Abstract
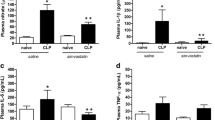
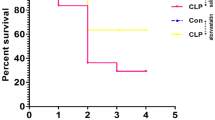
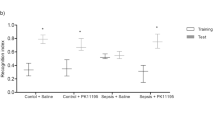
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy causes brain dysfunction that can result in cognitive impairments in sepsis survivor patients. In previous work, we showed that simvastatin attenuated oxidative stress in brain structures related to memory in septic rats. However, there is still a need to evaluate the long-term impact of simvastatin administration on brain neurodegenerative processes and cognitive damage in sepsis survivors. Here, we investigated the possible neuroprotective role of simvastatin in neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration conditions of brain structures related to memory in rats at 10 days after sepsis survival. Male Wistar rats (250–300 g) were submitted to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP, n = 42) or remained as non-manipulated (naïve, n = 30). Both groups were treated (before and after the surgery) by gavage with simvastatin (20 mg/kg) or an equivalent volume of saline and observed for 10 days. Simvastatin-treated rats that survived to sepsis showed a reduction in the levels of nitrate, IL1-β, and IL-6 and an increase in Bcl-2 protein expression in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, and synaptophysin only in the hippocampus. Immunofluorescence revealed a reduction of glial activation, neurodegeneration, apoptosis, and amyloid aggregates confirmed by quantification of GFAP, Iba-1, phospho Ser396-tau, total tau, cleaved caspase-3, and thioflavin-S in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. In addition, treated animals presented better performance in tasks involving habituation memory, discriminative, and aversive memory. These results suggest that statins exert a neuroprotective role by upregulation of the Bcl-2 and gliosis reduction, which may prevent the cognitive deficit observed in sepsis survivor animals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam N, Kandelman S, Mantz J, Chrétien F, Sharshar T (2013) Sepsis-induced brain dysfunction. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 11(2):211–221. https://doi.org/10.1586/eri.12.159
Ahn KS, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB (2007) Simvastatin potentiates TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis through the down-regulation of NF-kappaB-dependent antiapoptotic gene products: role of IkappaBalpha kinase and TGF-beta-activated kinase-1. J Immunol 178(4):2507–2516. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.178.4.2507
Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer P, O’Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, van Muiswinkel F, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 21(3):383–421
Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ (2005) Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunol 5(8):629–640. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1664
Ambrosini A, Louin G, Croci N, Plotkine M, Jafarian-Tehrani M (2005) Characterization of a rat model to study acute neuroinflammation on histopathological, biochemical and functional outcomes. J Neurosci Methods 144(2):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2004.11.002
Arranz AM, De Strooper B (2019) The role of astroglia in Alzheimer’s disease: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol 18(4):406–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(18)30490-3
Ayanian JZ, Fuchs CS, Stone RM (1988) Lovastatin and rhabdomyolysis. Ann Intern Med 109(8):682–683
Barichello T, Martins MR, Reinke A, Feier G, Ritter C, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2005) Cognitive impairment in sepsis survivors from cecal ligation and perforation. Crit Care Med 33(1):221–223; discussion 262-223. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000150741.12906.bd
Barichello T, Martins MR, Reinke A, Constantino LS, Machado RA, Valvassori SS, Moreira JCF, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2007) Behavioral deficits in sepsis-surviving rats induced by cecal ligation and perforation. Braz J Med Biol Res 40(6):831–837
Barker GR, Warburton EC (2011) Evaluating the neural basis of temporal order memory for visual stimuli in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 33(4):705–716. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07555.x
Benveniste EN, Nguyen VT, O’Keefe GM (2001) Immunological aspects of microglia: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 39(5–6):381–391
Blum CB (1994) Comparison of properties of four inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Am J Cardiol 73(14):3D–11D. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9149(94)90626-2
Bramblett GT, Goedert M, Jakes R, Merrick SE, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (1993) Abnormal tau phosphorylation at Ser396 in Alzheimer’s disease recapitulates development and contributes to reduced microtubule binding. Neuron 10(6):1089–1099
Brown GC, Neher JJ (2010) Inflammatory neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons. Mol Neurobiol 41(2–3):242–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-010-8105-9
Butterick TA, Igbavboa U, Eckert GP, Sun GY, Weisman GA, Müller WE, Wood WG (2010) Simvastatin stimulates production of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 via endothelin-1 and NFATc3 in SH-SY5Y cells. Mol Neurobiol 41(2–3):384–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-010-8122-8
Calsavara AC, Rodrigues DH, Miranda AS, Costa PA, Lima CX, Vilela MC, Rachid MA, Teixeira AL (2013) Late anxiety-like behavior and neuroinflammation in mice subjected to sublethal polymicrobial sepsis. Neurotox Res 24(2):103–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-012-9364-1
Calsolaro V, Edison P (2016) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: current evidence and future directions. Alzheimers Dement 12(6):719–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.02.010
Cassol OJ, Comim CM, Petronilho F, Constantino LS, Streck EL et al (2010) Low dose dexamethasone reverses depressive-like parameters and memory impairment in rats submitted to sepsis. Neurosci Lett 473(2):126–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.02.036
Catalão CHR, Santos-Júnior NN, da Costa LHA, Souza AO, Alberici LC, Rocha MJA (2017) Brain oxidative stress during experimental sepsis is attenuated by simvastatin administration. Mol Neurobiol 54(9):7008–7018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0218-3
Catalão CHR, Souza AO, Santos-Júnior NN, da Silva SC, da Costa LHA, Alberici LC, Rocha MJA, da Silva Lopes L (2019) Kaolin-induced hydrocephalus causes acetylcholinesterase activity dysfunction following hypothalamic damage in infant rats. Brain Res 1724:146408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146408
Chaipichit N, Krska J, Pratipanawatr T, Jarernsiripornkul N (2015) Statin adverse effects: patients’ experiences and laboratory monitoring of muscle and liver injuries. Int J Clin Pharm 37(2):355–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-015-0068-5
Chaudhry N, Duggal AK (2014) Sepsis associated encephalopathy. Adv Med 2014:762320–762316. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/762320
Chen CH, Zhou W, Liu S, Deng Y, Cai F, Tone M, Tone Y, Tong Y, Song W (2012) Increased NF-κB signalling up-regulates BACE1 expression and its therapeutic potential in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15(1):77–90. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1461145711000149
Chukwu JE, Pedersen JT, Pedersen L, Volbracht C, Sigurdsson EM et al (2018) Tau antibody structure reveals a molecular switch defining a pathological conformation of the tau protein. Sci Rep 8(1):6209. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24276-4
Comim CM, Barichello T, Grandgirard D, Dal-Pizzol F, Quevedo J, Leib SL (2013) Caspase-3 mediates in part hippocampal apoptosis in sepsis. Mol Neurobiol 47(1):394–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8354-x
Comim CM, Cassol-Jr OJ, Constantino LS, Felisberto F, Petronilho F, Rezin GT, Scaini G, Daufenbach JF, Streck EL, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2011a) Alterations in inflammatory mediators, oxidative stress parameters and energetic metabolism in the brain of sepsis survivor rats. Neurochem Res 36(2):304–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0320-2
Comim CM, Constantino LS, Petronilho F, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2011b) Aversive memory in sepsis survivor rats. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 118(2):213–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0502-8
Consiglio AR, Lucion AB (2000) Technique for collecting cerebrospinal fluid in the cisterna magna of non-anesthetized rats. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 5(1):109–114
da Costa LHA, Júnior NNDS, Catalão CHR, Sharshar T, Chrétien F et al (2017) Vasopressin impairment during sepsis is associated with hypothalamic intrinsic apoptotic pathway and microglial activation. Mol Neurobiol 54(7):5526–5533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0094-x
Deshpande A, Pasupuleti V, Rothberg MB (2015) Statin therapy and mortality from sepsis: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Med 128(4):410–417.e411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.10.057
Du G, Song Y, Zhang T, Ma L, Bian N et al (2014) Simvastatin attenuates TNF-α-induced apoptosis in endothelial progenitor cells via the upregulation of SIRT1. Int J Mol Med 34(1):177–182. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2014.1740
Elhayany A, Mishaal RA, Vinker S (2012) Is there clinical benefit to routine enzyme testing of patients on statins? Expert Opin Drug Saf 11(2):185–190. https://doi.org/10.1517/14740338.2012.630659
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35(4):495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Field RH, Gossen A, Cunningham C (2012) Prior pathology in the basal forebrain cholinergic system predisposes to inflammation-induced working memory deficits: reconciling inflammatory and cholinergic hypotheses of delirium. J Neurosci 32(18):6288–6294. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4673-11.2012
Figueiredo CP, Clarke JR, Ledo JH, Ribeiro FC, Costa CV, Melo HM, Mota-Sales AP, Saraiva LM, Klein WL, Sebollela A, de Felice FG, Ferreira ST (2013) Memantine rescues transient cognitive impairment caused by high-molecular-weight aβ oligomers but not the persistent impairment induced by low-molecular-weight oligomers. J Neurosci 33(23):9626–9634. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0482-13.2013
Fracassi A, Marangoni M, Rosso P, Pallottini V, Fioramonti M, Siteni S, Segatto M (2019) Statins and the brain: more than lipid lowering agents? Curr Neuropharmacol 17(1):59–83. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X15666170703101816
Franke C, Nöldner M, Abdel-Kader R, Johnson-Anuna LN, Gibson Wood W, Müller WE, Eckert GP (2007) Bcl-2 upregulation and neuroprotection in guinea pig brain following chronic simvastatin treatment. Neurobiol Dis 25(2):438–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2006.10.004
Gasparotto J, Girardi CS, Somensi N, Ribeiro CT, Moreira JCF, Michels M, Sonai B, Rocha M, Steckert AV, Barichello T, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F, Gelain DP (2018) Receptor for advanced glycation end products mediates sepsis-triggered amyloid-β accumulation, tau phosphorylation, and cognitive impairment. J Biol Chem 293(1):226–244. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.786756
Gorina R, Font-Nieves M, Márquez-Kisinousky L, Santalucia T, Planas AM (2011) Astrocyte TLR4 activation induces a proinflammatory environment through the interplay between MyD88-dependent NFκB signaling, MAPK, and Jak1/Stat1 pathways. Glia 59(2):242–255. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.21094
Granja C, Lopes A, Moreira S, Dias C, Costa-Pereira A, Carneiro A, JMIP Study Group (2005) Patients’ recollections of experiences in the intensive care unit may affect their quality of life. Crit Care 9(2):R96–R109. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc3026
Greenwood J, Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2006) Statin therapy and autoimmune disease: from protein prenylation to immunomodulation. Nat Rev Immunol 6(5):358–370. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1839
Guo JT, Yu J, Grass D, de Beer FC, Kindy MS (2002) Inflammation-dependent cerebral deposition of serum amyloid a protein in a mouse model of amyloidosis. J Neurosci 22(14):5900–5909
Handa O, Stephen J, Cepinskas G (2008) Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide in activation and dysfunction of cerebrovascular endothelial cells during early onsets of sepsis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295(4):H1712–H1719. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00476.2008
Heneka MT (2019) Microglia take centre stage in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Immunol 19(2):79–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-018-0112-5
Heneka MT, McManus RM, Latz E (2018) Inflammasome signalling in brain function and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 19(10):610–621. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-018-0055-7
Hernandes MS, D’Avila JC, Trevelin SC, Reis PA, Kinjo ER et al (2014) The role of Nox2-derived ROS in the development of cognitive impairment after sepsis. J Neuroinflammation 11:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-11-36
Hopkins RO, Weaver LK, Collingridge D, Parkinson RB, Chan KJ, Orme JF Jr (2005) Two-year cognitive, emotional, and quality-of-life outcomes in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171(4):340–347. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200406-763OC
Hopkins RO, Weaver LK, Pope D, Orme JF, Bigler ED et al (1999) Neuropsychological sequelae and impaired health status in survivors of severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.160.1.9708059
Hough CL, Curtis JR (2005) Long-term sequelae of critical illness: memories and health-related quality of life. Crit Care 9(2):145–146. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc3483
Hshieh TT, Fong TG, Marcantonio ER, Inouye SK (2008) Cholinergic deficiency hypothesis in delirium: a synthesis of current evidence. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 63(7):764–772
Imamura Y, Wang H, Matsumoto N, Muroya T, Shimazaki J, Ogura H, Shimazu T (2011) Interleukin-1β causes long-term potentiation deficiency in a mouse model of septic encephalopathy. Neuroscience 187:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.04.063
Iwashyna TJ, Ely EW, Smith DM, Langa KM (2010) Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA 304(16):1787–1794. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.1553
Jackson JC, Gordon SM, Ely EW, Burger C, Hopkins RO (2004) Research issues in the evaluation of cognitive impairment in intensive care unit survivors. Intensive Care Med 30(11):2009–2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-004-2422-2
Jeong A, Suazo KF, Wood WG, Distefano MD, Li L (2018) Isoprenoids and protein prenylation: implications in the pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention of Alzheimer’s disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 53(3):279–310. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2018.1458070
Johnson-Anuna LN, Eckert GP, Keller JH, Igbavboa U, Franke C, Fechner T, Schubert-Zsilavecz M, Karas M, Müller WE, Wood WG (2005) Chronic administration of statins alters multiple gene expression patterns in mouse cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312(2):786–793. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.104.075028
Johnson-Anuna LN, Eckert GP, Franke C, Igbavboa U, Müller WE, Wood WG (2007) Simvastatin protects neurons from cytotoxicity by up-regulating Bcl-2 mRNA and protein. J Neurochem 101(1):77–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04375.x
Jänicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR, Porter AG (1998) Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem 273(16):9357–9360
Kettenmann H, Kirchhoff F, Verkhratsky A (2013) Microglia: new roles for the synaptic stripper. Neuron 77(1):10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.12.023
Kim EH, Jang MH, Shin MC, Lim BV, Kim HB, Kim YJ, Chung JH, Kim CJ (2002) Acupuncture increases cell proliferation and neuropeptide Y expression in dentate gyrus of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett 327(1):33–36
Kopterides P, Falagas ME (2009) Statins for sepsis: a critical and updated review. Clin Microbiol Infect 15(4):325–334. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02750.x
Li L, Zhang W, Cheng S, Cao D, Parent M (2012) Isoprenoids and related pharmacological interventions: potential application in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 46(1):64–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8253-1
Liddelow SA, Barres BA (2017) Reactive astrocytes: production, function, and therapeutic potential. Immunity 46(6):957–967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2017.06.006
Liddelow SA, Guttenplan KA, Clarke LE, Bennett FC, Bohlen CJ, Schirmer L, Bennett ML, Münch AE, Chung WS, Peterson TC, Wilton DK, Frouin A, Napier BA, Panicker N, Kumar M, Buckwalter MS, Rowitch DH, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Stevens B, Barres BA (2017) Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 541(7638):481–487. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21029
Liu H, Yang J, Wang K, Niu T, Huang D (2019) Moderate- and low-dose of atorvastatin alleviate cognition impairment induced by high-fat diet via Sirt1 activation. Neurochem Res 44(5):1065–1078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02738-z
Lu D, Shen L, Mai H, Zang J, Liu Y, Tsang CK, Li K, Xu A (2019) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors attenuate neuronal damage by suppressing oxygen glucose deprivation-induced activated microglial cells. Neural Plast 2019:7675496–7675415. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7675496
Maramattom BV (2007) Sepsis associated encephalopathy. Neurol Res 29(7):643–646. https://doi.org/10.1179/016164107X240233
Martin CP, Talbert RL, Burgess DS, Peters JI (2007) Effectiveness of statins in reducing the rate of severe sepsis: a retrospective evaluation. Pharmacotherapy 27(1):20–26. https://doi.org/10.1592/phco.27.1.20
Matsuzaki H, Tamatani M, Mitsuda N, Namikawa K, Kiyama H, Miyake S, Tohyama M (1999) Activation of Akt kinase inhibits apoptosis and changes in Bcl-2 and Bax expression induced by nitric oxide in primary hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem 73(5):2037–2046
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V, Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC, Yarasheski KE, Bateman RJ (2010) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 330(6012):1774. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1197623
McManus RM, Heneka MT (2017) Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration: new insights. Alzheimers Res Ther 9(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-017-0241-2
McQuade A, Blurton-Jones M (2019) Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease: exploring how genetics and phenotype influence risk. J Mol Biol 431(9):1805–1817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2019.01.045
Mehl A, Harthug S, Lydersen S, Paulsen J, Åsvold BO, Solligård E, Damås JK, Edna TH (2015) Prior statin use and 90-day mortality in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bloodstream infection: a prospective observational study. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 34(3):609–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2269-6
Michels M, Vieira AS, Vuolo F, Zapelini HG, Mendonça B, Mina F, Dominguini D, Steckert A, Schuck PF, Quevedo J, Petronilho F, Dal-Pizzol F (2015) The role of microglia activation in the development of sepsis-induced long-term cognitive impairment. Brain Behav Immun 43:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2014.07.002
Mina F, Comim CM, Dominguini D, Cassol-Jr OJ, Dall Igna DM et al (2014) Il1-β involvement in cognitive impairment after sepsis. Mol Neurobiol 49(2):1069–1076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8581-9
Naiki H, Higuchi K, Hosokawa M, Takeda T (1989) Fluorometric determination of amyloid fibrils in vitro using the fluorescent dye, thioflavin T1. Anal Biochem 177(2):244–249
Nemzek JA, Xiao HY, Minard AE, Bolgos GL, Remick DG (2004) Humane endpoints in shock research. Shock 21(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.shk.0000101667.49265.fd
Oliveira-Pelegrin GR, Basso PJ, Rocha MJ (2014) Cellular bioenergetics changes in magnocellular neurons may affect copeptin expression in the late phase of sepsis. J Neuroimmunol 267(1–2):28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.12.006
Oliveira-Pelegrin GR, Basso PJ, Soares AS, Martinez MR, Riester KD, Rocha MJA (2013) Cleaved caspase-3 expression in hypothalamic magnocellular neurons may affect vasopressin secretion during experimental polymicrobial sepsis. J Neuroimmunol 258:10–16
Olivieri R, Michels M, Pescador B, Ávila P, Abatti M, Cucker L, Burger H, Dominguini D, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F (2018) The additive effect of aging on sepsis-induced cognitive impairment and neuroinflammation. J Neuroimmunol 314:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2017.11.014
Ostrowski SM, Johnson K, Siefert M, Shank S, Sironi L, Wolozin B, Landreth GE, Ziady AG (2016) Simvastatin inhibits protein isoprenylation in the brain. Neuroscience 329:264–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.04.053
Pan S, Wu Y, Pei L, Li S, Song L, Xia H, Wang Y, Yu Y, Yang X, Shu H, Zhang J, Yuan S, Shang Y (2018) BML-111 reduces neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in mice with sepsis via the SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Cell Neurosci 12:267. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00267
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam
Pekny M, Pekna M, Messing A, Steinhäuser C, Lee JM, Parpura V, Hol EM, Sofroniew MV, Verkhratsky A (2016) Astrocytes: a central element in neurological diseases. Acta Neuropathol 131(3):323–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1513-1
Piechota M, Barylski M, Hannam S, Piechota-Urbańska M, Banach M (2013) Rationale of statin therapy in septic patients. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 11(5):795–800
Posada-Duque RA, Velasquez-Carvajal D, Eckert GP, Cardona-Gomez GP (2013) Atorvastatin requires geranylgeranyl transferase-I and Rac1 activation to exert neuronal protection and induce plasticity. Neurochem Int 62(4):433–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.01.026
Qin L, Xie X, Fang P, Lin J (2019) Prophylactic simvastatin treatment modulates the immune response and increases survival of mice following induction of lethal sepsis. J Int Med Res 300060519858508. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519858508
Ransohoff RM (2016) How neuroinflammation contributes to neurodegeneration. Science 353(6301):777–783. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aag2590
Reis PA, Alexandre PC, D’Avila JC, Siqueira LD, Antunes B et al (2017) Statins prevent cognitive impairment after sepsis by reverting neuroinflammation, and microcirculatory/endothelial dysfunction. Brain Behav Immun 60:293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.11.006
Saheki A, Terasaki T, Tamai I, Tsuji A (1994) In vivo and in vitro blood-brain barrier transport of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors. Pharm Res 11(2):305–311
Santos-Junior NN, Catalão CH, Costa LH, Rossignoli BB, Dos-Santos RC et al (2018) Alterations in hypothalamic synaptophysin and death markers may be associated with vasopressin impairment in sepsis survivor rats. J Neuroendocrinol:e12604. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12604
Sastre M, Dewachter I, Landreth GE, Willson TM, Klockgether T, van Leuven F, Heneka MT (2003) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists modulate immunostimulated processing of amyloid precursor protein through regulation of beta-secretase. J Neurosci 23(30):9796–9804
Satou T, Cummings BJ, Cotman CW (1995) Immunoreactivity for Bcl-2 protein within neurons in the Alzheimer’s disease brain increases with disease severity. Brain Res 697(1–2):35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(95)00748-f
Schwalm MT, Pasquali M, Miguel SP, Dos Santos JP, Vuolo F et al (2014) Acute brain inflammation and oxidative damage are related to long-term cognitive deficits and markers of neurodegeneration in sepsis-survivor rats. Mol Neurobiol 49(1):380–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8526-3
Semmler A, Okulla T, Sastre M, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L, Heneka MT (2005) Systemic inflammation induces apoptosis with variable vulnerability of different brain regions. J Chem Neuroanat 30(2–3):144–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2005.07.003
Semmler A, Frisch C, Debeir T, Ramanathan M, Okulla T, Klockgether T, Heneka MT (2007) Long-term cognitive impairment, neuronal loss and reduced cortical cholinergic innervation after recovery from sepsis in a rodent model. Exp Neurol 204(2):733–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.01.003
Semmler A, Hermann S, Mormann F, Weberpals M, Paxian SA, Okulla T, Schäfers M, Kummer MP, Klockgether T, Heneka MT (2008) Sepsis causes neuroinflammation and concomitant decrease of cerebral metabolism. J Neuroinflammation 5:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-5-38
Semmler A, Widmann CN, Okulla T, Urbach H, Kaiser M, Widman G, Mormann F, Weide J, Fliessbach K, Hoeft A, Jessen F, Putensen C, Heneka MT (2013) Persistent cognitive impairment, hippocampal atrophy and EEG changes in sepsis survivors. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84(1):62–69. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2012-302883
Shankar GM, Walsh DM (2009) Alzheimer’s disease: synaptic dysfunction and Aβ. Mol Neurodegener 4(1):48
Shetty AK, Upadhya R, Madhu LN, Kodali M (2019) Novel insights on systemic and brain aging, stroke, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Dis 10(2):470–482. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2019.0330
Sonneville R, Verdonk F, Rauturier C, Klein IF, Wolff M, Annane D, Chretien F, Sharshar T (2013) Understanding brain dysfunction in sepsis. Ann Intensive Care 3(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/2110-5820-3-15
Sprung CL, Peduzzi PN, Shatney CH, Schein RM, Wilson MF et al (1990) Impact of encephalopathy on mortality in the sepsis syndrome. The Veterans Administration Systemic Sepsis Cooperative Study Group. Crit Care Med 18(8):801–806
Steckert AV, Comim CM, Igna DM, Dominguini D, Mendonça BP et al (2015) Effects of sodium butyrate on aversive memory in rats submitted to sepsis. Neurosci Lett 595:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.04.019
Stein A, Stroobants S, Gieselmann V, D’Hooge R, Matzner U (2015) Anti-inflammatory therapy with simvastatin improves neuroinflammation and CNS function in a mouse model of metachromatic leukodystrophy. Mol Ther 23(7):1160–1168. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2015.69
Taccone FS, Castanares-Zapatero D, Peres-Bota D, Vincent JL, Berre’ J et al (2010) Cerebral autoregulation is influenced by carbon dioxide levels in patients with septic shock. Neurocrit Care 12(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-009-9289-6
Tamatani M, Ogawa S, Niitsu Y, Tohyama M (1998) Involvement of Bcl-2 family and caspase-3-like protease in NO-mediated neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 71(4):1588–1596. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.71041588.x
Tian M, Qingzhen L, Zhiyang Y, Chunlong C, Jiao D, Zhang L, Li W (2019) Attractylone attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy and cognitive dysfunction by inhibiting microglial activation and neuroinflammation. J Cell Biochem 120:7101–7108. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27983
van Gool WA, van de Beek D, Eikelenboom P (2010) Systemic infection and delirium: when cytokines and acetylcholine collide. Lancet 375(9716):773–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61158-2
Vasudevan AR, Hamirani YS, Jones PH (2005) Safety of statins: effects on muscle and the liver. Cleve Clin J Med 72(11):990–993, 996-1001. https://doi.org/10.3949/ccjm.72.11.990
Vianna MR, Alonso M, Viola H, Quevedo J, de Paris F, Furman M, de Stein ML, Medina JH, Izquierdo I (2000) Role of hippocampal signaling pathways in long-term memory formation of a nonassociative learning task in the rat. Learn Mem 7(5):333–340
Viatour P, Bentires-Alj M, Chariot A, Deregowski V, de Leval L, Merville MP, Bours V (2003) NF- kappa B2/p100 induces Bcl-2 expression. Leukemia 17(7):1349–1356. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402982
Vickers S, Duncan CA, Vyas KP, Kari PH, Arison B, Prakash SR, Ramjit HG, Pitzenberger SM, Stokker G, Duggan DE (1990) In vitro and in vivo biotransformation of simvastatin, an inhibitor of HMG CoA reductase. Drug Metab Dispos 18(4):476–483
Vuletic S, Riekse RG, Marcovina SM, Peskind ER, Hazzard WR, Albers JJ (2006) Statins of different brain penetrability differentially affect CSF PLTP activity. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 22(5–6):392–398. https://doi.org/10.1159/000095679
Wahab F, Santos-Junior NN, de Almeida Rodrigues RP, Costa LHA, Catalão CHR, Rocha MJA (2016) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist decreases hypothalamic oxidative stress during experimental sepsis. Mol Neurobiol 53(6):3992–3998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9338-4
Wan YD, Sun TW, Kan QC, Guan FX, Zhang SG (2014) Effect of statin therapy on mortality from infection and sepsis: a meta-analysis of randomized and observational studies. Crit Care 18(2):R71. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc13828
Weberpals M, Hermes M, Hermann S, Kummer MP, Terwel D, Semmler A, Berger M, Schafers M, Heneka MT (2009) NOS2 gene deficiency protects from sepsis-induced long-term cognitive deficits. J Neurosci 29(45):14177–14184. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3238-09.2009
Widmann CN, Heneka MT (2014) Long-term cerebral consequences of sepsis. Lancet Neurol 13(6):630–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70017-1
Wood WG, Igbavboa U, Muller WE, Eckert GP (2013) Statins, Bcl-2, and apoptosis: cell death or cell protection? Mol Neurobiol 48(2):308–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8496-5
Xiong H, McCabe L, Costello J, Anderson E, Weber G, Ikezu T (2004) Activation of NR1a/NR2B receptors by soluble factors from APP-stimulated monocyte-derived macrophages: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 25(7):905–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.09.007
Xu Y, Yan J, Zhou P, Li J, Gao H, Xia Y, Wang Q (2012) Neurotransmitter receptors and cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 97(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.02.002
Xue C, Lin TY, Chang D, Guo Z (2017) Thioflavin T as an amyloid dye: fibril quantification, optimal concentration and effect on aggregation. R Soc Open Sci 4(1):160696. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.160696
Yang CH, Kao MC, Shih PC, Li KY, Tsai PS, Huang CJ (2015) Simvastatin attenuates sepsis-induced blood-brain barrier integrity loss. J Surg Res 194(2):591–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2014.11.030
Young GB, Bolton CF, Austin TW, Archibald YM, Gonder J, Wells GA (1990) The encephalopathy associated with septic illness. Clin Invest Med 13(6):297–304
Zheng X, Liao Y, Wang J, Hu S, Rudramurthy GR, Swamy MK, Rohit KC, Wang Y (2018) The antineuroinflammatory effect of simvastatin on lipopolysaccharide activated microglial cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018:9691085–9691089. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9691085
Zhuo Y, Zhang S, Li C, Yang L, Gao H, Wang X (2018) Resolvin D1 promotes SIRT1 expression to counteract the activation of STAT3 and NF-κB in mice with septic-associated lung injury. Inflammation 41(5):1762–1771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0819-2
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Marcelo Batalhão for the use of the Nitric Oxide Analyzer (Sievers Instruments Nitric Oxide Analyzer). Technical support by Nadir Fernandes and Renato Meireles is gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank Dr. Klaus Hartfelder for his assistance with English language.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001 and by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP, grants 2015/12152, 2017/12462-0, 2018/02854-0 and 2018/10089-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study involves the use of rats. All animal experiments in this study were carried out according to an Institutional Ethics Committee approved protocol (CEUA protocol number: 2019.1.51.58.6).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Catalão, C.H.R., Santos-Junior, N.N., da Costa, L.H.A. et al. Simvastatin Prevents Long-Term Cognitive Deficits in Sepsis Survivor Rats by Reducing Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Neurotox Res 38, 871–886 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00222-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00222-z