Abstract
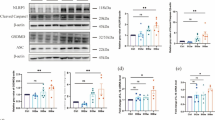
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is mainly characterized by chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) with multiple brain injuries. Nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD)–like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is considered the most important factor inducing and maintaining inflammation. However, the role of NLRP3 and its underlying mechanism in CIH-elicited neuroinflammation remains unclear. We constructed an OSA-related CIH in vivo model and assessed the rats’ cognitive behavior in the Morris water maze. The combination of miR-223-3p and NLRP3 was confirmed by the TargetScan database, double luciferase reporter gene experiment, and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) experiment. Western blot and ELISA assay were used to analyze the effects of miR-223-3p targeting NLRP3 on the expression of pyroptotic or inflammatory factors in vivo in CIH rats. Severe cognitive impairment was observed in rats at week 6 post-treatment, with increased inflammatory factors in the blood and hippocampus, heightened NLRP3 expression, and low miR-223-3p levels. And the good binding activity of the two was confirmed by dual luciferase reporter and RIP experiments. Next, we found that silencing NLRP3 or overexpression of miR-223-3p in the CIH model could improve cognitive deficits and reduce the level of proinflammatory factors and pyroptosis factors in rats. Finally, based on silencing NLRP3 or overexpression miR-223-3p, we confirmed that there was a regulatory relationship between miR-223-3p and NLRP3. Our results suggested that the NLRP3/ miR-223-3p axis played a role in attenuating CIH-induced neuroinflammation.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed in this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bai C, Zhu Y, Dong Q et al (2022) Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces the pyroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Bioengineered 13(3):7528–7540. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2047394
Chandrakantan A, Adler AC, Tohsun M et al (2021) Intermittent hypoxia and effects on early learning/memory: exploring the hippocampal cellular effects of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Anesth Analg 133(1):93–103. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000005273
Chen YC, Hsu PY, Su MC et al (2021) MicroRNA sequencing analysis in obstructive sleep apnea and depression: anti-oxidant and MAOA-inhibiting effects of mir-15b-5p and miR-92b-3p through targeting PTGS1-NF-κB-SP1 signaling. Antioxidants (basel, Switzerland) 10(11):1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111854
Colpaert RMW, Calore M (2021) Epigenetics and microRNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Genomics 113(2):540–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.12.042
Dandoy-Dron F, Griffond B, Mishal Z et al (2003) Scrg1, a novel protein of the CNS is targeted to the large dense-core vesicles in neuronal cells. Eur J Neurosci 18(9):2449–2459. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.03009.x
Díaz-García E, García-Tovar S, Alfaro E et al (2022) Inflammasome activation: a keystone of proinflammatory response in obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 205(11):1337–1348. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202106-1445OC
Fernandes M, Mari L, Chiaravalloti A et al (2022) 18F-FDG PET, cognitive functioning, and CSF biomarkers in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea before and after continuous positive airway pressure treatment. J Neurol 269(10):5356–5367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11182-z
Gu C, Shim S, Shin J et al (2005) The EphA8 receptor induces sustained MAP kinase activation to promote neurite outgrowth in neuronal cells. Oncogene 24(26):4243–4256. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208584
Holbrook JA, Jarosz-Griffiths HH, Caseley E et al (2021) Neurodegenerative disease and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Pharmacol 12:643254. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643254
Hu Z, Lv X, Chen L et al (2019) Protective effects of microRNA-22-3p against retinal pigment epithelial inflammatory damage by targeting NLRP3 inflammasome. J Cell Physiol 234(10):18849–18857. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28523
Huang Y, Xu W, Zhou R (2021) NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol 18(9):2114–2127. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-021-00740-6
Ismael S, Ahmed HA, Adris T et al (2021) The NLRP3 inflammasome: a potential therapeutic target for traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res 16(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.286951
Jacinto JGP, Häfliger IM, Akyürek EE et al (2021) KCNG1-related syndromic form of congenital neuromuscular channelopathy in a crossbred calf. Genes 12(11):1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111792
Kaminska M, O’Sullivan M, Mery VP et al (2022) Inflammatory markers and BDNF in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in Parkinson’s disease (PD). Sleep Med 90:258–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2021.11.018
Kerget B, Kerget F, Kahraman ÇY et al (2021) The relationship between NLRP3 rs10159239 and Vaspin rs2236242 gene variants and obstructive sleep apnea. Ups J Med Sci 126. https://doi.org/10.48101/ujms.v126.7603
Khuu MA, Nallamothu T, Castro-Rivera CI et al (2021) Stage-dependent effects of intermittent hypoxia influence the outcome of hippocampal adult neurogenesis. Sci Rep 11(1):6005. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85357-5
Li K, Wei P, Qin Y et al (2017) MicroRNA expression profiling and bioinformatics analysis of dysregulated microRNAs in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Medicine 96(34):e7917. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007917
Li B, Dasgupta C, Huang L et al (2020) MiRNA-210 induces microglial activation and regulates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Cell Mol Immunol 17(9):976–991. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0257-6
Li S, Sun Y, Song M et al (2021) NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis exerts a crucial role in astrocyte pathological injury in mouse model of depression. JCI Insight 6(23):e146852. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.146852
Li C, Zhang L, Bu X et al (2022) LncRNA NORAD promotes the progression of myocardial infarction by targeting the miR-22-3p/PTEN axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 54(4):463–473. https://doi.org/10.3724/abbs.2022037
Liang L, Gu X, Shen HJ et al (2021) Chronic intermittent hypoxia reduces the effects of glucosteroid in asthma via activating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Front Physiol 12:703281. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.703281
Liu X, Chen L, Duan W et al (2022) Abnormal functional connectivity of hippocampal subdivisions in obstructive sleep apnea: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Front Neurosci 16:850940. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.850940
Ma J, Shang S, Wang J et al (2018) Identification of miR-22-3p, miR-92a-3p, and miR-137 in peripheral blood as biomarker for schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 265:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2018.03.080
Martinez B, Peplow PV (2022) MicroRNA biomarkers in frontotemporal dementia and to distinguish from Alzheimer’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neural Regen Res 17(7):1412–1422. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.330591
Menzies B, Teng A, Burns M et al (2022) Neurocognitive outcomes of children with sleep disordered breathing: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev 63:101629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2022.101629
Patel SR (2019) Obstructive sleep apnea. Ann Intern Med 171(11):ITC81–ITC96. https://doi.org/10.7326/AITC201912030
Rahmani S, Kadkhoda S, Ghafouri-Fard S (2022) Synaptic plasticity and depression: the role of miRNAs dysregulation. Mol Biol Rep 49(10):9759–9765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07461-7
Ravanidis S, Bougea A, Papagiannakis N et al (2020) Validation of differentially expressed brain-enriched microRNAs in the plasma of PD patients. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 7(9):1594–1607. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.51146
Ren N, Jiang T, Wang C et al (2020) LncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 inhibits gastric cancer (GC) development and sensitizes chemoresistant GC cells to cisplatin by regulating miR-223–3p/NLRP3 axis. Aging 12(11):11025–11041. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103314
Ren Y, Sun-Waterhouse D, Ouyang F et al (2022) Apple phenolic extracts ameliorate lead-induced cognitive impairment and depression- and anxiety-like behavior in mice by abating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis via the miR-22-3p/SIRT1 axis. Food Funct 13(5):2647–2661. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo03750a
Seda G, Han TS (2020) Effect of obstructive sleep apnea on neurocognitive performance. Sleep Med Clin 15(1):77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2019.10.001
Shi J, Gao W, Shao F (2017) Pyroptosis: gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem Sci 42(4):245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.10.004
Slouka D, Windrichova J, Rezackova H et al (2021) The potential of miR-499 plasmatic level as a biomarker of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Biomark Med 15(12):1011–1019. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm-2020-0826
Turner K, Zambrelli E, Lavolpe S et al (2019) Obstructive sleep apnea: neurocognitive and behavioral functions before and after treatment. Funct Neurol 34(2):71–78
Wali SO, Manzar MD, Abdelaziz MM et al (2021) Putative associations between inflammatory biomarkers, obesity, and obstructive sleep apnea. Ann Thorac Med 16(4):329–336. https://doi.org/10.4103/atm.atm_644_20
Wang Q, Wang Y, Zhang J et al (2022) Silencing MR-1 protects against myocardial injury induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia by targeting Nrf2 through antioxidant stress and anti-inflammation pathways. J Healthc Eng 2022:3471447. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3471447
Wu X, Gong L, Xie L et al (2021) NLRP3 deficiency protects against intermittent hypoxia-induced neuroinflammation and mitochondrial ROS by promoting the PINK1-Parkin pathway of mitophagy in a murine model of sleep apnea. Front Immunol 12:62816. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.628168
Xu C, Owen JE, Gislason T et al (2021) Quantitative analysis of size and regional distribution of corpora amylacea in the hippocampal formation of obstructive sleep apnoea patients. Sci Rep 11(1):20892. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-99795-8
Yan YR, Zhang L, Lin YN et al (2021) Chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction mediates endothelial injury via the TXNIP/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway. Free Radical Biol Med 165:401–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.01.053
Zapater A, Benítez ID, Santamaria-Martos F et al (2022) Endogenous controls and microRNA profile in female patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sci Rep 12(1):1916. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05782-y
Zhang YX, Zhang XT, Li HJ et al (2021) Antidepressant-like effects of helicid on a chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression rat model: inhibiting the IKK/IκBα/NF-κB pathway through NCALD to reduce inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol 93:107165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107165
Zhang Y, Wang M, Zhang X et al (2022) Helicid improves lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of C6 cells by regulating SH2D5 DNA methylation via the CytC/caspase9/caspase3 signaling pathway. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2022:9242827. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9242827
Zhou J, Zhao Y, Guo YJ et al (2021) A rapid juvenile murine model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): chronic intermittent hypoxia exacerbates Western diet-induced NASH. Life Sci 276:119403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119403
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Li Q et al (2022) Downregulation of lncRNA NEAT1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Central-Eur J Immunol 47(1):8–19. https://doi.org/10.5114/ceji.2022.115628
Funding
The research was funded by the Provincial Natural Science Foundation Project of Anhui, China (No. 2208085MH232), the Key Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Provincial Department of Education (grant no. KJ2021A0858), and the Young Scientific Research Project Training Fund of Wannan Medical College (WK2022F06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LSF conceived and designed the study. C. W., W. X., and Z. Y. X. wrote the main manuscript text and did this experiment and gathered data. J. W., N. Z., F. Q. S., and Q. L. analyzed the data. All authors reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent participate
All the experiments were approved by the ethics committee of Wannan Medical College (WNMC-AWE-2023021). No patient was involved in this study.
Animal ethics
The animal experiments were performed following the United States National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH Publication No. 85–23, revised 1985). The animal protocol was approved by the ethics committee of Wannan Medical College (WNMC-AWE-2023021).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Xing, W., Zhang, Y. et al. NLRP3/miR-223-3p axis attenuates neuroinflammation induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 342 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01268-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01268-w