Abstract
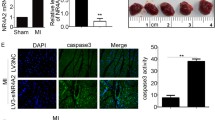
Cardiomyocyte death is a major event of myocardial infarction. Previously, we and others have shown that E3 ligase-mediated protein turnover plays a critical role in cardiac injury. In this study, we sought to determine the role of a newly identified E3 ligase, neuregulin receptor degradation protein-1 (Nrdp1), on cardiac ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. I/R injury markedly upregulated Nrdp1 expression in heart tissue. To elucidate the role of Nrdp1 in I/R-induced cardiac injury, neonatal cardiomyocytes were infected with adenoviral constructs expressing wild-type, dominant-negative Nrdp1 genes. Increased Nrdp1 expression enhanced I/R-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation as compared with the green fluorescent protein (GFP) control; these effects were attenuated by overexpression of a dominant-negative Nrdp1 (C34S/H36Q). Furthermore, cardiac-specific Nrdp1 overexpression in vivo in mouse significantly increased infarct size, the number of TUNEL-positive nuclei and inflammatory cells, as well as mortality, as compared with wild-type mice after I/R injury. The mechanisms underlying these effects were associated with the downregulation of an Nrdp1 substrate, ErbB3, accompanied by suppression of its downstream targets AKT, ERK1/2, and activation of p38 and JNK1/2. Together, these results provide evidence for an important role for Nrdp1 in regulating I/R-induced cardiac injury. Nrdp1 may constitute a new therapeutic target for ameliorating the I/R-induced cardiac injury.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong SC (2004) Protein kinase activation and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res 61:427–436. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.09.031S000863630300662x
Baines CP, Molkentin JD (2005) STRESS signaling pathways that modulate cardiac myocyte apoptosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol 38:47–62 (S0022-2828(04)00325-6)
Boengler K, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Drexler H, Heusch G, Schulz R (2008) The myocardial JAK/STAT pathway: from protection to failure. Pharmacol Ther 120:172–185 (S0163-7258(08)00140-x)
Bowden RA, Ding ZM, Donnachie EM, Petersen TK, Michael LH, Ballantyne CM, Burns AR (2002) Role of alpha4 integrin and VCAM-1 in CD18-independent neutrophil migration across mouse cardiac endothelium. Circ Res 90:562–569. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000013835.53611.97
Camenisch TD, Schroeder JA, Bradley J, Klewer SE, McDonald JA (2002) Heart-valve mesenchyme formation is dependent on hyaluronan-augmented activation of ErbB2-ErbB3 receptors. Nat Med 8:850–855. doi:10.1038/nm742nm742
Cao Z, Wu X, Yen L, Sweeney C, Carraway KL 3rd (2007) Neuregulin-induced ErbB3 downregulation is mediated by a protein stability cascade involving the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nrdp1. Mol Cell Biol 27:2180–2188 (MCB.01245-06)
Diamonti AJ, Guy PM, Ivanof C, Wong K, Sweeney C, Carraway KL 3rd (2002) An RBCC protein implicated in maintenance of steady-state neuregulin receptor levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:2866–2871. doi:10.1073/pnas.052709799
Eefting F, Rensing B, Wigman J, Pannekoek WJ, Liu WM, Cramer MJ, Lips DJ, Doevendans PA (2004) Role of apoptosis in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res 61:414–426. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.12.023S0008636303007910
Feng Y, Zhao H, Xu X, Buys ES, Raher MJ, Bopassa JC, Thibault H, Scherrer-Crosbie M, Schmidt U, Chao W (2008) Innate immune adaptor MyD88 mediates neutrophil recruitment and myocardial injury after ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1311–H1318 (00119.2008)
Fuller SJ, Sivarajah K, Sugden PH (2008) ErbB receptors, their ligands, and the consequences of their activation and inhibition in the myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:831–854 (S0022-2828(08)00343-x)
Ha T, Hua F, Li Y, Ma J, Gao X, Kelley J, Zhao A, Haddad GE, Williams DL, Browder IW, Kao RL, Li C (2006) Blockade of MyD88 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy and decreases cardiac myocyte apoptosis in pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy in vivo. Am J Physiol 290:H985–994 (00720.2005)
Hauser HP, Bardroff M, Pyrowolakis G, Jentsch S (1998) A giant ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme related to IAP apoptosis inhibitors. J Cell Biol 141:1415–1422. doi:10.1083/jcb.141.6.1415
Heusch G (2009) No risk, no… cardioprotection? A critical perspective. Cardiovasc Res 84:173–175 (cvp298)
Heusch G, Boengler K, Schulz R (2008) Cardioprotection: nitric oxide, protein kinases, and mitochondria. Circulation 118:1915–1919. doi:118/19/1915
Hosoda T, Kajstura J, Leri A, Anversa P (2010) Mechanisms of myocardial regeneration. Circ J 74:13–17. doi:JST.JSTAGE/circj/CJ-09-0665
Li F, Xie P, Fan Y, Zhang H, Zheng L, Gu D, Patterson C, Li H (2009) C terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation and survival through ubiquitin-mediated degradation of FoxO1. J Biol Chem 284:20090–20098. doi:M109.017046
Li HH, Kedar V, Zhang C, McDonough H, Arya R, Wang DZ, Patterson C (2004) Atrogin-1/muscle atrophy F-box inhibits calcineurin-dependent cardiac hypertrophy by participating in an SCF ubiquitin ligase complex. J Clin Invest 114:1058–1071. doi:10.1172/JCI22220
Li HH, Willis MS, Lockyer P, Miller N, McDonough H, Glass DJ, Patterson C (2007) Atrogin-1 inhibits Akt-dependent cardiac hypertrophy in mice via ubiquitin-dependent coactivation of Forkhead proteins. J Clin Invest 117:3211–3223. doi:10.1172/JCI31757
Li T, Wang Y, Liu C, Hu Y, Wu M, Li J, Guo L, Chen L, Chen Q, Ha T, Li C, Li Y (2009) MyD88-dependent nuclear factor-kappaB activation is involved in fibrinogen-induced hypertrophic response of cardiomyocytes. J Hypertens 27:1084–1093. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3283293c93
Liao YH, Cheng X (2006) Autoimmunity in myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 112:21–26 (S0167-5273(06)00560-2)
Logue SE, Gustafsson AB, Samali A, Gottlieb RA (2005) Ischemia/reperfusion injury at the intersection with cell death. J Mol Cell Cardiol 38:21–33 (S0022-2828(04)00330-x)
Lopez-Neblina F, Toledo AH, Toledo-Pereyra LH (2005) Molecular biology of apoptosis in ischemia and reperfusion. J Invest Surg 18:335–350 (K3574075H438W921)
Negro A, Brar BK, Lee KF (2004) Essential roles of Her2/erbB2 in cardiac development and function. Recent Prog Horm Res 59:1–12. doi:10.1210/rp.59.1.1
Opie LH, Commerford PJ, Gersh BJ, Pfeffer MA (2006) Controversies in ventricular remodelling. Lancet 367:356–367 (S0140-6736(06)68074-4)
Orlowski RZ (1999) The role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:303–313. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400505
Qiu XB, Goldberg AL (2002) Nrdp1/FLRF is a ubiquitin ligase promoting ubiquitination and degradation of the epidermal growth factor receptor family member, ErbB3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14843–14848. doi:10.1073/pnas.232580999
Qiu XB, Markant SL, Yuan J, Goldberg AL (2004) Nrdp1-mediated degradation of the gigantic IAP, BRUCE, is a novel pathway for triggering apoptosis. EMBO J 23:800–810. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600075
Riethmacher D, Sonnenberg-Riethmacher E, Brinkmann V, Yamaai T, Lewin GR, Birchmeier C (1997) Severe neuropathies in mice with targeted mutations in the ErbB3 receptor. Nature 389:725–730. doi:10.1038/39593
Skyschally A, van Caster P, Boengler K, Gres P, Musiolik J, Schilawa D, Schulz R, Heusch G (2009) Ischemic postconditioning in pigs: no causal role for RISK activation. Circ Res 104:15–18 (CIRCRESAHA.108.186429)
Toth A, Nickson P, Qin LL, Erhardt P (2006) Differential regulation of cardiomyocyte survival and hypertrophy by MDM2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem 281:3679–3689 (M509630200)
Wang C, Chen T, Zhang J, Yang M, Li N, Xu X, Cao X (2009) The E3 ubiquitin ligase Nrdp1 ‘preferentially’ promotes TLR-mediated production of type I interferon. Nat Immunol 10:744–752 (ni.1742)
Wu X, Yen L, Irwin L, Sweeney C, Carraway KL 3rd (2004) Stabilization of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nrdp1 by the deubiquitinating enzyme USP8. Mol Cell Biol 24:7748–7757. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.17.7748-7757.200424/17/7748
Xie P, Guo S, Fan Y, Zhang H, Gu D, Li H (2009) Atrogin-1/MAFbx enhances simulated ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes through degradation of MAPK phosphatase-1 and sustained JNK activation. J Biol Chem 284:5488–5496 (M806487200)
Yen L, Cao Z, Wu X, Ingalla ER, Baron C, Young LJ, Gregg JP, Cardiff RD, Borowsky AD, Sweeney C, Carraway KL 3rd (2006) Loss of Nrdp1 enhances ErbB2/ErbB3-dependent breast tumor cell growth. Cancer Res 66:11279–11286 (66/23/11279)
Yet SF, Tian R, Layne MD, Wang ZY, Maemura K, Solovyeva M, Ith B, Melo LG, Zhang L, Ingwall JS, Dzau VJ, Lee ME, Perrella MA (2001) Cardiac-specific expression of heme oxygenase-1 protects against ischemia and reperfusion injury in transgenic mice. Circ Res 89:168–173. doi:10.1161/hh1401.093314
Zhang C, Xu Z, He XR, Michael LH, Patterson C (2005) CHIP, a cochaperone/ubiquitin ligase that regulates protein quality control, is required for maximal cardioprotection after myocardial infarction in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H2836–H2842 (01122.2004)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from China National Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars (81025001; HL, 30888004; JD) and the Beijing high-level talents program (PHR20110507; HL).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Y. Zhang and Y. Zeng contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
395_2011_157_MOESM2_ESM.eps
ErbB3 receptor was expressed in the mouse heart. a The expression levels of ErbB3 mRNA in the hearts of wild-type (WT) and TG6 mice were detected by RT-PCR. Lane 1: sterilized distilled water used instead of DNA template; Lanes 2-5: ErbB3 used as DNA template. b Western blot analysis of endogenous ErbB3 protein levels from the hearts of WT and TG6 mice. c Left-ventricular sections from WT and TG6 mice stained with anti-IgG (left) or anti-ErbB3 (middle and right) antibody. Brown staining indicates ErbB3 expression. Bar = 50 μm (EPS 8554 kb)
395_2011_157_MOESM3_ESM.eps
Effect of Nrdp1 overexpression on other substrates of Nrdp1 after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R). Western blot analysis of protein levels of BRUCE, MyD88 and TBK1 from at the border area of the myocardium from WT and TG6 mice (n=5). A representative blot is shown for each condition (EPS 1004 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zeng, Y., Wang, M. et al. Cardiac-specific overexpression of E3 ligase Nrdp1 increases ischemia and reperfusion-induced cardiac injury. Basic Res Cardiol 106, 371–383 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-011-0157-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-011-0157-0