Abstract
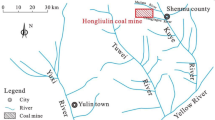
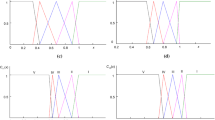
It is essential to assess mine water quality before this resource can be comprehensively utilized. The objective of this paper was to develop an integrated approach that can be applied for mine water quality assessment. An improved analytic hierarchy process (IAHP) method was used to calculate the weights of evaluation parameters, while fuzzy variable sets were used to determine the classification of mine water quality. Guojiawan mining area in Shaanxi Province, China, was chosen as the study area for this research and concentrations of total dissolved solids, chemical oxygen demand, chloride, sulfate, fluoride, and arsenic, as well as pH were utilized as water quality assessment factors. A total of 16 water samples, 13 samples from Guojiawan coal mine and three samples from Beiniuchuan River near the mine, were collected. The results show that four of these samples belonged to class III (roof water and river water) and encompass 25% of the total, and it can be used for domestic drinking, irrigation and industrial purposes, directly. While three belonged to class V and were derived from the auxiliary and main haulage roadways as well as the 51140 face cutting. They can be used for some industrial purpose after corresponding treatment. This latter group of samples accounted for 18.75% of the overall total, while the remaining nine were evaluated as class IV, encompassing 56.25% of the total, and they can be used for irrigation directly and domestic drinking after proper treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annapoorna H, Janardhana MR (2015) Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking purpose in rural areas surrounding a defunct copper mine. Procedia 4:685–692
Ashwani KT, Prasoon KS, Mukesh KM (2016) Environmental geochemistry and a quality assessment of mine water in the West Bokaro Coalfield, India. Mine Water Environ 35(4):525–535
Buragohain M, Bhuyan B, Sarma HP (2010) Seasonal variations of lead, arsenic, cadmium and aluminium contamination of groundwater in Dhemaji District, Assam, India. Environ Monit Assess 170(1–4):345–351
Chen SY (2005) Theory and model of engineering variable fuzzy set-Mathamatical basis for fuzzy hydrology and water resources. J Dalian Univ Technol 45(2):308–312 (In Chinese, with English abstract)
Elham F, Asghari M, Fclass TC, Tsai GT (2017) Analysis and assessment of hydrochemical characteristics of Maragheh-Bonab Plain Aquifer, Northwest of Iran. Water Resour Manag 31:765–780
Hao J, Zhang Y, Jia Y (2017) Assessing groundwater vulnerability and its inconsistency with groundwater quality, based on a modified DRASTIC model: a case study in Chaoyang District of Beijing City. Arab J Geosci 10(6):144–149
Heikkinen PM, Räisänen ML, Johnson RH (2009) Geochemical characterisation of seepage and drainage water quality from two sulphide mine tailings impoundments: acid mine drainage versus neutral mine drainage. Mine Water Environ 28(1):30–49
Koffi KV, Obuobie E, Banning A et al (2017) Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and surface water for domestic and irrigation purposes in Vea catchment, Northern Ghana. Environ Earth Sci 76(4):185
Leung CM, Jiao JJ (2006) Heavy metal and trace element distributions in groundwater in natural slopes and highly urbanized spaces in Mid-Levels area, Hong Kong. Water Res 40(4):753–767
Li F, Phoon KK, Du X, Zhang M (2013) Improved IAHP method and its application in risk identification. J Construct Eng Manag 139(3):312–320
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J (2015) Heavy metal contamination of yellow river alluvial sediments, northwest china. Environ Earth Sci 73(7):3403–3415
Li FW, Zhu JZ, Deng XY, Li SF (2018) Assessment and uncertainty analysis of groundwater risk. Environ Res 160(2):140–151
Mandal A (2005) Radionuclide and trace element contamination from coal combustion from Kolaghat thermal power plant, India. Mater Flow Coal Utilization 88(4):617–624
Manoj S, Thirumurugan M, Elango L (2017) An integrated approach for assessment of groundwater quality in and around uranium mineralized zone, Gogi region, Karnataka, India. Arab J Geosci 557(10):4–17
Ministry of Land and Resources of the P. R. China (2017) Standards for groundwater quality (DZ/T 0290-2017). National standards for geological exploration of mineral resources, pp 7–10 (in Chinese)
Mohammad RM, Reza S, Ahmad M, Kooshiar AV, Sharareh L, Sogol O, Mehrnoosh A, Azita M (2013) Assessment of water quality in groundwater resources of Iran using a modified drinking water quality index. Ecol Ind 30:28–34
Mondal NC, Singh VP, Singh VS, Saxena VK (2010a) Determining the interaction between groundwater and saline water through groundwater major ions chemistry. J Hydrol 388(1):100–111
Mondal NC, Singh VS, Puranik SC, Singh VP (2010b) Trace element concentration in groundwater of Pesarlanka Island, Krishna Delta, India. Environ Monit Assess 163(1–4):215–227
Moore JW, Ramamoorthy S (1984) Heavy metals in natural waters. Springer-Verlag, New York
Nahar MN, Inaoka T, Fujimura M, Watanabe C, Shimizu H, Tasnim S, Sultana N (2014) Arsenic contamination in groundwater and its effects on adolescent intelligence and social competence in Bangladesh with special reference to daily drinking/cooking water intake. Environ Health Prev Med 19(2):151–158
Radojevic M, Bashkin VN (1999) Practical environmental analysis. Royal Chemical Soc Publ, London, pp 154–155
Rajesh R, Brindha K, Elango L (2015) Groundwater quality and its hydrochemical characteristics in a shallow weathered rock aquifer of southern India. Water Quality Exposure Health 7(4):515–524
Rajmohan N, Elango L (2004) Identification and evolution of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment in an area of the Palar and Cheyyar River basins, southern India. Environ Geol 46(1):47–61
Randall JH, William PJ (2017) Pathogen transport in groundwater systems: contrasts with traditional solute transport. Hydrogoly 25:921–930
Robins NS (2002) Groundwater quality in Scotland: major ion chemistry of the key groundwater bodies. Sci Total Environ 294(1):41–56
Saaty TL (2008) Decision-making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int J Service Sci 70(1):83–98
Silvert W (1997) Ecological impact classification with fuzzy sets. Ecol Model 96(1–3):1–10
Singh AK, Mahato MK, Neogi B (2010) Quality assessment of mine water in the Raniganj Coalfield Area, India. Mine Water Environ 29(4):248–262
Singh AK, Mahato MK, Neogi B, Tewary BK, Sinha A (2012) Environmental geochemistry and quality assessment of mine water of Jharia coalfield, India. Environ Earth Science 65:49–65
Song DY, Qin Y, Zhang JY, Wang WF, Zheng CG (2007) Concentration and distribution of trace elements in some coals from Northern China. Int J Coal Geol 69:179–191
Stamatis G, Alexakis D, Gamvroula D, Migiros G (2011) Groundwater quality assessment in Oropos–Kalamos basin, Attica, Greece. Environ Earth Sci 64(4):973–988
Tiwari AK, Singh PK, Mahato MK (2016) Environmental geochemistry and a quality assessment of mine water of the West Bokaro coalfield, India. Mine Water Environ 35:525–535
Vetrimurugan E, Brindha K, Elango L, Ndwandwe OM (2017) Human exposure risk to heavy metals through groundwater used for drinking in an intensively irrigated river delta. Appl Water Sci 7:1–14
Wang XY, Wang TT, Wang Q, Li RZ (2016a) Evaluation of floor water inrush based on fractal theory and an improved analytic hierarchy process. Mine Water Environ 36(1):1–9
Wang XY, Zhao W, Liu XM (2017) Identification of water inrush source from coalfield based on entropy weight-fuzzy variable set theory. J China Coal Soc 42(09):2433–2439 (In Chinese, with English abstract)
Wu J, Li P, Qian H (2015) Hydrochemical characterization of drinking groundwater with special reference to fluoride in an arid area of china and the control of aquifer leakage on its concentrations. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8575–8588
Xie QM, Xia YY (2004) Multi-objective decision-making method for the treatment scheme of landslide hazard. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing Mineral Metall Mater 11(2):101–105
Xie P, Yue S, Ding J, Wan Y, Li X, Ma J (2018) Degradation of organic pollutants by vacuum-ultraviolet (VUV): kinetic model and efficiency. Water Res 133:69–78
Yesilnacar MI, Kadiragagil Z (2013) Effects of acid mine drainage on groundwater quality: a case study from an open-pit copper mine in eastern Turkey. Bull Eng Geol Env 72(3–4):485–493
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant no. 2016YFC0501104), National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant no. SHJT-16-30.10), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41807221) technological innovation program of Tiandi science and technology company (2018-TD-MS072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiantian, W., Dewu, J., Jian, Y. et al. Assessing mine water quality using a hierarchy fuzzy variable sets method: a case study in the Guojiawan mining area, Shaanxi Province, China. Environ Earth Sci 78, 264 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8216-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8216-1