Abstract
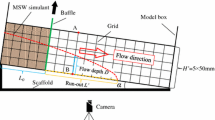
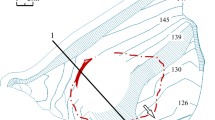
Flow slides at municipal solid waste (MSW) landfills can lead to a leak of toxic MSW and leachate over a large area, and result in serious pollution to the environment in the surrounding region. It is therefore important to predict the propagation of failed MSW in the environment, and then take protective measures. In this paper, a three-dimensional (3D) model based on the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method, which is an improved version of the previous two-dimensional (2D) model (Huang et al. in Waste Manag Res 31(3):256–264, 2013), is established to reproduce the propagation stage of the failed MSW across complex terrain. The Navier–Stokes equations and Bingham model are adopted as the governing equations and constitutive model, respectively. A no-slip boundary condition is incorporated to consider the effect of a solid boundary on the MSW movement. The 3D performance of the new model is verified and evaluated through the simulation of a MSW flow model test. The established 3D model and the former 2D model are applied to simulate a typical flow slide that occurred at the Ümraniye-Hekimbasi landfill. The final shape of the waste deposit simulated with the 3D model well matches the field observation; the performance of the new model in simulating flow slides for MSW in three dimensions across complex terrain is highlighted. The presented model can play a role in defining and mapping hazardous areas, and provide a means for the identification and design of appropriate protective measures for landfills with potential flow slides.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batchelor GK (1967) An introduction to fluid dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Blight GE (2004) A flow failure in a municipal solid waste landfill: the failure at Bulbul, South Africa. In: The skempton conference: advances in geotechnical engineering, Thomas Telford, London, 2, pp 777–788
Blight GE (2008) Slope failures in municipal solid waste dumps and landfills: a review. Waste Manag Res 26(5):448–463
Blight GE, Fourie AB (2005) Catastrophe revisited: disastrous flow failures of mine and municipal solid waste. Geotech Geol Eng 23:219–248
Bray JD, Zekkos D, Kavazanjian E, Athanasopoulos GA, Riemer MF (2009) Shear strength of municipal solid waste. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 135(6):709–722
Brink DP, Day PW, du Preez L (1999) Failure and remediation of Bulbul Drive landfill: KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. In: 7th International waste management and landfill symposium, Cagliari, Italy, pp 555–562
Brunner PH, Fellner J (2007) Setting priorities for waste management strategies in developing countries. Waste Manag Res 25(3):234–240
Caicedo B, Giraldo E, Yamin L, Soler N (2002) The landslide of Dona Juana landfill in Bogota: a case study. In: Proceedings of the 4th international congress on environmental geotechnics (4th ICEG), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 11–15 August 2002, pp 171–175
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M, Sacco C (2013) Modelling the post-failure stage of rainfall-induced landslides of the flow type. Can Geotech J 50(9):924–934
Chen YM, Luo CY, Ke H (2003) Geotechnical properties of municipal solid waste in China. In: Proceedings of the 12th Asian Regional conference on soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering 1–2, pp 365–368
Chugh AK, Stark TD, DeJong KA (2007) Reanalysis of a municipal landfill slope failure near Cincinnati, Ohio, USA. Can Geotech J 44(1):33–53
Dai ZL, Huang Y, Jiang FH, Huang MS (2015) Modeling the flow behavior of a simulated municipal solid waste. Bull Eng Geol Environ. doi:10.1007/s10064-015-0735-8
Ercolessi F (1997) A molecular dynamics primer. Spring College in Computational Physics, ICTP, Trieste, pp 24–25
Fan XM, Rossiter DG, van Westen CJ, Xu Q, Gorum T (2014) Empirical prediction of coseismic landslide dam formation. Earth Sci Process Landf 39(14):1913–1926
Gabr MA, Valero SN (1995) Geotechnical properties of municipal solid waste. Geotech Test J 18(2):241–251
Ghobadi MH, Babazadeh R, Bagheri V (2013) Siting MSW landfills by combining AHP with GIS in Hamedan province, western Iran. Environ Earth Sci 70(4):1823–1840
Gingold RA, Monaghan JJ (1977) Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics: theory and application to non-spherial stars. Mon Not R Astron 181:375–389
Haddad B, Pastor M, Palacios D, Munoz-Salinas E (2010) A SPH depth integrated model for Popocatépetl 2001 lahar (Mexico): sensitivity analysis and runout simulation. Eng Geol 114(3–4):312–329
Hamilton SM, Reyes DV, Kolb WW (1998) Remediation of a major landfill slope failure in Bogota, Columbia. In: Wastecon/ISWA World Congress, Charlotte, North Carolina, USA, pp 503–519
Hendron DM, Fernandez G, Prommer PJ, Giroud JP, Orozco LF (1999) Investigation of the cause of the 27 September 1997 slope failure at the Dona Juana landfill. In: 7th International waste management and landfill symposium, Cagliari, Italy, pp 545–554
Huang Y, Dai ZL, Zhang WJ, Huang MS (2013) SPH-based numerical simulations of flow slides in municipal solid waste landfills. Waste Manag Res 31(3):256–264
Hungr O (1995) A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides, debris flows, and avalanches. Can Geotech J 32(4):610–623
Jafari NH, Stark TD, Merry S (2013) The July 10 2000 Payatas landfill slope failure. Int J Geoeng Case Hist 2(3):208–228
Kocasoy G, Curi K (1995) The Ümraniye-Hekimbasi open dump accident. Waste Manag Res 13(4):305–314
Koelsch F, Fricke K, Mahler C, Damanhuri E (2005) Stability of landfills-the Bandung dumpsite disaster. In: 10th International waste management and landfill symposium, Sardinia, Cagliari
Komatina D, Jovanovic M (1997) Experimental study of steady and unsteady free surface flows with water-clay mixtures. J Hydraul Res 35(5):579–590
Libersky LD, Petschek AG, Carney TC, Hipp JR, Allahdadi FA (1993) High strain Lagrangian hydrodynamics: a three dimensional SPH code for dynamic material response. J Comput Phys 109(1):67–75
Liu GR, Liu MB (2003) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: a meshfree particle method. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., Singapore
Liu MB, Liu GR (2010) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH): an overview and recent developments. Arch Comput Methods Eng 17(1):25–76
Liu CL, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Zhang S, Yin MY, Ye H, Hou HB, Dong H, Zhang M, Jiang JM, Pei LX (2007) Assessing pollutions of soil and plant by municipal waste dump. Environ Geol 52(4):641–651
Liu ZB, Ma J, Li JM (2009) Stability analysis of the slope of municipal solid waste sanitary landfill. International Symposium on Environmental Science and Technology, Shanghai
Liu XL, Si WJ, Zhu CY, Yu W (2010) Analysis on stability of liner system located in slope of municipal solid waste landfill. In: Proceedings of the 7th international symposium on safety science and technology (ISSST), Hangzhou, China. Science Press, Beijing, China
Lu L, Wang ZJ, Huang XY, Zheng B, Arai K (2014) Dynamic and static combination analysis method of slope stability analysis during earthquake. Math Probl Eng. doi:10.1155/2014/573962
Lucy LB (1977) A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. Astron J 82(12):1013–1024
Machado SL, Karimpour-Fard M, Shariatmadari N, Carvalho MF, do Nascimento JCF (2010) Evaluation of the geotechnical properties of MSW in two Brazilian landfills. Waste Manag 30(12):2579–2591
McDougall S, Hungr O (2004) A model for the analysis of rapid landslide motion across three-dimensional terrain. Can Geotech J 41(6):1084–1097
Merry SM, Kavazanjian E, Fritz WU (2005) Reconnaissance of the July 10, 2000 Payatas landfill failure. ASCE J Perform Constr Facil 19(2):100–107
Monaghan JJ (1992) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Ann Rev Astron Astrophys 30:543–574
Monaghan JJ (1994) Simulating free surface flows with SPH. J Comput Phys 110(2):399–406
Monaghan JJ (2002) SPH compressible turbulence. Mon Not R Astron Soc 335(3):843–852
Monaghan JJ, Gingold RA (1983) Shock simulation by the particle method SPH. J Comput Phys 52:374–389
Monaghan JJ, Lattanzio JC (1985) A refined particle method for astrophysical problems. Astron Astrophys 149:135–143
Morris JP, Fox PJ, Zhu Y (1997) Modeling low reynolds number incompressible flows using SPH. J Comput Phys 136:214–226
Pastor M, Haddad B, Sorbino G, Cuomo S, Drempetic V (2009) A depth-integrated, coupled SPH model for flow-like landslides and related phenomena. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 33:143–172
Pastor M, Blanc T, Haddad B, Petrone S, Morles MS, Drempetic V, Issler D, Crosta G, Cascini L, Sorbino G (2014) Application of a SPH depth-integrated model to landslide run-out analysis. Landslides 11(5):793–812
Randles PW, Libersky LD (1996) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: some recent improvements and applications. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 139(1):375–408
Reddy KR, Hettiarachchi H, Parakalla NS, Gangathulasi J, Bogner JE (2009) Geotechnical properties of fresh municipal solid waste at Orchard Hills Landfill, USA. Waste Manag 29(2):952–959
Stark TD, Huvaj-Sarihan N, Li GC (2009) Shear strength of municipal solid waste for stability analyses. Environ Geol 57(8):1911–1923
Takeda H, Miyama SM, Sekiya M (1994) Numerical simulation of viscous flow by smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Progress Theor Phys 92(5):939–960
Thusyanthan NI, Madabhushi SPG, Singh S (2006a) Centrifuge modeling of solid waste landfill systems—part 1: development of a model municipal solid waste. Geotech Test J 29(3):217–222
Thusyanthan NI, Madabhushi SPG, Singh S (2006b) Centrifuge modeling of solid waste landfill systems—part 2: centrifuge testing of MSW simulant. Geotech Test J 29(3):223–229
Uzuoka R, Yashima A, Kawakami T, Konrod JM (1998) Fluid dynamics based prediction of liquefaction induced lateral spreading. Comput Geotech 22(3/4):234–282
Zekkos D, Bray JD, Kavazanjian E, Matasovic N, Rathje EM, Riemer MF, Stokoe KH (2006) Unit weight of municipal solid waste. J Geotech Geoenvironment Eng 132(10):1250–1261
Zhan LT, Chen YM, Ling WA (2008) Shear strength characterization of municipal solid waste at the Suzhou landfill, China. Eng Geol 97(3–4):97–111
Zhao H, Song EX (2012) A method for predicting co-seismic displacements of slopes for landslide hazard zonation. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 40:62–77
Zhu B, Yang CB, Wang L et al (2012) Compounding model MSW and Centrifugal model tests of landfill. In: Proceedings of the 1st China National symposium on coupled phenomena in geomaterials and environmental geotechnics, Hangzhou, pp 425–432 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) through Grant No. 2012CB719803.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Z., Huang, Y. A three-dimensional model for flow slides in municipal solid waste landfills using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Environ Earth Sci 75, 132 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4923-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4923-4