Abstract
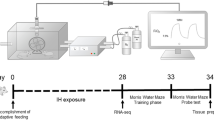
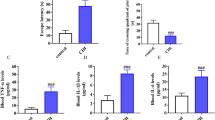
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) is known as a repeated obstruction of the upper airway during sleep, leading to generalized hypoxia episodes and associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. We mainly explored the role of neuregulin receptor degradation protein-1 (Nrdp1, also known as FLRF) in brain injury induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) in rats. Wistar rats were randomly divided into 4 groups (n = 12 per group), including the sham + adeno-associated virus-NC (AAV-NC) group, the sham + AAV-siNrdp1 group, the IH-4w (intermittent hypoxia for 4 weeks) + AAV-NC group, and the IH-4w + AAV-siNrdp1 group. Morphologic changes in brain tissue were observed by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. Apoptosis in the hippocampus was detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL) staining. Spatial learning and memory were assessed by the Morris water maze test. The expression of Nrdp1 mRNA and protein in the hippocampus was detected by qualitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting. The concentration of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in serum was detected via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits. Nrdp1 expression was increased after intermittent hypoxia exposure over time. Western blotting and H&E results showed that pathological changes of hippocampus neurons in chronic intermittent hypoxia rat were diminished by shNrdp1. Western blotting and TUNEL staining showed that apoptotic cells in the hippocampus of CIH rats were decreased by shNrdp1. The Morris water maze results proved that shNrdp1 improved spatial learning performance of chronic intermittent hypoxia rats. ELISA kits results showed that CIH-induced inflammatory response was decreased by shNrdp1. Western blotting and qRT-PCR results showed protein expression of ErbB3 in the hippocampus of CIH rats. Nrdp1 could regulate ErbB3 protein levels in brain-injured rats with CIH, which demonstrates that Nrdp1 is a potential therapeutic target in the cognition deficits associated with OSAS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buratti L, Luzzi S, Petrelli C et al (2016) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: an emerging risk factor for dementia. CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets) 15(6)
Caldeira MV, Salazar IL, Curcio M, Canzoniero LM, Duarte CB (2014) Role of the ubiquitin–proteasome system in brain ischemia: friend or foe? Prog Neurobiol 112:50–69
Can M, Uygur F, Tanrıverdi H et al (2016) Effect of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy on IL-23 in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Immunol Res 64(5–6):1–6
De Ceuninck L, Wauman J, Masschaele D et al (2013) Reciprocal cross-regulation between RNF41 and USP8 controls cytokine receptor sorting and processing. J Cell Sci 126(16):3770–3781
Destors M, Tamisier R, Galerneau L M, et al. (2017) [Pathophysiology of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and its cardiometabolic consequences]. Presse Medicale
Iglesias BG, Escarceller CJ, Robles IB et al (2016) Effectiveness of 6-months continuous positive airway pressure treactment in OSAS-related cognitive deficit in older adults. Behav Neurol 26(3):191–194
Mitchell RB, Kelly J, Call E, Yao N (2004) Long-term changes in quality of life after surgery for pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Arch Otolaryngol–Head Neck Surg 130(4):409–412
Qiu XB, Markant SL, Yuan J et al (2004) Nrdp1-mediated degradation of the gigantic IAP, BRUCE, is a novel pathway for triggering apoptosis. EMBO (Eur Mol Biol Organ) J 23(4):800–810
Shi H, Gong H, Cao K, Zou S, Zhu B, Bao H, Wu Y, Gao Y, Tang Y, Yu R (2015) Nrdp1-mediated ErbB3 degradation inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by reducing cytoplasmic localization of p27Kip1. J Neuro-Oncol 124(3):357–364
Song T, Wang L, Zhongfu MO et al (2014) Expression of p-Akt in ovarian serous carcinoma and its association with proliferation and apoptosis. Oncol Lett 7(1):59–64
Steinmetz J, Christensen KB, Lund T, Lohse N, Rasmussen LS, ISPOCD Group (2009) Long-term consequences of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Anesthesiology 110(3):548–555
Sun EG, Lee KH, Ko YS et al (2016) KITENIN functions as a fine regulator of ErbB4 expression level in colorectal cancer via protection of ErbB4 from E3-ligase Nrdp1-mediated degradation. Mol Carcinog
Wu Y, Wang L, Bao H, Zou S, Fu C, Gong H, Gao Y, Tang Y, Yu R, Shi H (2016) Nrdp1S, short variant of Nrdp1, inhibits human glioma progression by increasing Nrdp1-mediated ErbB3 ubiquitination and degradation. J Cell Mol Med 20(3):422–429
Yang K, Zhang Y, Wang T, et al. (2017) Nrdp1 increases ischemia induced primary rat cerebral cortical neurons and pheochromocytoma cells apoptosis via downregulation of HIF-1α protein[C]//
Yuan X, Deng Y, Guo X, Shang J, Zhu D, Liu H (2014) Atorvastatin attenuates myocardial remodeling induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in rats: partly involvement of TLR-4/MYD88 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 446(1):292–297
Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Wang M, Tian C, Ma X, Chen H, Fang Q, Jia L, du J, Li H (2011a) Cardiac-specific overexpression of E3 ligase Nrdp1 increases ischemia and reperfusion-induced cardiac injury[J]. Basic Res Cardiol 106(3):371–383
Zhang Y, Kang YM, Tian C, Zeng Y, Jia LX, Ma X, du J, Li HH (2011b) Overexpression of Nrdp1 in the heart exacerbates doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction in mice. PLoS One 6(6):e21104
Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Wang M, Tian C, Ma X, Chen H, Fang Q, Jia L, du J, Li H (2011c) Cardiac-specific overexpression of E3 ligase Nrdp1 increases ischemia and reperfusion-induced cardiac injury. Basic Res Cardiol 106(3):371–383
Zhao Y, Wang H, Li J et al (2015) Hippocampal mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is associated with intermittent hypoxia in a rat model of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Mol Med Rep
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Zhu, Z., Ren, Y. et al. Role of the Nrdp1 in Brain Injury Induced by Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia in Rats via Regulating the Protein Levels of ErbB3. Neurotox Res 38, 124–132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00195-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00195-z