Abstract
Background and Aim
Obesity is one of the greatest public health concerns worldwide. Weight loss surgeries have been increased in recent decades due to the world’s epidemic of obesity. The aim of this prospective study is investigating metabolic factors of morbid obese patients following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery.
Methods
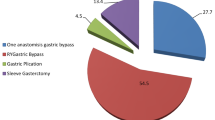
This was a nonrandomized prospective cohort study conducted from 2010 to 2013 on 60 consecutive patients who had body mass index (BMI) of more than 40 kg/m2 and met the surgical indication criteria of bariatric surgery. Upon discharge, patients were followed in outpatient clinic of Qaem Hospital, Mashhad, Iran, each 3 months for 12 months. Measurement of anthropometric and metabolic indices was done in each postoperative visit.
Results
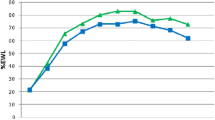
Mean BMI reduction was 15.26 ± 3.45 kg/m2 in the patients with an average value of 28.84 ± 3.94 (range from 22 to 40 kg/m2), which was significantly lower than the base value (p < 0.001). After a 12-month follow up, patients had lower low-density lipoprotein, triglycerides, and total cholesterol (p < 0.001 for all the variables), while achieving a greater high-density lipoprotein (p = 0.004). An improvement was seen in all of hypertensive patients after a 3-month follow up and blood pressure remained within normal limit in further follow ups. Complete remission was observed in all the patients with obstructive sleep apnea.
Conclusion
It appears reasonable that multidisciplinary treatment including surgical alternatives should be concerned for all morbidly obese patients, considering high rate of failure of conservative medical therapy in this setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gloy VL, Briel M, Bhatt DL, et al. Bariatric surgery versus non-surgical treatment for obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2013;347:f5934.
Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–5.
Ginter E, Simko V. Diabetes type 2 pandemic in 21st century. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2010;111:134–7.
Mann T, Tomiyama AJ, Westling E, Lew AM, Samuels B, Chatman J. Medicare’s search for effective obesity treatments: diets are not the answer. Am Psychol. 2007;62:220–33.
Tham JC, Howes N, le Roux CW. The role of bariatric surgery in the treatment of diabetes. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2014;5:149–57.
Allender S, Rayner M. The burden of overweight and obesity-related ill health in the UK. Obes Rev. 2007;8:467–73.
Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2011. Obes Surg. 2013;23:427–36.
Dixon JB, le Roux CW, Rubino F, Zimmet P. Bariatric surgery for type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2012;379:2300–11.
Trakhtenbroit MA, Leichman JG, Algahim MF, et al. Body weight, insulin resistance, and serum adipokine levels 2 years after 2 types of bariatric surgery. Am J Med. 2009;122:435–42.
Bendewald FP, Choi JN, Blythe LS, Selzer DJ, Ditslear JH, Mattar SG. Comparison of hand-sewn, linear-stapled, and circular-stapled gastrojejunostomy in laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2011;21:1671–5.
Ikramuddin S, Korner J, Lee WJ, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs intensive medical management for the control of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia: the Diabetes Surgery Study randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;309:2240–9.
Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1567–76.
Sjostrom L. Review of the key results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) trial—a prospective controlled intervention study of bariatric surgery. J Intern Med. 2013;273:219–34.
Bray GA, Ryan DH. Drug treatment of the overweight patient. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2239–52.
Csendes A, Smok G, Burgos AM. Histological findings in the liver before and after gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2006;16:607–11.
Furuya CK Jr, de Oliveira CP, de Mello ES, et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: preliminary findings after 2 years. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:510–4.
Mancia G, Carugo S, Grassi G, et al. Prevalence of left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertensive patients without and with blood pressure control: data from the PAMELA population. Pressioni Arteriose Monitorate E Loro Associazioni. Hypertension. 2002;39:744–9.
Jamal M, Wegner R, Heitshusen D, Liao J, Samuel I. Resolution of hyperlipidemia follows surgical weight loss in patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery: a 6-year analysis of data. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7:473–9.
Ikramuddin S, Kendrick M, Kellogg T, Sarr M. Open and laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: Our techniques. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007;11:217–28.
Bambs C, Cerda J, Escalona A. Morbid obesity in a developing country: the Chilean experience. Bull World Health Organ. 2008;86:813–4.
Azizi F. Bariatric surgery for obesity and diabetes. Arch Iran Med. 2013;16:182–6.
Garcia-Marirrodriga I, Amaya-Romero C, Ruiz-Diaz GP, et al. Evolution of lipid profiles after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2012;22:609–16.
Bueter M, Lowenstein C, Olbers T, et al. Gastric bypass increases energy expenditure in rats. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:1845–53.
Miras AD, Chuah LL, Lascaratos G, et al. Bariatric surgery does not exacerbate and may be beneficial for the microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:e81.
Borg CM, le Roux CW, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, Patel AG, Aylwin SJ. Progressive rise in gut hormone levels after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass suggests gut adaptation and explains altered satiety. Br J Surg. 2006;93:210–5.
Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1577–85.
Dixon AF, Dixon JB, O’Brien PE. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding induces prolonged satiety: a randomized blind crossover study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:813–9.
O’Brien PE, Dixon JB. Lap-band: outcomes and results. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2003;13:265–70.
Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa JJ, et al. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science. 1999;284:1362–5.
Nakatani H, Kasama K, Oshiro T, Watanabe M, Hirose H, Itoh H. Serum bile acid along with plasma incretins and serum high-molecular weight adiponectin levels are increased after bariatric surgery. Metabolism. 2009;58:1400–7.
Pournaras DJ, Glicksman C, Vincent RP, et al. The role of bile after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in promoting weight loss and improving glycaemic control. Endocrinology. 2012;153:3613–9.
Kashyap SR, Bhatt DL, Wolski K, et al. Metabolic effects of bariatric surgery in patients with moderate obesity and type 2 diabetes: analysis of a randomized control trial comparing surgery with intensive medical treatment. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:2175–82.
Promintzer-Schifferl M, Prager G, Anderwald C, et al. Effects of gastric bypass surgery on insulin resistance and insulin secretion in nondiabetic obese patients. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011;19:1420–6.
Benaiges D, Flores-Le-Roux JA, Pedro-Botet J, et al. Impact of restrictive (sleeve gastrectomy) vs hybrid bariatric surgery (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass) on lipid profile. Obes Surg. 2012;22:1268–75.
Asztalos BF, Swarbrick MM, Schaefer EJ, et al. Effects of weight loss, induced by gastric bypass surgery, on HDL remodeling in obese women. J Lipid Res. 2010;51:2405–12.
Hanusch-Enserer U, Zorn G, Wojta J, et al. Non-conventional markers of atherosclerosis before and after gastric banding surgery. Eur Heart J. 2009;30:1516–24.
Lubrano C, Mariani S, Badiali M, et al. Metabolic or bariatric surgery? Long-term effects of malabsorptive vs restrictive bariatric techniques on body composition and cardiometabolic risk factors. Int J Obes. 2010;34:1404–14.
Habib P, Scrocco JD, Terek M, Vanek V, Mikolich JR. Effects of bariatric surgery on inflammatory, functional and structural markers of coronary atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 2009;104:1251–5.
Nguyen NT, Varela E, Sabio A, Tran CL, Stamos M, Wilson SE. Resolution of hyperlipidemia after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;203:24–9.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–72.
Gill RS, Karmali S, Sharma AM. Treating type 2 diabetes mellitus with sleeve gastrectomy in obese patients. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011;19:701–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical considerations
The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee in Research of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Conflicts of interest
SF-s, MM, AT, PR, FR, SH, ED-M, ZSSS, MS, MGM, MTR, AN, SMRP, SA, ST, FF, and MN declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics statement
The study was performed in a manner to conform with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 and 2008, concerning human and animal rights, and the authors followed the policy concerning informed consent as shown in springer.com.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fallahi-shahabad, S., Mazidi, M., Tavasoli, A. et al. Metabolic improvement of morbid obese patients following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery: A prospective study in Mashhad, Iran. Indian J Gastroenterol 35, 195–200 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-016-0661-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-016-0661-0