Abstract
The smoothened sonic hedgehog (Smo-Shh) pathway is one mechanism that influences neurogenesis, including brain cell differentiation and development during childhood. Shh signaling dysregulation leads to decreased target gene transcription, which contributes to increased neuronal excitation, apoptosis, and neurodegeneration, eventually leading to neurological deficits. Neuropsychiatric disorders such as OCD and related neurological dysfunctions are characterized by neurotransmitter imbalance, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and impaired neurogenesis, disturbing the cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical (CSTC) link neuronal network. Despite the availability of several treatments, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, some individuals may not benefit much from them. Several trials on the use of antipsychotics in the treatment of OCD have also produced inadequate findings. This evidence-based review focuses on a potential pharmacological approach to alleviating OCD and associated neuronal deficits by preventing neurochemical alterations, in which sonic hedgehog activators are neuroprotective, lowering neuronal damage while increasing neuronal maintenance and survival. As a result, stimulating SMO-Shh via its potential activators may have neuroprotective effects on neurological impairment associated with OCD. This review investigates the link between SMO-Shh signaling and the neurochemical abnormalities associated with the progression of OCD and associated neurological dysfunctions.
Graphical Abstract
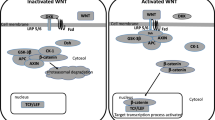
Role of Smo-Shh signaling in serotonergic neurogenesis and in maintaining their neuronal identity. The Shh ligand activates two main transcriptional factors known as Foxa2 and Nkx2.2, which again activates another transcriptional factor, GATA (GATA2 and GATA3), in post mitotic precursor cells of serotonergic neurons—following increased expression of Pet-1 and Lmx1b after GATA regulates the expression of many serotonergic enzymes such as TPH2, SERT, VMAT, slc6a4, Htr1a, Htr1b (Serotonin receptor enzymes), and MAO that regulate and control the release of serotonin and maintain their neuronal identity after their maturation. Abbreviation: Foxa2: Forkhead box; GATA: Globin transcription factor; Lmx1b: LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 beta; TPH2: Tryptophan hydroxylase 2; Htr1a: Serotonin receptor 1a; Htr1b: Serotonin receptor 1b; SERT: Serotonin transporter; VMAT: Vesicular monoamine transporter; MAO: Monoamine oxidase




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ACH:
-
Acetylcholine
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- BAX:
-
Bcl-2-associated X protein
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- CBT:
-
Cognitive behavior therapy
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CSTC:
-
Cortico-striatal-thalamo cortical
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- DAT:
-
Dopamine transporter
- DG:
-
Dentate gyrus
- FOXA2:
-
Forkhead box
- GATA:
-
Globin transcription factor
- GLI:
-
Glioma-associated homolog
- GLIR:
-
Glioma-associated homolog repressor
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- HPCS:
-
Human precursor cells
- ICH:
-
Intracerebral hemorrhage
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1beta
- LMX1B:
-
LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 beta
- MAO:
-
Monoamine oxidase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MHB:
-
Midbrain hindbrain boundary
- mRNA:
-
Messenger ribonucleic acid
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- Ngn2:
-
Neurogenin 2
- NPCs:
-
Neural progenitor cells
- NSCs:
-
Neural stem cells
- OCD:
-
Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- Pitx3:
-
Pituitary homeobox 3
- PTCH1:
-
Patched-1
- PUR:
-
Purmorphamine
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SAG:
-
SHH agonist
- SERT:
-
Serotonin transporter
- SGZ:
-
Subgranular zone
- SHH:
-
Sonic hedgehog
- SMO:
-
Smoothened
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- SSRI:
-
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- SUFU:
-
Suppressor of fused
- SVZ:
-
Subventricular zone
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- VMAT:
-
Vesicular monoamine transporter
References
Abeliovich A, Hammond R (2007) Midbrain dopamine neuron differentiation: factors and fates. Dev Biol 304(2):447–454
Abramyan J (2019) Hedgehog signaling and embryonic craniofacial disorders. J Dev Biol 7(2):9
Agarwala S, Sanders TA, Ragsdale CW (2001) Sonic hedgehog control of size and shape in midbrain pattern formation. Science 291(5511):2147–2150
Al-Ayadhi LY (2012) Relationship between Sonic hedgehog protein, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and oxidative stress in autism spectrum disorders. Neurochem Res 37(2):394–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0624-x
Altaba ARi, Palma V, Dahmane N (2002) Hedgehog-Gli signalling and the growth of the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn704
Aoto K, Trainor PA (2015) Co-ordinated brain and craniofacial development depend upon Patched1/XIAP regulation of cell survival. Hum Mol Genet 24(3):698–713
Arvin KL, Han BH, Du Y, Lin SZ, Paul SM, Holtzman DM (2002) Minocycline markedly protects the neonatal brain against hypoxicischemic injury. Ann Neurol 52:54–61
Atmaca M, Yildirim H, Ozdemir H, Tezcan E, Poyraz AK (2007) Volumetric MRI study of key brain regions implicated in obsessive–compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31(1):46–52
Atmaca N, Atmaca HT, Kanici A, Anteplioglu T (2014) Protective effect of resveratrol on sodium fluoride-induced oxidative stress, hepatotoxicity and neurotoxicity in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 70:191–197
Attwells S, Setiawan E, Wilson AA, Rusjan PM, Mizrahi R, Miler L, Meyer JH (2017) Inflammation in the neurocircuitry of obsessive-compulsive disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 74(8):833–840
Bagheri-Mohammadi S (2021) Adult neurogenesis and the molecular signalling pathways in brain: the role of stem cells in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Int J Neurosci 1–13. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2020.1865953
Bahrami N, Bayat M, Mohamadnia A, Khakbiz M, Yazdankhah M, Ai J, Ebrahimi-Barough S (2017) Purmorphamine as a Shh signaling activator small molecule promotes motor neuron differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on nanofibrous PCL scaffold. Mol Neurobiol 54(7):5668–5675
Beliveau V, Svarer C, Frokjaer VG, Knudsen GM, Greve DN, Fisher PM (2015) Functional connectivity of the dorsal and median raphe nuclei at rest. Neuroimage 116:187–195
Blaess S, Corrales JD, Joyner AL (2006) Sonic hedgehog regulates Gli activator and repressor functions with spatial and temporal precision in the mid/hindbrain region. Development 133(9):1799–1809
Bonsi P, Cuomo D, Martella G, Madeo G, Schirinzi T, Puglisi F, Pisani A (2011) Centrality of striatal cholinergic transmission in basal ganglia function. Front Neuroanat 5:6
Bouldin CM, Gritli-Linde A, Ahn S, Harfe BD (2010) Shh pathway activation is present and required within the vertebrate limb bud apical ectodermal ridge for normal autopod patterning. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(12):5489–5494
Breunig JJ, Sarkisian MR, Arellano JI, Morozov YM, Ayoub AE, Sojitra S, Wang B, Flavell RA, Rakic P, Town T (2008) Primary cilia regulate hippocampal neurogenesis by mediating sonic hedgehog signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(35):13127–13132. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804558105
Briscoe J, Sussel L, Serup P, Hartigan-O’Connor D, Jessell TM, Rubenstein JLR, Ericson J (1999) Homeobox gene Nkx2. 2 and specification of neuronal identity by graded Sonic hedgehog signalling. Nature 398(6728):622–627
Bronstein YL, Cummings J (2001) Neurochemistry of frontal-subcortical circuits. Frontale subcortical circuits in psychiatry and neurological disorders. Guilford Press, New York
Cai W, Ma W, Wang G-t, Li Y-j, Shen W-d (2019) Antidepressant, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects of electroacupuncture through sonic hedgehog–signaling pathway in a rat model of poststroke depression. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 15:1403–1411
Calzà J, Gürsel DA, Schmitz-Koep B, Bremer B, Reinholz L, Berberich G, Koch K (2019) Altered cortico-striatal functional connectivity during resting state in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Front Psychiatry 10:319
Chechneva OV, Mayrhofer F, Daugherty DJ, Krishnamurty RG, Bannerman P, Pleasure DE, Deng W (2014) A Smoothened receptor agonist is neuroprotective and promotes regeneration after ischemic brain injury. Cell Death Dis 5(10):e1481–e2148
Cheng L, Chen CL, Luo P, Tan M, Qiu M, Johnson R, Ma Q (2003) Lmx1b, Pet-1, and Nkx2. 2 coordinately specify serotonergic neurotransmitter phenotype. J Neurosci 23(31):9961–9967
Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, Young KE, Corden JL, Westphal H, Beachy PA (1996) Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature 383(6599):407–413
Cordes SP (2005) Molecular genetics of the early development of hindbrain serotonergic neurons. Clin Genet 68:487–494
Craven SE, Lim KC, Ye W, Engel JD, de Sauvage F, Rosenthal A (2004) Gata2 specifies serotonergic neurons downstream of sonic hedgehog. Development 131(5):1165–1173
Dai RL, Zhu SY, Xia YP, Mao L, Mei YW, Yao YF, Hu B (2011) Sonic hedgehog protects cortical neurons against oxidative stress. Neurochem Res 36(1):67–75
Dantzer R, O’Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008) From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(1):46–56
Dard RF, Dahan L, Rampon C (2019) Targeting hippocampal adult neurogenesis using transcription factors to reduce Alzheimer’s disease-associated memory impairments. Hippocampus 29(7):579–586
Decloedt EH, Stein DJ (2010) Current trends in drug treatment of obsessive–compulsive disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 6:233
De Luca A, Cerrato V, Fucà E, Parmigiani E, Buffo A, Leto K (2015) Sonic hedgehog patterning during cerebellar development. Cell Mol Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2065-1
Delgado-Acevedo C, Estay SF, Radke AK, Sengupta A, Escobar AP, Henríquez-Belmar F, Moya PR (2019) Behavioral and synaptic alterations relevant to obsessive-compulsive disorder in mice with increased EAAT3 expression. Neuropsychopharmacology 44(6):1163–1173
Demarque M, Spitzer NC (2010) Activity-dependent expression of Lmx1b regulates specification of serotonergic neurons modulating swimming behavior. Neuron 67(2):321–334
Deneris ES, Wyler SC (2012) Serotonergic transcriptional networks and potential importance to mental health. Nat Neurosci 15(4):519
Dessaud E, McMahon AP, Briscoe J (2008) Pattern formation in the vertebrate neural tube: a sonic hedgehog morphogen-regulated transcriptional network. Development 135(15):2489–2503
Ding YQ, Marklund U, Yuan W, Yin J, Wegman L, Ericson J, Chen ZF (2003) Lmx1b is essential for the development of serotonergic neurons. Nat Neurosci 6(9):933–938
Dogan B, Ertekin E, Turkdogan FT, Memis CO, Sevincok L (2019) Cortico-thalamo-striatal circuit components’ volumes and their correlations differ significantly among patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder: a case–control MRI study. Psychiatry Clin Psychopharmacol 29(2):162–170
Dold M, Aigner M, Lanzenberger R, Kasper S (2013) Antipsychotic augmentation of serotonin reuptake inhibitors in treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a meta-analysis of double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16(3):557–574
Dolmazon V, Alenina N, Markossian S, Mancip J, van de Vrede Y, Fontaine E et al (2011) Forced expression of LIM homeodomain transcription factor 1b enhances differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into serotonergic neurons. Stem Cells Dev 20:301–311. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2010.0224
Dong XX, Wang Y, Qin ZH (2009) Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30(4):379–387
Dorfman A, Szechtman H, Eilam D (2019) Social interaction modulates the intensity of compulsive checking in a rat model of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Behav Brain Res 359:156–164
Dubourg C, Bendavid C, Pasquier L, Henry C, Odent S, David V (2007) Holoprosencephaly. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2(1):1–14
El-Akabawy G, Rattray I, Johansson SM, Gale R, Bates G, Modo M (2012) Implantation of undiferentiated and pre-diferentiated human neural stem cells in the R6/2 transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. BMC Neurosci 13(1):97
Elia D, Madhala D, Ardon E, Reshef R, Halevy O (2007) Sonic hedgehog promotes proliferation and differentiation of adult muscle cells: Involvement of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Mol Cell Res 1773(9):1438–1446
Ersan S, Bakir S, Ersan EE, Dogan O (2006) Examination of free radical metabolism and antioxidant defence system elements in patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30(6):1039–1042
Escobar AP, Wendland JR, Chávez AE, Moya PR (2019) The neuronal glutamate transporter EAAT3 in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Front Pharmacol 10:1362
Faghih H, Javeri A, Amini H, Taha MF (2019) Directed differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells to dopaminergic neurons in low-serum and serum-free conditions. Neurosci Lett 708:134353
Favaro R, Valotta M, Ferri AL, Latorre E, Mariani J, Giachino C, Nicolis SK (2009) Hippocampal development and neural stem cell maintenance require Sox2-dependent regulation of Shh. Nat Neurosci 12(10):1248–1256
Fernandes-Silva H, Correia-Pinto J, Moura RS (2017) Canonical sonic hedgehog signaling in early lung development. J Dev Biol 5(1):3
Fish EW, Parnell SE, Sulik KK, Baker LK, Murdaugh LB, Lamson D, Williams KP (2017) Preaxial polydactyly following early gestational exposure to the smoothened agonist, SAG, in C57BL/6J mice. Birth Defects Res 109(1):49–54
Fogel JL, Chiang C, Huang X, Agarwala S (2008) Ventral specification and perturbed boundary formation in the mouse midbrain in the absence of Hedgehog signaling. Dev Dyn Off Publ Am Assoc Anat 237(5):1359–1372
Fuccillo M, Rallu M, McMahon AP, Fishell G (2004) Temporal requirement for hedgehog signaling in ventral telencephalic patterning. Development 131(20):5031–5040
Fyodorov D, Nelson T, Deneris E (1998) Pet-1, a novel ETS domain factor that can activate neuronal nAchR gene transcription. J Neurobiol 34(2):151–163
Gandy K, Kim S, Sharp C, Dindo L, Maletic-Savatic M, Calarge C (2017) Pattern separation: a potential marker of impaired hippocampal adult neurogenesis in major depressive disorder. Front Neurosci 11:571
Gao H, Dou L, Shan L, Sun Y, Li W (2018) Proliferation and committed differentiation into dopamine neurons of neural stem cells induced by the active ingredients of radix astragali. NeuroReport 29(7):577
Gao J, Zhou Y, Yang X, Luo J, Meng F, Zheng D, Li Z (2019) Abnormalities within and beyond the cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuitry in medication-free patients with OCD revealed by the fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations and resting-state functional connectivity. Neurosci lett 712:134449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134449
Ghanizadeh A (2012) Malondialdehyde, Bcl-2, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase may mediate the association of sonic hedgehog protein and oxidative stress in autism. Neurochem Res 37(4):899–901
Gong Q, Chen H, Farbman AI (2009) Olfactory sensory axon growth and branching is influenced by sonic hedgehog. Dev Dyn Off Publ Am Assoc Anat 238(7):1768–1776
Gonzalez-Reyes LE, Chiang CC, Zhang M, Johnson J, Arrillaga-Tamez M, Couturier NH, Durand DM (2019) Sonic Hedgehog is expressed by hilar mossy cells and regulates cellular survival and neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Sci Rep 9(1):1–20
Gonzalez-Reyes LE, Verbitsky M, Blesa J, Jackson-Lewis V, Paredes D, Tillack K, Kottmann AH (2012) Sonic hedgehog maintains cellular and neurochemical homeostasis in the adult nigrostriatal circuit. Neuron 75(2):306–319
Gu D, Wang S, Zhang S, Zhang P, Zhou G (2017) Directed transdifferentiation of Müller glial cells to photoreceptors using the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway agonist purmorphamine. Mol Med Rep 16(6):7993–8002. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7652
Güldenpfennig M, Wolmarans DW, Du Preez JL, Stein DJ, Harvey BH (2011) Cortico-striatal oxidative status, dopamine turnover and relation with stereotypy in the deer mouse. Physiol Behav 103(3–4):404–411
Gupta Ria et al (2022) Smo-Shh agonist purmorphamine prevents neurobehavioral and neurochemical defects in 8-OH-DPAT-induced experimental model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Brain Sci 12(3):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12030342
Haldipur P, Govindan S, Bharti U, Sarkar C, Iyengar S, Gressens P, Mani S (2012) Expression of sonic hedgehog during cell proliferation in the human cerebellum. Int J Dev Neurosci 30(8):652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2012.03.264
Hamasaki T, Goto S, Nishikawa S, Ushio Y (2003) Neuronal cell migration for the developmental formation of the mammalian striatum. Brain Res Rev 41(1):1–12
Hammond R, Blaess S, Abeliovich A (2009) Sonic hedgehog is a chemoattractant for midbrain dopaminergic axons. PLoS ONE 4(9):e7007
Han Y-G, Spassky N, Romaguera-Ros M, Garcia-Verdugo J-M, Aguilar A, Schneider-Maunoury S, Alvarez-Buylla A (2008) Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia are required for the formation of adult neural stem cells 11(3):277–284
Haroon E, Raison CL, Miller AH (2012) Psychoneuroimmunology meets neuropsychopharmacology: translational implications of the impact of inflammation on behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 37(1):137–162
Harwell CC, Parker PR, Gee SM, Okada A, McConnell SK, Kreitzer AC, Kriegstein AR (2012) Sonic hedgehog expression in corticofugal projection neurons directs cortical microcircuit formation. Neuron 73(6):1116–1126
Hassan W, Eduardo Barroso Silva C, Mohammadzai IU, Batista Teixeira da Rocha J, Landeira-Fernandez J (2014) Association of oxidative stress to the genesis of anxiety: implications for possible therapeutic interventions. Curr Neuropharmacol 12(2):120–139
Hatalova H, Radostova D, Pistikova A, Vales K, Stuchlik A (2017) Detrimental effect of clomipramine on hippocampus-dependent learning in an animal model of obsessive-compulsive disorder induced by sensitization with d2/d3 agonist quinpirole. Behav Brain Res 317:210–217
Hendricks T, Francis N, Fyodorov D, Deneris ES (1999) The ETS domain factor Pet-1 is an early and precise marker of central serotonin neurons and interacts with a conserved element in serotonergic genes. J Neurosci 19(23):10348–10356
Hendricks TJ, Fyodorov DV, Wegman LJ, Lelutiu NB, Pehek EA, Yamamoto B, Deneris ES (2003) Pet-1 ETS gene plays a critical role in 5-HT neuron development and is required for normal anxiety-like and aggressive behavior. Neuron 37(2):233–247
Herdi O, Sayar-Akaslan D, İlhan RS, Çolak B, Duman B (2020) Associations between subclinical inflammatory markers and OCD: a retrospective study. Psychiatry Res 290:113065
Hill AS, Sahay A, Hen R (2015) Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to reduce anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 40(10):2368–2378
Hill SA, Blaeser AS, Coley AA, Xie Y, Shepard KA, Harwell CC, Garcia ADR (2019) Sonic hedgehog signaling in astrocytes mediates cell type-specific synaptic organization. Elife 8:e45545
Hong SB, Shin YW, Kim SH, Yoo SY, Lee JM, Kim IY, Kwon JS (2007) Hippocampal shape deformity analysis in obsessive–compulsive disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 257(4):185–190
Hu Q, Li T, Wang L, Xie Y, Liu S, Bai X, Wang Z (2017) Neuroprotective effects of a smoothened receptor agonist against early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Front Cell Neurosci 10:306
Huang S-S, Cheng H, Tang C-M, Nien M-W, Huang Y-S, Lee I-H, Yin J-H, Kuo TBJ, Yang Cheryl CH, Tsai S-K, Yang D-I (2013) Anti-oxidative, anti-apoptotic, and pro-angiogenic effects mediate functional improvement by sonic hedgehog against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp Neurol 247:680–688
Hynes M, Porter JA, Chiang C, Chang D, Tessier-Lavigne M, Beachy PA, Rosenthal A (1995) Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons by Sonic hedgehog. Neuron 15(1):35–44
Ida T, Hara M, Nakamura Y, Kozaki S, Tsunoda S, Ihara H (2008) Cytokine-induced enhancement of calcium-dependent glutamate release from astrocytes mediated by nitric oxide. Neurosci Lett 432(3):232–236
Ingham PW, McMahon AP (2001) Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev 15(23):3059–3087
Jacobs BL, Tanapat P, Reeves AJ, Gould E (1998) Serotonin stimulates the production of new hippocampal granule neurons via the 5HT1A receptor in the adult rat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 24(6):1992
Janikova M, Brozka H, Radostova D, Svoboda J, Stuchlik A (2019) No effect of riluzole and memantine on learning deficit following quinpirole sensitization-An animal model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Physiol Behav 204:241–247
Jeong J, Mao J, Tenzen T, Kottmann AH, McMahon AP (2004) Hedgehog signaling in the neural crest cells regulates the patterning and growth of facial primordia. Genes Dev 18(8):937–951
Ji H, Miao J, Zhang X, Du Y, Liu H, Li S, Li L (2012) Inhibition of sonic hedgehog signaling aggravates brain damage associated with the down-regulation of Gli1, Ptch1 and SOD1 expression in acute ischemic stroke. Neurosci Lett 506(1):1–6
Jia YF, Wininger K, Peyton L, Ho AMC, Choi DS (2021) Astrocytic glutamate transporter 1 (GLT1) deficient mice exhibit repetitive behaviors. Behav Brain Res 396:112906
Jiménez-Moreno N, Stathakos P, Antón Z, Shoemark DK, Sessions RB, Witzgall R, Caldwell M, Lane JD (2019) LIR-dependent LMX1A/LMX1B autophagy crosstalk shapes human midbrain dopaminergic neuronal resilience.bbioRxiv 636712. https://doi.org/10.1101/636712
Jin F, Wu Q, Lu YF, Gong QH, Shi JS (2008) Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol on 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 600(1–3):78–82
Jin Y, Barnett A, Zhang Y, Yu X, Luo Y (2017) Poststroke sonic hedgehog agonist treatment improves functional recovery by enhancing neurogenesis and angiogenesis. Stroke 48(6):1636–1645
Jung WH, Kang DH, Kim E, Shin KS, Jang JH, Kwon JS (2013) Abnormal corticostriatal-limbic functional connectivity in obsessive–compulsive disorder during reward processing and resting-state. NeuroImage Clin 3:27–38
Kandemir H, Abuhandan M, Aksoy N, Savik E, Kaya C (2013) Oxidative imbalance in child and adolescent patients with obsessive compulsive disorder. J Psychiatr Res 47(11):1831–1834
Kar SK, Choudhury I (2016) An empirical review on oxidative stress markers and their relevance in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int J Nutr Pharmacol Neurol Dis 6(4):139
Karagüzel EÖ, Arslan FC, Uysal EK, Demir S, Aykut DS, Tat M, Karahan SC (2019) Blood levels of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha and cognitive functions in patients with obsessive compulsive disorder. Compr Psychiatry 89:61–66
Karthik S, Sharma LP, Narayanaswamy JC (2020) Investigating the role of glutamate in obsessive-compulsive disorder: Current perspectives. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 16:1003
Ke Z, Caiping S, Qing Z, Xiaojing W (2015) Sonic hedgehog–Gli1 signals promote epithelial–mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer by mediating PI3K/AKT pathway. Med Oncol 32(1):368
Kempermann G, Song H, Gage FH (2015) Neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7(9):a018812
Kim JY, Koh HC, Lee JY, Chang MY, Kim YC, Chung HY, Lee SH (2003) Dopaminergic neuronal differentiation from rat embryonic neural precursors by Nurr1 overexpression. J Neurochem 85(6):1443–1454
Kirillova I, Novikova I, Auge J, Audollent S, Esnault D, Encha-Razavi F, Lazjuk G, Attie-Bitach T, Vekemans M (2000) Expression of the Sonic hedgehog gene in human embryos with neural tube defects. Teratology 61:347–354
Konuk N, Tekin IO, Ozturk U, Atik L, Atasoy N, Bektas S, Erdogan A (2007) Plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in obsessive compulsive disorder. Mediators Inflamm 2007:65704. https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/65704
Koo MS, Kim EJ, Roh D, Kim CH (2010) Role of dopamine in the pathophysiology and treatment of obsessive–compulsive disorder. Expert Rev Neurother 10(2):275–290
Korff S, Stein DJ, Harvey BH (2008) Stereotypic behaviour in the deer mouse: pharmacological validation and relevance for obsessive compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32(2):348–355
Korff S, Stein DJ, Harvey BH (2009) Cortico-striatal cyclic AMP-phosphodiesterase-4 signalling and stereotypy in the deer mouse: attenuation after chronic fluoxetine treatment. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92(3):514–520
Krabbe G, Minami SS, Etchegaray JI, Taneja P, Djukic B, Davalos D, Gan L (2017) Microglial NFκB-TNFα hyperactivation induces obsessive–compulsive behavior in mouse models of progranulin-deficient frontotemporal dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(19):5029–5034
Krueger KC, Deneris ES (2008) Serotonergic transcription of human FEV reveals direct GATA factor interactions and fate of Pet1-deficient serotonin neuron precursors. J Neurosci 28:12748–12758. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4349-08.2008
Kuo HY, Liu FC (2019) Synaptic wiring of corticostriatal circuits in Basal Ganglia: Insights into the Pathogenesis of Neuropsychiatric Disorders. eNeuro 6(3):ENEURO.0076-19.2019. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0076-19.2019
Lai K, Kaspar BK, Gage FH, Schaffer DV (2003) Sonic hedgehog regulates adult neural progenitor proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Nat Neurosci 6(1):21–27
Lee S, Kim Y, Li E, Park S (2012) Ghrelin protects spinal cord motoneurons against chronic glutamate excitotoxicity by inhibiting microglial activation. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Off J Korean Neurochem Soc Korean Soc Pharmacol 16(1):43
Lewis PM, Gritli-Linde A, Smeyne R, Kottmann A, McMahon AP (2004) Sonic hedgehog signaling is required for expansion of granule neuron precursors and patterning of the mouse cerebellum. Dev Biol 270(2):393–410
Li G, Fang Li, Fernández G, Pleasure SJ (2013a) The ventral hippocampus is the embryonic origin for adult neural stem cells in the Dentate Gyrus. Neuron 78(4):658–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.03.019
Li T, Zhang J, Liu R-Y, Lian Z-G, Chen X-L, Ma L, Sun H-M, Zhao Y-L (2013b) The role of the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Neurosci Lett 552:81–86
Li PJ, Guo YQ, Ding PY, Liu RB, Deng F, Feng XX, Yan WJ (2019) Neuroprotective effects of a Smoothened receptor agonist against postoperative cognitive dysfunction by promoting autophagy in the dentate gyrus of aged rats. Neurol Res 41(10):867–874. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2019.1628411
Lissemore JI, Sookman D, Gravel P, Berney A, Barsoum A, Diksic M, Benkelfat C (2018) Brain serotonin synthesis capacity in obsessive-compulsive disorder: effects of cognitive behavioral therapy and sertraline. Transl Psychiatry 8(1):1–10
Liu D, Bai X, Ma W, Xin D, Chu X, Yuan H, Wang Z (2020a) Purmorphamine attenuates neuro-inflammation and synaptic impairments after hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal mice via Shh signaling. Front Pharmacol 11:204
Liu D, Bai X, Ma W, Xin D, Chu X, Yuan H, Qiu J, Ke H, Yin S, Chen W, Wang Z (2020b) Purmorphamine Attenuates Neuro-Inflammation and Synaptic Impairments After Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury in Neonatal Mice via Shh Signaling. Front Pharmacol 11:204. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00204
Luhmann HJ, Fukuda A, Kilb W (2015) Control of cortical neuronal migration by glutamate and GABA. Front Cell Neurosci 9:4
Lui H, Zhang J, Makinson SR, Cahill MK, Kelley KW, Huang HY, Huang EJ (2016) Progranulin deficiency promotes circuit-specific synaptic pruning by microglia via complement activation. Cell 165(4):921–935
Lull ME, Block ML (2010) Microglial activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics 7(4):354–365
Luo Y (2012) The function and mechanisms of Nurr1 action in midbrain dopaminergic neurons, from development and maintenance to survival. Int Rev Neurobiol 102:1–22
Machold R, Hayashi S, Rutlin M, Muzumdar MD, Nery S, Corbin JG, Fishell G (2003) Sonic hedgehog is required for progenitor cell maintenance in telencephalic stem cell niches. Neuron 39(6):937–950
Mahar I, Bambico FR, Mechawar N, Nobrega JN (2014) Stress, serotonin, and hippocampal neurogenesis in relation to depression and antidepressant effects. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 38:173–192
Mallard C, Tremblay M-E, Vexler ZS (2018) Microglia and neonatal brain injury. Neuroscience S0306452218300393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.01.023
Matise MP, Epstein DJ, Park HL, Platt KA, Joyner AL (1998) Gli2 is required for induction of floor plate and adjacent cells, but not most ventral neurons in the mouse central nervous system. Development (Cambridge, England) 125(15):2759–2770. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.125.15.2759
Meng QH, Liu HB, Wang JB (2016) Polydatin ameliorates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by decreasing apoptosis and oxidative stress through activating sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 96:215–225
Miyazaki K, Narita N, Narita M (2005) Maternal administration of thalidomide or valproic acid causes abnormal serotonergic neurons in the offspring: implication for pathogenesis of autism. Int J Dev Neurosci 23(2–3):287–297
Monday HR, Younts TJ, Castillo PE (2018) Long-term plasticity of neurotransmitter release: emerging mechanisms and contributions to brain function and disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 41:299–322
Moss J, Bolam JP (2008) A dopaminergic axon lattice in the striatum and its relationship with cortical and thalamic terminals. J Neurosci 28(44):11221–11230
Muñoz A, Lopez-Lopez A, Labandeira CM, Labandeira-Garcia JL (2020) Interactions between the serotonergic and other neurotransmitter systems in the Basal Ganglia: Role in Parkinson’s Disease and Adverse Effects of L-DOPA. Front Neuroanat 14:26. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2020.00026
Muscatello MRA, Bruno A, Pandolfo G, Micò U, Scimeca G, Romeo VM, Zoccali RA (2011) Effect of aripiprazole augmentation of serotonin reuptake inhibitors or clomipramine in treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 31(2):174–179
Nazeer A, Latif F, Mondal A, Azeem MW, Greydanus DE (2020) Obsessive-compulsive disorder in children and adolescents: epidemiology, diagnosis and management. Transl Pediatr 9(Suppl 1):S76
Nestadt G, Grados M, Samuels JF (2010) Genetics of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am 33(1):141–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psc.2009.11.001
Nguyen V, Sabeur K, Maltepe E, Ameri K, Bayraktar O, Rowitch DH (2018) Sonic hedgehog agonist protects against complex neonatal cerebellar injury. Cerebellum 17(2):213–227
Nie B, Nie T (2010) Clinical study on electroacupuncture treatment for post-stroke depression. J Acupunct Tuina Sci 8(6):336–339
O’Neill J, Piacentini J, Chang S, Ly R, Lai TM, Armstrong CC, Nurmi EL (2017) Glutamate in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder and response to cognitive-behavioral therapy: randomized clinical trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 42(12):2414–2422
Özyurt G, Binici NC (2019) The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in adolescent obsessive-compulsive disorder: Does comorbid anxiety disorder affect inflammatory response? Psychiatry Res 272:311–315
Palma V, Lim DA, Dahmane N, Sánchez P, Brionne TC, Herzberg CD, i Altaba AR (2005) Sonic hedgehog controls stem cell behavior in the postnatal and adult brain. Development 132(2):335–344
Parent A, Hazrati LN (1995) Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. I. The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Brain Res Rev 20(1):91–127
Pascual O, Ben Achour S, Rostaing P, Triller A, Bessis A (2012) Microglia activation triggers astrocyte-mediated modulation of excitatory neurotransmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(4):E197–E205
Pauls DL, Abramovitch A, Rauch SL, Geller DA (2014) Obsessive–compulsive disorder: an integrative genetic and neurobiological perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci 15(6):410–424
Peng L, Yin J, Ge M, Wang S, Xie L, Li Y, Ma K (2019) Isoflurane post-conditioning ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by enhancing angiogenesis through activating the Shh/Gli signaling pathway in rats. Front Neurosci 13:321
Pereira J, Johnson Warren E, O’Brien SJ, Jarvis ED, Zhang G, Gilbert MTP, Vasconcelos V, Antunes A, Escriva H (2014) Evolutionary genomics and adaptive evolution of the Hedgehog gene family (Shh, Ihh and Dhh) in vertebrates. PLoS ONE 9(12):e74132
Peterson R, Turnbull J (2012) Sonic hedgehog is cytoprotective against oxidative challenge in a cellular model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci 47:31–41
Petralia RS, Wang YX, Mattson MP, Yao PJ (2011a) Sonic hedgehog distribution within mature hippocampal neurons. Commun Integr Biol 4(6):775–777
Petralia RS, Schwartz CM, Wang YX, Mattson MP, Yao PJ (2011b) Subcellular localization of Patched and Smoothened, the receptors for Sonic hedgehog signaling, in the hippocampal neuron. J Comp Neurol 519(18):3684–3699
Pietrelli A, Matković L, Vacotto M, Lopez-Costa JJ, Basso N, Brusco A (2018) Aerobic exercise upregulates the BDNF-Serotonin systems and improves the cognitive function in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 155:528–542
Pittenger C, Bloch MH, Williams K (2011) Glutamate abnormalities in obsessive compulsive disorder: neurobiology, pathophysiology, and treatment. Pharmacol Ther 132(3):314–332
Pittenger C, Bloch MH, Wasylink S, Billingslea E, Simpson R, Jakubovski E et al (2015) Riluzole augmentation in treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: a pilot randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry 76:1075–1084. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.14m09123
Placzek M, Briscoe J (2018) Sonic hedgehog in vertebrate neural tube development. Int J Devel Biol 62(1-2–3):225–234
Poulin JF, Gaertner Z, Moreno-Ramos OA, Awatramani R (2020) Classification of midbrain dopamine neurons using single-cell gene expression profiling approaches. Trends Neurosci 43(3):155–169
Qin S, Sun D, Zhang C, Tang Y, Zhou F, Zheng K, Tang R, Zheng Y (2019) Downregulation of sonic hedgehog signaling in the hippocampus leads to neuronal apoptosis in high-fat diet-fed mice. Behav Brain Res 367:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.03.055
Rahi S, Mehan S (2022) Understanding abnormal SMO-SHH signaling in autism spectrum disorder: potential drug target and therapeutic goals. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42(4):931–953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-01010-1
Rahi S, Gupta R, Sharma A, Mehan S (2021) Smo-Shh signaling activator purmorphamine ameliorates neurobehavioral, molecular, and morphological alterations in an intracerebroventricular propionic acid-induced experimental model of autism. Hum Exp Toxicol 40(11):1880–1898. https://doi.org/10.1177/09603271211013456
Rao NP, Venkatasubramanian G, Ravi V, Kalmady S, Cherian A, Yc JR (2015) Plasma cytokine abnormalities in drug-naïve, comorbidity-free obsessive–compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res 229(3):949–952
Rivell A, Petralia RS, Wang Y-X, Clawson E, Moehl K, Mattson MP, Yao PJ (2019) Sonic hedgehog expression in the postnatal brain. Biol Open bio.040592. https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.040592
Roussa E, Farkas LM, Krieglstein K (2004) TGF-β promotes survival on mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons in cooperation with Shh and FGF-8. Neurobiol Dis 16(2):300–310
Ruzzano L, Borsboom D, Geurts HM (2015) Repetitive behaviors in autism and obsessive–compulsive disorder: New perspectives from a network analysis. J Autism Dev Disord 45(1):192–202
Sagai T, Amano T, Maeno A, Ajima R, Shiroishi T (2019) SHH signaling mediated by a prechordal and brain enhancer controls forebrain organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(47):23636–23642. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1901732116
Santore LA, Gerber A, Gioia AN, Bianchi R, Talledo F, Peris TS, Lerner MD (2020) Felt but not seen: Observed restricted repetitive behaviors are associated with self-report—but not parent-report—obsessive-compulsive disorder symptoms in youth with autism spectrum disorder. Autism 24(4):983–994
Saxena S, Rauch SL (2000) Functional neuroimaging and the neuroanatomy of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am 23(3):563–586
Shao S, Wang G-L, Raymond C, Deng X-H, Zhu X-L, Wang D, Hong L-P (2017) Activation of Sonic hedgehog signal by Purmorphamine, in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, protects dopaminergic neurons and attenuates inflammatory response by mediating PI3K/AKt signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 16(2):1269–1277
Shehabeldin R, Lutz D, Karsak M, Frotscher M, Krieglstein K, Sharaf A (2019) Correction: Reelin controls the positioning of brainstem serotonergic raphe neurons. PLoS ONE 14(1):e0211849
Shin JO, Song J, Choi HS, Lee J, Lee K, Ko HW, Bok J (2019) Activation of sonic hedgehog signaling by a Smoothened agonist restores congenital defects in mouse models of endocrine-cerebro-osteodysplasia syndrome. EBioMedicine 49:305–317
Shitasako S, Ito Y, Ito R, Ueda Y, Shimizu Y, Ohshima T (2017) Wnt and Shh signals regulate neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation in the optic tectum of adult zebrafish. Dev Neurobiol 77(10):1206–1220
Shrivastava A, Kar SK, Sharma E, Mahdi AA, Dalal PK (2017) A study of oxidative stress biomarkers in obsessive compulsive disorder. J Obsessive Compuls Relat Disord 15:52–56
Silberberg G, Bolam JP (2015) Local and afferent synaptic pathways in the striatal microcircuitry. Curr Opin Neurobiol 33:182–187
Silveri MM, Sneider JT, Crowley DJ, Covell MJ, Acharya D, Rosso IM, Jensen JE (2013) Frontal Lobe γ-Aminobutyric acid levels during adolescence: Associations with impulsivity and response inhibition. Biol Psychiat 74(4):296–304
Şimşek Ş, Gençoğlan S, Yüksel T (2016) DNA damage and antioxidants in treatment naïve children with obsessive–compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res 237:133–137
Sivanandam TM, Thakur MK (2012) Traumatic brain injury: a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(5):1376–1381
Song L, Liu Y, Yu Y, Duan X, Qi S, Liu Y (2012) Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons by multidirectional repulsion. Cell Res 22(4):697–716
Song NN, Huang Y, Yu X, Lang B, Ding YQ, Zhang L (2017) Divergent roles of central serotonin in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci 11:185
Sousa VH, Fishell G (2010) Sonic hedgehog functions through dynamic changes in temporal competence in the developing forebrain. Curr Opin Genet Dev 20(4):391–399
Sreenivasmurthy SG, Liu JY, Song JX, Yang CB, Malampati S, Wang ZY, Li M (2017) Neurogenic traditional Chinese medicine as a promising strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 18(2):272
Stracke J, Otten W, Tuchscherer A, Puppe B, Düpjan S (2017) Serotonin depletion induces pessimistic-like behavior in a cognitive bias paradigm in pigs. Physiol Behav 174:18–26
Sullivan GM, Armstrong RC (2017) Transplanted adult neural stem cells express sonic hedgehog in vivo and suppress white matter neuroinflammation after experimental traumatic brain injury. Stem cells Int 2017:9342534. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9342534
Surmeier DJ, Carrillo-Reid L, Bargas J (2011) Dopaminergic modulation of striatal neurons, circuits, and assemblies. Neuroscience 198:3–18
Suzuki M, Nelson AD, Eickstaedt JB, Wallace K, Wright LS, Svendsen CN (2006) Glutamate enhances proliferation and neurogenesis in human neural progenitor cell cultures derived from the fetal cortex. Eur J Neurosci 24(3):645–653
Swistowska AM, da Cruz AB, Han Y, Swistowski A, Liu Y, Shin S, Zhan M, Rao MS, Zeng X (2010) Stage-specific role for Shh in dopaminergic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells induced by stromal cells. Stem Cells Dev 19(1):71–82
Tan IL, Wojcinski A, Rallapalli H, Lao Z, Sanghrajka RM, Stephen D, Joyner AL (2018) Lateral cerebellum is preferentially sensitive to high sonic hedgehog signaling and medulloblastoma formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115(13):3392–3397
Tang M, Luo SX, Tang V, Huang EJ (2013) Temporal and spatial requirements of Smoothened in ventral midbrain neuronal development. Neural Dev 8(1):1–17
Tayyab M, Farheen S, Khanam N, Hossain MM, Shahi MH (2019) Antidepressant and neuroprotective effects of naringenin via sonic hedgehog-GLI1 cell signaling pathway in a rat model of chronic unpredictable mild stress. NeuroMol Med 21(3):250–261
Teraoka H, Russell C, Regan J, Chandrasekhar A, Concha ML, Yokoyama R,... Wilson SW, (2004) Hedgehog and Fgf signaling pathways regulate the development of tphR-expressing serotonergic raphe neurons in zebrafish embryos. J Neurobiol 60(3):275–288
Threlfell S, Clements MA, Khodai T, Pienaar IS, Exley R, Wess J, Cragg SJ (2010) Striatal muscarinic receptors promote activity dependence of dopamine transmission via distinct receptor subtypes on cholinergic interneurons in ventral versus dorsal striatum. J Neurosci 30(9):3398–3408
Tichy J, Zinke J, Bunz B, Meyermann R, Harter PN, Mittelbronn M (2015) Expression profile of sonic hedgehog pathway members in the developing human fetal brain. BioMed Res Int 2015:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/494269
Trazzi S, Fuchs C, Valli E, Perini G, Bartesaghi R, Ciani E (2013) The amyloid precursor protein (APP) triplicated gene impairs neuronal precursor differentiation and neurite development through two different domains in the Ts65Dn mouse model for Down syndrome. J Biol Chem 288(29):20817–20829. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.451088 (Retraction published J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 6;295(10):3392)
Umathe SN, Vaghasiya JM, Jain NS, Dixit PV (2009) Neurosteroids modulate compulsive and persistent behavior in rodents: Implications for obsessive–compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33(7):1161–1166
Vicario N, Bernstock JD, Spitale FM, Giallongo C, Giunta MAS, Li Volti G, Gulisano M, Leanza G, Tibullo D, Parenti R, Gulino R (2019) Clobetasol modulates adult neural stem cell growth via canonical hedgehog pathway activation. Int J Mol Sci 20(8):1991
Volpicelli F, Perrone-Capano C, Bellenchi GC, Colucci-D’Amato L, di Porzio U (2020) Molecular regulation in dopaminergic neuron development. Cues to unveil molecular pathogenesis and pharmacological targets of neurodegeneration. Int J Mol Sci 21(11):3995
Wada T, Honda M, Minami I, Tooi N, Amagai Y, Nakatsuji N, Aiba K (2009) Highly efficient differentiation and enrichment of spinal motor neurons derived from human and monkey embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 4(8):e6722
Wang X, Fan G, Wei F, Bu Y, Huang W (2019) Hyperoside protects rat ovarian granulosa cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury by sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact 310:108759
Wang Y, Li M, Xu X, Song M, Tao H, Bai Y (2012) Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) promotes neural progenitor cell proliferation and sonic hedgehog pathway activation during adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Mol Nutr Food Res 56(8):1292–1303. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201200035
Welch JM, Lu J, Rodriguiz RM, Trotta NC, Peca J, Ding JD, Feng G (2007) Cortico-striatal synaptic defects and OCD-like behaviours in Sapap3-mutant mice. Nature 448(7156):894–900
Welter ML, Burbaud P, Fernandez-Vidal S, Bardinet E, Coste J, Piallat B, Mallet L (2011) Basal ganglia dysfunction in OCD: subthalamic neuronal activity correlates with symptoms severity and predicts high-frequency stimulation efficacy. Transl Psychiatry 1(5):e5–e5
Wu SM, Tan KS, Chen H, Beh TT, Yeo HC, Ng SKL, Chan KKK (2012) Enhanced production of neuroprogenitors, dopaminergic neurons, and identification of target genes by overexpression of sonic hedgehog in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 21(5):729–741
Wu J, He J, Tian X, Zhong J, Li H, Sun X (2020) Activation of the hedgehog pathway promotes recovery of neurological function after traumatic brain injury by protecting the neurovascular unit. Transl Stroke Res 11(4):720–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-019-00771-2
Xia YP, Dai RL, Li YN, Mao L, Xue YM, He QW, Hu B (2012) The protective effect of sonic hedgehog is mediated by the propidium iodide 3-kinase/AKT/Bcl-2 pathway in cultured rat astrocytes under oxidative stress. Neuroscience 209:1–11
Xing G, Zhao T, Zhang X, Li H, Li X, Cui P, Li M, Li D, Zhang N, Jiang W (2020) Astrocytic sonic hedgehog alleviates intracerebral hemorrhagic brain injury via modulation of blood-brain barrier integrity. Front Cell Neurosci 14:575690. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.575690
Xu Q, Guo L, Moore H, Waclaw RR, Campbell K, Anderson SA (2010) Sonic hedgehog signaling confers ventral telencephalic progenitors with distinct cortical interneuron fates. Neuron 65(3):328–340
Yang Y, Calakos N (2013) Presynaptic long-term plasticity. Front Synaptic Neurosci 5:8
Yang H, Zhu Q, Cheng J, Wu Y, Fan M, Zhang J, Wu H (2019) Opposite regulation of Wnt/β-catenin and Shh signaling pathways by Rack1 controls mammalian cerebellar development. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(10):4661–4670
Yao PJ, Petralia RS, Ott C, Wang YX, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Mattson MP (2015) Dendrosomatic sonic hedgehog signaling in hippocampal neurons regulates axon elongation. J Neurosci 35(49):16126–16141
Yin S, Bai X, Xin D, Li T, Chu X, Ke H, Han M, Chen W, Li X, Wang Z (2020) Neuroprotective effects of the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in ischemic injury through promotion of synaptic and neuronal health. Neural Plast 2020:8815195. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8815195
Zhang XY, Yao JK (2013) Oxidative stress and therapeutic implications in psychiatric disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 46:197–199
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Cui L, Chen R, Zhang C, Li Y, He T, Zhu X, Shen Z, Dong L, Zhao J, Wen Y, Zheng X, Li P (2017) Salvianolic Acids for Injection (SAFI) promotes functional recovery and neurogenesis via sonic hedgehog pathway after stroke in mice. Neurochem Int 110:38–48
Zhang J, Zhang ZG, Li Y, Ding X, Shang X, Lu M, Chopp M (2015) Fingolimod treatment promotes proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurobiol Dis 76:57–66
Zhou FC, Sari Y, Zhang JK, Goodlett CR, Li TK (2001) Prenatal alcohol exposure retards the migration and development of serotonin neurons in fetal C57BL mice. Dev Brain Res 126(2):147–155
Zhu Y, Fan Q, Han X, Zhang H, Chen J, Wang Z, Li Y (2015) Decreased thalamic glutamate level in unmedicated adult obsessive–compulsive disorder patients detected by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Affect Dis 178:193
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Chairman, Mr. Parveen Garg, and Director, Dr. G. D. Gupta, ISF College of Pharmacy, Moga (Punjab), India, for their great vision and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The investigation, writing (original draft), writing (review), Ria Gupta (A.P.); formal analysis, re-review, re-editing, Swesha Chhabra (S.C), Aditi Giri (A.G.), Kajal Sherawat (K.J); conceptualization, resources, supervision, writing (review and editing), Sidharth Mehan (S.M.). All data were generated in-house, and no paper mill was used. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of this work, ensuring integrity and accuracy. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, R., Mehan, S., Chhabra, S. et al. Role of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Activation in the Prevention of Neurological Abnormalities Associated with Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder. Neurotox Res 40, 1718–1738 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00586-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00586-4