemizel E, Gültekin F, FıratErsoy A (2020) Major, trace, and rare earth element geochemistry of the Ayder and İkizdere (Rize, NE Turkey) geothermal waters: Constraints for water-rock interactions. Geothermics 86:101810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2020.101810
HatipoğluTemizel E, Gültekin F, FıratErsoy A, Kara Gülbay R (2021) Multi-isotopic (O, H, C, S, Sr, B, Li) characterization of waters in a low-enthalpy geothermal system in Havza (Samsun). Turkey Geothermics 97:102240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102240
Hemberger J, Lobina S, Krug von Nidda HA, Tristan N, Ivanov VYu, Mukhin AA, Balbashov AM, Loidl A (2004) Complex interplay of 3d and 4ƒ magnetism in La1-xGdxMnO3. Phys Rev B 70:24414. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.70.024414
Hounslow AW (1995) Water quality data: analysis and interpretation. CRC Press, LLC Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Johannesson KH, Lyons WB (1995) Rare-earth element geochemistry of Colour Lake, an acidic freshwater lake on Axel Heiberg Island, Northwest Territories, Canada. Chem Geol 119(1–4):209–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)00099-T
Johannesson KH, Zhou X (1999) Origin of middle rare earth element enrichments in acid waters of a Canadian High Arctic Lake. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:153–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00291-9
Johannesson KH, Lyons WB, Bird DA (1994) Rare earth element concentrations and speciation in alkaline lakes from the western. U.s.a. Geophys Res Lett 21(9):773–776. https://doi.org/10.1029/94GL00005
Johannesson KH, Zhou X, Guo C, Stetzenbach KJ, Hodge VF (2000) Origin of rare earth element signatures in groundwaters of circumneutral pH from southern Nevada and eastern California, USA. Chem Geol 164(3–4):239–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00152-7
Johannesson KH, Hawkins DL Jr, Cortes A (2006) Do Archean chemical sediments record ancient seawater rare earth element patterns? Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70(4):871–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.10.013
Kaasalainen H, Stefansson A, Giroud N, Arnorsson S (2015) The geochemistry of trace elements in geothermal fluids, Iceland. Appl Geochem 62:207–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.02.003
Leybourne MI, Goodfellow WD, Boyle DR, Hall GM (2000) Rapid development of negative Ce anomalies in surface waters and contrasting REE patterns in groundwaters associated with Zn–Pb massive sulphide deposits. Appl Geochem 15:695–723
Liu H, Pourret O, Guo H, Xing L, Zhan Y, Li F, Shao J, Niu H, Liang X, Li C (2016) Geochemical behaviors of rare earth elements in groundwater along a flow path in the North China Plain. J Asian Earth Sci 117:33–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.11.021
McDonough WF, Sun SS, Ringwood AE, Jagoutz E, Hofmann AW (1992) Potassium, rubidium, and cesium in the Earth and Moon and the evolution of the mantle of the Earth. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56(3):1001–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(92)90043-I
Migaszewski ZM, Galuszka A, Migaszewski A (2014) The study of rare earth elements in farmer’s well waters of the Podwioeniowka acid mine drainage area (southcentral Poland). Environ Monit Assess 186:1609–1622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3478-7
Minarik L, Zigova A, Bendl J, Skrivan P, Stastny M (1998) The behaviour of rare-earth elements and Y during the rock weathering and soil formation in the Ricany granite massif, central Bohemia. Sci Total Environ 215(1–2):101–111
Möller P, Dulski P, Savaşcın Y, Conrad M (2004) Rare earth elements, yttrium and Pb isotope ratios in thermal spring and well waters of West Anatolia, Turkey: a hydrochemical study of their origin. Chem Geol 206(1–2):97–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.01.009
Oliveri Y, Cangemi M, Capasso G, Saiano F (2019) Pathways and fate of REE in the shallow hydrothermal aquifer of Vulcano island (Italy). Chem Geol 512:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.02.037
Öztürk A (1979) Ladik-Destek dolayının stratigrafisi. Türkiye Jeoloji Kurumu Bülteni 22:27–34 (in Turkish)
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. USGS Water Resour Investig 99:4259. https://doi.org/10.3133/wri994259
Pasvanoğlu S, Çelik M (2018) A conceptual model for groundwater flow and geochemical evolution of thermal fluids at the Kızılcahamam geothermal area, Galatian volcanic Province. Geothermics 71:88–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2017.08.012
Pasvanoğlu S, Çelik M (2019) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and conceptual model of Çamlıdere low temperature geothermal prospect, northern Central Anatolia. Geothermics 79:82–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2019.01.004
Quillinan S, Nye C, Engle M et al (2018) Assessing rare earth element concentrations in geothermal and oil and gas produced waters: A potential domestic source of strategic mineral commodities (Final Report). United States: N.p. https://doi.org/10.2172/1509037
Şener MF (2019) A new approach to Kırşehir (Turkey) geothermal waters using REY, major elements and isotope geochemistry. Environ Earth Sci 78:75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8068-8
Shakeri A, Ghoreyshinia S, Mehrabi B, Delavari M (2015) Rare earth elements geochemistry in springs from Taftan geothermal area SE Iran. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 304:49–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2015.07.023
Sholkovitz ER (1995) The aquatic chemistry of rare earth elements in rivers and estuaries. Aquat Geochem 1:1–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01025229
Sholkovitz ER, Piepgras DJ, Jacobsen SB (1989) The pore water chemistry of rare earth elements in Buzzards Bay sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:2847–2856. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(89)90162-2
Sönmez Ö (2018) Havza (Samsun) Yöresinin Jeolojisi. Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Cumhuriyet Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Sivas
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD, Norry MJ (eds) Magmatism in the ocean basins, vol 42. Geol Soc Spec Publ, pp 313–345. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Sverjensky DA (1984) Europium redox equilibria in aqueous solution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 67(1):70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(84)90039-6
Tang J, Johannesson KH (2010) Rare earth elements adsorption onto Carrizo sand: influence of strong solution complexation. Chem Geol 279:120–133
Tang J, Johnnesson KH (2006) Controls on the geochemistry of rare earth elements along a groundwater flow path in the Carrizo Sand aquifer, Texas, USA. Chem Geol 225:156–171
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust. Its composition and evolution: an examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks. Blackwell, Oxford
Temizel İ (2014) Mineralogical, textural, and petrochemical evidence of magma mingling and mixing in the Tertiary monzogabbroic stocks around the Bafra (Samsun) area in Turkey: implications of coeval mafic and felsic magma interactions. Mineral Petrol 108:353–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-013-0304-4
Temizel İ, Arslan M, Yücel C, AbdioğluYazar E, Kaygusuz A, Aslan Z (2019) U-Pb geochronology, bulk-rock geochemistry and petrology of Late Cretaceous syenitic plutons in the Gölköy (Ordu) area (NE Turkey): implications for magma generation in a continental arc extension triggered by slab roll-back. J Asian Earth Sci 171:305–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.01.004
Temizel İ, Arslan M, Yücel C, AbdioğluYazar E, Kaygusuz A, Aslan Z (2020) Eocene tonalite-granodiorite from the Havza (Samsun) area, northern Turkey: Adakite-like melts of lithospheric mantle and crust generated in a post-collisional setting. Int Geol Rev 62(9):1131–1158. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2019.1625077
Tweed SO, Weaver TR, Cartwright I, Schaefer B (2006) Behavior of rare earth elements in groundwater during flow and mixing in fractured rock aquifers: an example from the Dandenong Ranges, southeast Australia. Chem Geol 234(3–4):291–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.006
Van Middlesworth PE, Wood SA (1998) The aqueous geochemistry of the rare earth elements and yttrium. Part 7. REE, Th and U contents in thermal springs associated with the Idaho batholith. Appl Geochem 13(7):861–884
Wampler JM, Krogstad EJ, Elliot WC, Kahn B, Kaplan DI (2012) Long-term selective retention of natural Cs and Rb by highly weathered coastal plain soils. Environ Sci Technol 46(7):3837–3843. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2035834
Wang M, Zhou X, Liu Y, Xu H, Wu Y, Zhuo L (2020) Major, trace and rare earth elements geochemistry of geothermal waters from the Rehai high-temperature geothermal field in Tengchong of China. Appl Geochem 119:104639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104639
Willis SS (2010) Trace element geochemistry in groundwater flow systems. Dissertation, Doctor of Philosophy the University of Texas at Arlington
Yuan J, Mao X, Wang Y, Zhide D, Leihui H (2014) Geochemistry of rare-earth elements in shallow groundwater, northeastern Guangdong Province. Chin J Chem 33:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0659-1
Zhang YF, Tan HB, Zhang W, Wei HZ, Tao D (2016) Geochemical constraint on origin and evolution of solutes in geothermal springs in western Yunnan, China. Chem Erde 76(1):63–75
Zhang Y, Zhou X, Liu H, Fang B (2020) Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the hot springs in the Simao Basin in southwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 79:121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8883-y
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Turkish Scientific Research Council (TÜBİTAK project number: 118Y308) for financial support. The authors are grateful to Prof Dr. Mehmet Arslan for his critical comments on the manuscript and help with the English of the final text. The authors also thank Prof. Dr. İrfan Temizel for his contribution to field work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Fieldwork, laboratory studies, trace, and rare earth element data interpretations were performed by EHT and FG. Sample preparation, rock definitions, and laboratory studies were performed by RKG and AFE. The first draft of the manuscript was written by EHT and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hatipoğlu Temizel, E., Gültekin, F., Fırat Ersoy, A. et al. Geochemistry of rare earth and trace elements in springs and surface water in the Havza (Samsun) area, NE Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 82, 511 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11206-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11206-5