Abstract
The lacustrine sediments and geomorphological data from the Bor Plain situated at elevations between 1050 and 1100 m in southern Central Anatolia provide record between 9800 and 6700 yr cal BP of climate changes and events. The main aim of this study is to determine the relationship between the location of Neolithic sites and the deposition and recession phases of the lake during Holocene. The geomorphological history of the Bor Plain and palynological results allows us to reconstruct the relationship between the Holocene environment and reconstruction of Neolithic settlements within a spatially well-defined lacustrine landscape of ~ 600 km2. A 75 ± 13 ka aged terrace, consisting almost entirely of calcite and situated about 76 m above the plain floor, indicates that the plain was covered with a paleolake in the transition from MIS 5 to MIS 4. Considering the low total organic carbon and the high CaCO3 clay values, we conclude that the lake slowly receded in 9867 ± 39 cal BP. However, the presence of aquatic herbaceous forms such as Nymphaceae and Cyperaceae indicates an increase in the water level of the lake during 6776 ± 35 cal BP, after which it transitioned to a dried lake. Thus, the progression and recession phases of the lake became the determining factor in the site selection of Neolithic settlements on mounds by which are found the plain floor at elevations between 1090 and 1100 m in this period on the Bor Plain.

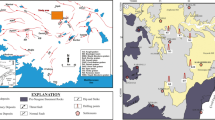
modified from D’Alfonso, 2010)

modified from Ulu 2009) of northern part of Bor Plain and center, and location of drill core (location 1)

modified from Atabey et al. 1990) of south of Bor Plain and Location 2 where sample was taken


modified from Erol, 1991). b Mounds on Holocene and Pleistocene terraces in front of Mt. Melendiz



. b Fluvial deposition between two mud sediments transported by streams during humid conditions showing (side-by-side): increase in lake level and actual soil; recent drying of lake level at Çıplaktepe mound situated between 34°23′05.41"E and 37°54′05.72" N (UTM, ED50, Zone 36 N)








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J, Maslin M, Thomas E (1999) Sudden climate transition during the Quaternary. Prog Phys Geogr 23(1):1–36
Asouti E (2009) The relationship between Early Holocene climate change and Neolithic settlement in Central Anatolia, Turkey: current issues and prospects for future research. Documenta Praehistorica 26:1–5
Atabey E, Göncüoğlu CM, Turhan N (1990) 1/100,000 Scale Geology Map, Kozan-J19 section of the map. General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration Publish, Ankara
Ayala G, Wainwright J, Waller J, Hodara C, Lloyd JM, Leng M, Doherty C (2017) Palaeoenvironmental reconstruction of the alluvial landscape of Neolithic Çatalhöyük, central southern Turkey: the implications forearly agriculture and responses to environmental change. J Archaeol Sci 86:30–43
Baird D (2002) Early Holocene settlement in central Anatolia: problems and prospects as seen from the Konya Plain. In: Thissen L, Gerard F (eds) The Neolithic of Central Anatolia. Internal developments and external relations during the 9th-6th millennia cal. BP. Ege Yayınları, Istanbul
Baird D (2007) The Boncuklu project: the origins of sedentism, cultivation and herding in central Anatolia. Anatolian Archaeology 13:14–17
Baird D (2012) The Late Epipaleolithic, Neolithic and Chalcolithic of the Anatolian Plateau, 13,000–4000 BC. In: Potts DT (ed) A companion to the archaeology of the ancient Near East. Wiley-Blackwell, Malden
Balatti S, Balza EM (2012) Kınık Höyük and Southern Cappadocia (Turkey): geo-archaeological activities landscapes and social spaces. In: Hofmann R, Moetz FK, Müller J (eds) International Workshop on socio-environmental dynamics over the last 12,00 years the creation of landscape II. Verlag Dr. Rodolf Habelt GmbH, Bonn
Bartov Y, Goldstein SL, Stein M, Enzel Y (2003) Catastrophic arid episodes in the Eastern Mediterranean linked with the North Atlantic Heinrich events. Geology 31:439–442
Bayer Altın T (2010) Distribution of pleateaus (Yayla) and sheep-barns according to topographic factors around melendiz and hasan mountains. Coğrafi Bilimler Dergisi 8(2):189–211 ((in Turkish))
Bayer Altın T, Barak B, Altın BN (2012) Change in precipitation and temperature amounts over three decades in Central Anatolia, Turkey. Atmospheric and Climate Sciences 2:107–125
Bayer Altın T, El Ouahabi M, Fagel N (2015) Environmental and climatic changes during the Pleistocene-Holocene in the Bor Plain, Central Anatolia, Turkey. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 440:564–578
Bayer Altın T, Fagel N (2015) Environmental and climatic changes in the Bor plain from Pleistocene to Holocene. Report No. TUBİTAK-BİDEB2219 Project (Unpublished).
Behre KE (1989) Biostratigraphy of the last glacial period in Europe. Quatern Sci Rev 8:25–44
Berger J-F, Lespez L, Kuzucuoğlu C, Glais A, Haurani F, Barra A, Guilaine J (2016) Interactions between climate change and human activities during the early to mid-Holocene in the Eastern Mediterranean basins. Clim past 12:1847–1877
Bıçakçı E, Faydalı E (2002) Tepecik-Çiftlik 2000 studies. 23rd excavation results meeting. Ankara: Republic of Turkey Ministry of Culture and Tourism Publications. (in Turkish).
Bıçakçı E (2007) Tepecik-Çiftlik. The oldest monuments of humanity 12,000 years ago Anatolia. Karlsruhe 135–470.
Bordaz J (1969) The suberde excevations, South-Western Turkey: an Interim report. Türk Arkeoloji Dergisi XVII/2: 43–71.
Boyer P, Roberts N, Baird D (2006) Holocene environment and settlement on the Çarşamba alluvial fan, South-Central Turkey: integrating geoarchaeology and archaeological field survey. Geoarchaeology 21(7):675–698
Calvo JP, Blanc-Valleron MM, Rodríguez-Arandía JP et al (1999) Authigenic clay minerals in continental evaporitic environments. In: Thiry M, Simon-Coinçon R (eds) Palaeoweathering, palaeosurfaces and related continental deposits. Springer, Oxford, pp 129–151
Cardarelli A, Frangipane M, Cazzella A, Peroni R (2010) Le Ragioni del Cambiamento/Reasons for Change. Scienze delle Antichità 15, Roma La Sapienza.
Celeste AA, Francus P, Brigham-Grette J (2007) Sedimentology, clay mineralogy and grain-size as indicators of 65 ka of climate change from El’gygytgyn Crater Lake, Northeastern Siberia. J Paleolimnol 37:105–122
Çinaroğlu A (1987) New Iron Age Discoveries around Niğde. Anadolu 2. IX. Excavation Results. Republic of Turkey Ministry of Culture and Tourism Publication, Ankara.
Cook HE, Johnson PD, Matti JC, Zemmels I (1975) Methods of sample preparation and x-ray diffraction data analysis. Initial Repts. Deep Sea Drilling Project Natl. Sci Foundat 38:999–1007
D’Alfonso L (2010) Geo-Archaeological Survey in Northern Tyanitis and the Ancient History of Southern Cappadocia. In: D’Alfonso L, Balza ME, Mora C (eds) Geo-archaeological Activities in Southern Cappadocia. Italian University Press, Pavia
D’Alfonso L, Mora C (2010) Viaggi anatolici dell’Universita di Pavia. Rapporto preliminare della quarta campagna di ricognizione archeologica nella Tyanitide settentrionale (2009). Athenaeum 98:569–576
Dansgaard W, Johnsen SJ, Clausen HB et al (1993) Evidence for general instability of past climate from a 250-kyr ice-core record. Nature 364:218–220
de Beaulieu JL, Reille M (1984) The pollen sequence of Les Echets (France): a new element for the chronology of the Upper Pleistocene. Géogr Phys Quat 38:3–9
De Meester T (1970) Soil map of the Great Konya Basin, Turkey. Wageningen, Research Report, Agricultural University, Netherlands
Dedeoğlu F (2008) Cultural Transformation and Settlement System of Southwestern Anatolia from Neolithic to LBA: A Case Study from Denizli/Çivril Plain. In: Córdoba JM, Molist M, Pérez CM, Rubio I, Martínez S (eds.) Proceedings of the 5th International Congress on the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East, Madrid, pp 687–601.
Dhont D, Chorowicz J, Yürür T (1999) The Bolkar Mountains (Central Taurides, Turkey): a Neogene extensional thermal uplift? Geol Bull Turk 42:69–87
Dirik K, Erol O (2000) Tectonomorphological evolution of Tuzgölü and surrounding area, Central Anatolia-Turkey. Türkiye Petrol Jeologları Derneği Özel Sayı 5:27–46 ((in Turkish))
Dong S, Li Z, Chen Q, Wei Z (2018) Total organic carbon and its environmental significance for the surface sediments in groundwater recharged lakes from the Badain Jaran Desert, northwest China. J Limnol 77(1):121–129
Eastwood WJ, Roberts N, Lamb HF, Tibby JC (1999) Holocene environmental change in southwest Turkey: a palaeoecological record of lake ve catchment–related changes. Quatern Sci Rev 18:671–696
Eastwood WJ, Leng MJ, Roberts M, Davis B (2007) Holocene climate change in the eastern Mediterranean region: a comparison of stable isotope and pollen data from Lake Gölhisar, southwest Turkey. J Quat Sci 22:327–341
Eastwood WJ, Gümüşçü O, Yiğitbaşıoğlu H, Haldon JF, England A (2009) Integrating palaeoecological and archaeo-historical records: Land use and landscape change in Cappadocia (central Turkey) since late Antiquity. In: Vorderstrasse T, Roodenberg J (eds) Archaeology of the Countryside in Medieval Anatolia. Pihans, Leiden.
Erol O (1971) Geomorphological evidence of the recessional phases of the pluvial lakes in the Konya, Tuzgölü and Burdur basins in Anatolia. Annals of the Geographical Research Institute 3(4):13–52
Erol O (1978) The quaternary history of the lake basins of Central Anatolia and Southern Anatolia. In: Brice WC (ed) The environmental history of the near east and middle east since the late ice age. Academic Press, London
Erol O (1979) The Neogene and Quaternary erosion cycles of Turkey in relation to the erosional surfaces and their correlated sediments. Bulletin of Geomorphology 8:1–40 ((in Turkish))
Erol O (1980) Quaternary pluvial and interpluvial conditions in Anatolia and environmental changes especially in South-central Anatolia since the last glaciation. Ann Geogr Res Inst 9(9):5–16
Erol O (1991) The relationship between the phases of the development of the Konya-Karapinar obruks and the Pleistocene Tuz Gölü and Konya pluvial lakes, Turkey. Deniz Bilimleri Ve Coğrafya Enstitüsü Bülteni 7:5–49 ((in Turkish))
Erol O (1999) A geomorphological study of the Sultansazlığı Lake, central Anatolia. Quatern Sci Rev 18:647–657
Erol O (1981) Quaternary pluvial and interpluvial conditions in Anatolia and environmental changes in south-central Anatolia since the last glaciation. In: Frey W, Uerpmann HP (eds) Beitrage zur Umweltgeschichte des Vorderen Orients. Wiesbaden: Beih. Zum Tübinger Atlas des Volderen Orient. Reihe A (Naturwissenscahften) vol 8, pp 101–109
Erol O (1984) Geomorphology and neotectonics of the pluvial lake basins in the Taurus Belt and South Central Anatolia. In: Tekeli O, Göncüoğlu CM (eds) International Symposium on Geology of the Taurus Belt. General Directorate for Mineral Research and Exploration, Ankara.
Erol O (1997) Geomorphologic arguments for mid-to late hocene enviromental change in Central Anatolian (Pluvial) Lake Basins. In: Dalfes HN, Kukla G, Weiss H (eds.) Climate change in the third millenium BC. NATO ASI, Book Series 49, Global Enviromental Change 49, Springer, Heidelberg, pp 321–350.
Esin U (1996) Aşıklı, ten thousand years ago: a habitation model from Central Anatolia. Habitat II:31–42 ((in Turkish))
Fairbridge R, Erol O, Karaca M, Yılmaz Y (1997) Background to Mid-Holocene Climatic Change in Anatolia and Adjacent Regions. In: Dalfes HN, Kukla G, Weiss H (eds) Third Millennium BP Climate Change and Old World Collapse. NATO ASI, Book Series l Global Enviromental Change 49, Springer, Heidelberg, pp 595–610.
Gérard F, Thissen L (eds) (2001) The Neolithic of Central Anatolia: internal developments and external relations during the 9th-6th Millennia CAL BP. Ege Yayınları, İstanbul.
Fontugne M, Kuzucuogğlu C, Karabiyikoğlu M, Hatte C, Patre J-F (1999) From Pleniglacial to Holocene. A 14C chronostratigraphy of environmental changes in the Konya plain. Turkey Quatern Sci Rev 18:573–591
French D, Hillman G, Payne S, Payne RJ (1972) Excavations at Can Hasan III. In: Higgs E (ed) Papers in economic prehistory: studies by members and associates of the British Academy major research project in the early history of agriculture. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1969–1970
Fuhrmann A (2002) Geochemical indicators of paleoenvironmental and paleoclimatic change in ancient and recent lake deposits: facies models, facies distributions and hydrocarbon aspects Dissertation, Berlin Technical University.
Galan E, Pozo M (2011) Palygorskite and sepiolite deposits in continental environments. Description, genetic patterns and sedimentary settings. In: Galan E, Singer A (eds) Developments in Clay Science 3. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gaudette HE, Flight WR, Toner L, Folger W (1974) Aninexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediments. J Sediment Petrol 44:249–253
Göncüoğlu CM (1986) Geochronological data from the southern part (Niğde area) of the Central Anatolian masif. MTA Dergisi 105–106:83–96
Grimm EC (1987) CONISS: A Fortran 77 program for stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis by the method of incremental sum of squares. Comput Geosci 13:13–35
Grootes PM, Stuiver M, White JWC, Johnsen SJ, Jouzel J (1993) Comparison of the oxygen isotope records from the GISP2 and GRIP Greenland ice cores. Nature 366:552–554
Gürel A, Lermi A (2008) Geo-archaeological activities in southern Cappadocia, Turkey. In: D’Alfonso L, Balza ME, Mora C (eds) Geo-archaeological activities in southern Cappadocia—Turkey. StMed 22. Italian Universty Press, Pavia
Gürel A, Lermi A (2010) Pleistocene-holocene fills of the Bor-Ereğli Plain (Central Anatolia): recent geo-archaeological contributions. In: D’Alfonso L, Balza ME, Mora C (eds) Geo-archaeological activities in Southern Cappadocia. Pavia University Press, Pavia
Hawkins JD (1982) The Neo-Hittites States in Syria and Anatolia. In: Boardman J, Edwards IES, Hammond NGL, Sollberger E (eds) The Prehistory of the Balkans, the Middle East and the Aegean World, Tenth to Eighth Centuries BP Cambridge. The Cambridge Ancient History III Part I., Cambridge
Hawkins JD (2000) Corpus of the Hieroglyphic Luwian Inscriptions. Vol. I: Inscriptions of the Iron Age. Part 2: Text, Amuq, Aleppo, Hama, Tabal, Asur Letters, Miscellaneous, Seals, Indices. de Gruyter, Berlin.
Hodder I (1996) On the surface: Çatalhöyük 1993–95. Çatalhöyük Project Vol. 1. Monograph 22. Cambridge Press, London
Howard AJ, Macklin MG, Passmore DG (2003) The alluvial archaeology of Europe. Swets Publishers, Rotterdam
Inoue K, Saito M, Naruse T (1998) Physicochemical, mineralogical, and geochemical characteristics of lacustrine sediments of the Konya Basin, Turkey, and their significance in relation to climatic change. Geomorphology 23:229–243
Jones MD, Roberts N (2008) Interpreting lake isotope records of Holocene environmental change in the Eastern Mediterranean. Quatern Int 181:32–38
Jones MD, Roberts N, Leng MJ, Türkeş M (2006) A high-resolution late Holocene lake isotope record from Turkey and links to North Atlantic and monsoon climate. Geology 43:361–364
Kansu SA (1944) Finds of Mesolithic culture in Anatolia. Dil Ve Tarih-Coğrafya Fakültesi Dergisi 2:673–682 ((in Turkish))
Karabıyıkoğlu M, Kuzucuoğlu C, Fontugne M (1999) Facies and depositional sequences of the Late Pleistocene Göçü shoreline system, Konya basin, Central Anatolia: implications for reconstructing lake-level changes. Quatern Sci Rev 18:593–609
Klotz S, Guiot J, Mosbrugger V (2003) Continental European Eemian and early Würmian climateevolution: comparing signals using different quantitativereconstruction approaches based on polen. Global Planet Change 36:277–294
Kühl N, Litt T, Ohlwein C, Hanse A (2007) Eemian and Early Weichselian temperature and precipitation variability in northern Germany. Quatern Sci Rev 26(25):3311–3317
Kürçer A, Gökten YE (2014) Paleoseismological three dimensional virtual photography method, case study: Duru-2012 Trench, Tuz Gölü Fault Zone, Central Anatolia, Turkey. Türkiye Jeoloji Bülteni 57:45–71 ((in Turkish))
Kuzucuoğlu C (2013) Geomorphology of the Melendiz River in Cappadocia (Turkey): setting of pre-pottery Neolithic sites of Aşıklı and Musular, and climate reconstruction during the onset of the Holocene. Geogr Fis Dinam Quat 36:95–105
Kuzucuoğlu C (2015) The rise and fall of the Hittite State in central Anatolia: how, when, where, did climate intervene. In: Beyer D, Henry O, Tibet A (eds) La Cappadoce méridionale de la préhistoire à la période byzantine, 3èmes Rencontres d’archéologie de l’IFEA. IFEA, Istanbul
Kuzucuoğlu C, Karabıyıkoğlu M, Parish R (1998) The dune systems of the Konya Plain (Turkey). Their relation to the environmental changes in Central Anatolia during Late Pleistocene and Holocene. Geomorphology 23:257–271
Kuzucuoğlu C, Bertaux J, Black S, Denefle M, Fontugne M, Karabıyıkoğlu M, Kashima K, Limondin-Lozouet N, Mouralis D, Orth P (1999) Reconstruction of climatic changes during the Late Pleistocene, based on sediment records from the Konya Basin (Central Anatolia, Turkey). Geol J 34:175–198
Kuzucuoğlu C, Dörfler W, Kunesch S, Goupille F (2011) Mid- to late Holocene climate change in central Turkey: the Tecer Lake record. The Holocene 21(1):173–188
Kuzucuoğlu C, Dumoulin J-P, Saulnier-Copard S (2018a) Geomorphological and Palaeoenvironmental Setting of Aşıklı Höyük. In: Özbaşaran M, Duru G, Stiner M (eds) The early settlement at Aşıklı Höyük, Essays in Honor of Ufuk Esin. Ege Yay, Istanbul
Kuzucuoğlu C, Demir M, Gürel A, Dumoulin J-P, Maner Ç (2018b) From post-LGM to Holocene evolution of environments in the Ereğli Basin: first results from geological indicators. NÖHÜ, Mühendislik Fakültesi Özel Sayı 3(7):1214–1219
Kuzucuoglu C (2019) Geomorphological landscapes in the Konya Plain and surroundings. In: Kuzucuoğlu C, Çiner A, Kazancı N (eds) Landscapes and landforms of Turkey. Springer, Berlin
Kuzucuoğlu C (2002) The environmental frame in Central Anatolia from the 9th to 6th millenia cal BC. An introduction to the study of relations between environmental conditions and the development of human societies. In: Gerard F and Thissen L (eds.) Internal Developments and External Relations During the 9th – 6th Millennia Cal BC, Ege Yayınları, Istanbul, pp 33–58.
Landmann G, Reimer A, Kempe S (1996) Climatic induced lake level changes of Lake Van/Turkey during the transition Pleistocene/Holocene. Global Biogeochem Cycles 10(4):797–808
Litt T, Krastel S, Sturm M, Kipfer R, Örcen S, Heumann G, Franz SO, Ülgen UB, Niessen F (2009) “Paleovan”, International Continental Scientific Drilling Program (ICDP): site survey results ve perspectives. Quatern Sci Rev 28:1555–1567
Maner C (2017) Preliminary report on the forth season of the Konya-Eregli survey (Keyar) 2016. Anatolia Antiqua XXV: 95–113.
Matessi A, Dalkılıç E, D’Alfonso L (2018) Settlement patterns, ancıent routes and envıronmental change in south Cappadocia (Turkey), during the Holocene. Niğde Ömer Halisdemir Üniversitesi Mühendislik Bilimleri Dergisi 7(3):1107–1112
Mellaart J (1961) Early cultures of the south Anatolian Plateau. Anatol Stud 11:159–184
Mellaart J (1967) Çatal Hüyük: A Neolithic town in Anatolia. Thames and Hudson, London
Miller R (2007) Civilizing climate. Social response to climate changes in the ancient near East. Altamira Press, Plymouth
Mizota C, Toh N, Matsuhisa Y (1987) Origin of cristobalite in soils derived from volcanic ash in temperate and tropical regions. Geoderma 39:323–330
Nicoll K, Küçükuysal C (2013) Emerging multi-proxy records of late quaternary palaeoclimate dynamics in Turkey and the surrounding region. Turk J Earth Sci 22:126–142
Oktay FY (1982) Stratigraphy and geological evolution of Ulukışla and its surroundings. Türkiye Jeoloji Kurumu Bülteni 25:15–23 ((in Turkish))
Özbaşaran M (2011) The Neolithic on the plateau. In: Mc Mahon G, Steadman S (eds) The Oxford handbok of ancient Anatolia: (10.000–323 BCE). Oxford University Press, Oxford
Özbek M (2009) Remodeled human skulls in Köşk Höyük (Niğde) Neolithic Village. J Hacettepe Univ 26:146–162 ((in Turkish))
Öztan A (2002) Köşk Höyük: anadolu arkeolojisine yeni katkilar. TÜBA-AR 5:55–69
Öztan A (2003) Anadolu’da bir Neolitik ve Kalkolitik yerleşme: Köşk Höyük. Colloquium Anatolicum II:69–86
Reed JM, Roberts N, Leng MJ (1999) An evaluation of the diatom response to Late Quaternary environmental change in two lakes in the Konya Basin, Turkey, by comparison with stable isotope data. Quatern Sci Rev 18:631–646
Reille M (1998) Pollen et spores d’Europe et d’Afrique du nord, supplement 2 Laboratoire de Botanique Historique et Palynologie. Springer, Marseille ((in French))
Riding JB (2021) A guide to preparation protocols in palynology. Palynology. https://doi.org/10.1080/01916122.2021.1878305
Roberts N (1979) The geomorphological development of the Karaman Region, South Central Turkey. Bull Geomorphol 8:77–83
Roberts N (1982) A note on the geomorphological environment of Çatal Höyük, Turkey. J Archaeol Sci 9(4):341–348
Roberts N, Black S, Boyer P, Eastwood WJ, Griffiths HI, Lamb HF, Leng MJ, Parish R, Reed MJ, Twigg D, Yiğitbaşoğlu H (1999) Chronology and stratigraphy of Late Quaternary sediments in the Konya Basin, Turkey: results from the KOPAL project. Quat Sci Rev 18:611–630
Roberts N, Reed J, Leng MJ, Kuzucuoglu C, Fontugne M, Bertaux J, Woldring H, Bottema S, Black S, Hunt E, Karabiyikoglu M (2001) The tempo of Holocene climatic change in the eastern Mediterranean region: new high-resolution crater-lake sediment data from central Turkey. The Holocene 11:721–736
Roberts N, Eastwood W, Kuzucuoğlu C, Fiorentino G, Caracuta V (2011) Climatic, vegetation and cultural change in the eastern Mediterranean during the mid-Holocene environmental transition. The Holocene 21(1):147–162
Roberts N, Reed JM (2009) Mediterranean lakes, wetlands and Holocene environmental change. In: Woodward J (ed) The Physical Geography of the Mediterranean 1st ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Roberts N, Boyer P, Merrick J (2007) The KOPAL on-site and off-site excavations at Çatalhöyük. In: Hodder I (ed) Excavating Çatalhöyük: Reports from the 1995–1999 seasons. McDonald Institute Monographs 37. Cambridge: McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research and British Institute.
Rosada G, Lachin MT (2010) Excavations at Tyana/Kemerhisar. Republic of Turkey Ministry of Culture and Tourism Publication, Ankara, p 32
Rosen AM (2007) Civilizing Climate. Social Responses to Climate Change in the Ancient Near East. Altamira Press, Plymouth.
Rossignol-Strick M (1999) The Holocene climatic optimum and pollen records of sapropel 1 in the eastern Mediterranean, 9000–6000 BP. Quatern Sci Rev 18:515–530
Sant DA, Mathew G, Khadkikar SA, Gogte V, Gundurao TK (2003) Co-existent cristobalite and iridium at 65 Ma, Anjar Intertrappeans, Kachchh, Western India. Cretac Res 24:105–110
Shackleton NJ (1969) The last interglacial in the marine and terrestrial records. Proceedings of the Royal Society London B 174:135–154
Singer A (2002) Palygorskite and sepiolite-the enigmatic clay minerals. Berichte Der Deutchen Ton Tonmineralgruppe 9:203–216
Solotchina EP, Prokopenko AA, Kuzmin MI, Solotchin PA, Zhdanova AN (2009) Climate signals in sediment mineralogy of Lake Baikal and Lake Hovsgol during the LGM-Holocene transition and the 1-Ma carbonate record from the HDP-04 drill core. Quatern Int 205(1–2):38–52
Taylor KC, Alley RB, Doyle GA, Alley RB, Grootes PM, Mayewski PA, White JWC, Barlow LK (1993) The flickering switch of late Pleistocene climate change. Nature 361:432–436
Türkecan A, Kuzucuoğlu C, Mouralis D, Pastre J-F, Atıcı Y, Guillou H, Fontugne M. (2004) Upper Pleistocene Volcanism and Paleogeography in Cappadocia, Turkey. Report No. 10652. General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration, Ankara.
Türkeş M (2005) Climate of southern part of the Middle Kızılırmak Sub-Region (Cappadocia District) and its vulnerability to desertification. Ege Coğrafya Dergisi 14:73–97 ((in Turkish))
Türkeş M (2013) Climate Changes: from the Cambrian to the Pleistocene, and from the Late Holocene to the 21st Century. Ege Coğrafya Dergisi 22:1–25 ((in Turkish))
Tyson RV (1995) Sedimentary Organic Matter. Chapman and Hall, London
Ülgen UB, Franz OS, Biltekin D et al (2012) Climatic and environmental evolution of Lake Iznik (NW Turkey) over the last ~4700 years. Quatern Int 274:88–101
Ulu Ü (2009) 1/100.000 Scale Geology Map, Karaman-M32 section of the map, No: 127. General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration, Ankara.
Van Zeist W, Woldring H (1978) A Postglacial pollen diagram from Lake Van in East Anatolia. Rev Palaeobot Palynol 26:249–276
Van Andel TH, Runnels CN, Pope KO (1986) Five thousand years of land use and abuse in the Southern Argolid, Greece. Hesperia 55:103–128
Vita-Finzi C (1969) The Mediterranean valleys. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wohlfarth B (2013) A review of Early Weichselian climate (MIS 5d-a) in Europe, Svensk Kärnbränslehantering AB. Technical Report No. TR-13–03, Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co.
Yang B, Wang J, Liu J (2019) A 1556 year-long early summer moisture reconstruction for the Hexi Corridor. Northwestern China Sci China Earth Sci 62:953–963
Yasuda Y, Kitagawa H, Nakagawa T (2000) The earliest record of major anthropogenic deforestation in the Ghab Valley, Northwest Syria: a Palynological Study. Quatern Int 73–74:127–136
Zeder M (2011) The origins of agriculture in the Near East. Curr Anthropol 52:221–235
Van Zeist W, Bottema S (1991) Late Quaternary vegetation of the Near East. Beihefte zum Tübinger Atlas de Vorderen Orients, Reihe A18. Dr Ludwig Reichert Verlag, Wiesbaden.
Acknowledgements
This research was founded by TUBİTAK-3001 (Project No. 116Y498). We are grateful to Emrecan Seyrek for taking samples and accompanying us on field trips. Anonymous reviewers are thanked for their valuable ideas and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayer Altın, T., Kayseri-Özer, M.S. & Altın, B.N. The Holocene terraces of the desiccated Bor Lake and Neolithic occupation in Bor Plain, Central Anatolia, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 80, 525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09835-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09835-9