Abstract
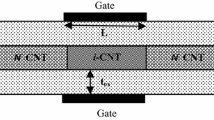
A mathematical model for the effect of oxide thickness on ambient conduction is provided in the Schottky Barrier Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Field Effect Transistor (SB-CNTFET). To develop them as the future of IC (integrated circuit) technology, the suppression of ambipolar behaviour in SB-CNTFET is imperative. The ambipolar nature of SB-CNTFET contributes to a high amount of leakage current. tox ≈ 49.91nm uses a dielectric of gate oxide with a thickness to inhibit the ambipolar behaviour. In an SB-CNTFET, the conductance is regulated by the electrical field at the source/drain contacts and the band bending length at the contacts is determined by tox. Therefore, the prime parameter tox that affects the Schottky barrier width and the subthreshold area. The suppression of ambipolar property is presented. The SB-CNTFET is produced using high-K dielectrics such as Zirconium dioxide. This work discusses the suppression of ambipolar activity in SB-CNTFETs without reducing the Ion current using an appropriate dielectric with optimum thickness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas I, Saeed T, Alhothuali M (2021) Hyperbolic two-temperature photo-thermal interaction in a semiconductor medium with a cylindrical cavity. Silicon 13(6):1871–1878
Arefinia Z, Orouji AA (2009) Novel attributes in the performance and scaling effects of carbon nanotube field-effect transistors with halo doping. Superlattices Microstruct 45(6):535–546
Assiri AS, Hussien AG, Amin M (2020) Ant lion optimization: variants, hybrids, and applications. IEEE Access 8:77746–77764
Atzori L, Iera A, Morabito G (2010) The internet of things: A survey. Comput Netw 54 (15):2787–2805
Avouris P, Appenzeller J, Martel R, Wind SJ (2003) Carbon nanotube electronics. Proc IEEE 91(11):1772–1784
Bao Z, Cui G, Chen J, Sun T, Xiao Y (2018) A novel random walk algorithm with compulsive evolution combined with an optimum-protection strategy for heat exchanger network synthesis. Energy 152:694–708
Behera TM, Mohapatra SK, Samal UC, Khan MS, Daneshmand M, Gandomi AH (2019) I-sep: An improved routing protocol for heterogeneous wsn for iot-based environmental monitoring. IEEE Internet Things J 7(1):710–717
Behera TM, Mohapatra SK, Samal UC, Khan MS, Daneshmand M, Gandomi AH (2019) Residual energy-based cluster-head selection in wsns for iot application. IEEE Internet Things J 6(3):5132–5139
Behera TM, Samal UC, Mohapatra SK (2018) Energy-efficient modified leach protocol for iot application. IET Wirel Sens Syst 8(5):223–228
Bhatt VD, Joshi S, Becherer M, Lugli P (2017) Flexible, low-cost sensor based on electrolyte gated carbon nanotube field effect transistor for organo-phosphate detection. Sensors 17(5):1147
Chen W, Zhang Z, Feng Z, Chen Y, Jiang K, Fan S, Iskander M (2008) Measurement of polarized nano-material (pnm) for microwave applications. In: 2008 IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium digest. IEEE, pp 1577–1580
Choi J, An SJ (2020) Backside metallization of ag–sn–ag multilayer thin films and die attach for semiconductor applications. J Electron Mater: 1–7
Dürkop T, Getty S, Cobas E, Fuhrer M (2004) Extraordinary mobility in semiconducting carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett 4(1):35–39
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: MHS’95. Proceedings of the sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science. IEEE, pp 39–43
Elhadidy H, Mahi F, Franc J, Musiienko A, Dedic V, Schneeweiss O (2019) Calculations of high-frequency noise spectral density of different cdte metal–semiconductor–metal schottky contacts. J Electron Mater 48(12):7806–7812
Endoh T, Momma Y (2007) Study of 30-nm double-gate mosfet with halo implantation technology using a two-dimensional device simulator. IEICE Trans Electron 90(5):1000–1005
Guo G, Mandal M, Jing Y (2012) A robust detector of known signal in non-gaussian noise using threshold systems. Signal Process 92(11):2676–2688
Guo J, Datta S, Lundstrom M (2004) A numerical study of scaling issues for schottky-barrier carbon nanotube transistors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 51(2):172–177
Huo X, Zhang M, Chan PC, Liang Q, Tang Z (2004) High frequency s parameters characterization of back-gate carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. In: IEDM technical digest. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2004. IEEE, pp 691–694
Hwang H, Lee DH, Hwang JM (1996) Degradation of mosfets drive current due to halo ion implantation. In: International electron devices meeting. Technical Digest. IEEE, pp 567–570
Ieong M, Narayanan V, Singh D, Topol A, Chan V, Ren Z (2006) Transistor scaling with novel materials. Materials Today 9(6):26–31
Javey A, Guo J, Wang Q, Lundstrom M, Dai H (2003) Ballistic carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Nature 424(6949):654–657
Javey A, Kong J (2009) Carbon nanotube electronics. Springer Science & Business Media
Jiang L, Li T, Jing N, Kim NS, Guo M, Liang X (2017) Cnfet-based high throughput simd architecture. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 37 (7):1331–1344
John D, Castro L, Pereira P, Pulfrey D (2004) A schrödinger-poisson solver for modeling carbon nanotube fets. In: Proc. NSTI Nanotech, vol 3
Kilic H, Yuzgec U, Karakuzu C (2020) A novel improved antlion optimizer algorithm and its comparative performance. Neural Comput and Applic 32(8):3803–3824
Kumar A, Srivastava S, Saxena S, Tripathi SL (2020) (ba/pb) x sr 1- x tio 3 based capacitive sensor with lanio 3 electrode for higher tunability. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31(22):20387–20399
Lin YM, Appenzeller J, Avouris P (2004) Ambipolar-to-unipolar conversion of carbon nanotube transistors by gate structure engineering. Nano Lett 4(5):947–950
Liu F, Chen W, Zhang Z, Feng Z, Chen Y, Zhang H (2009) Measurement on dipole antenna with light polarized nano-material (pnm) textile reflector. In: 2009 IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium digest. IEEE, pp 1069–1072
Mendiratta N, Tripathi SL (2020) A review on performance comparison of advanced mosfet structures below 45 nm technology node. J Semicond 41(6):061401
Messaoud RB (2020) Extraction of uncertain parameters of double-diode model of a photovoltaic panel using ant lion optimization. SN Appl Sci 2(2):1–8
Monica PR, Sreedevi V (2019) Suppression of ambipolar conduction in schottky barrier carbon nanotube field effect transistors: Modeling, optimization using particle swarm intelligence, and fabrication. Comput Model Eng Sci 119(3):577–591
Naderi A, Keshavarzi P, Orouji AA (2011) Ldc–cntfet: A carbon nanotube field effect transistor with linear doping profile channel. Superlattices Microstruct 50(2):145–156
Nouri-Bayat R, Kashani-Nia AR (2017) Designing a carbon nanotube field-effect transistor with high transition frequency for ultra-wideband application. Engineering 9(1):22–35
Odintsov AA (2000) Schottky barriers in carbon nanotube heterojunctions. Phys Rev Lett 85 (1):150
Pourfath M (2007) Numerical study of quantum transport in carbon nanotube-based transistors. Ph.D thesis
Radosavljević M, Heinze S, Tersoff J, Avouris P (2003) Drain voltage scaling in carbon nanotube transistors. Appl Phys Lett 83(12):2435–2437
Ramezani M, Bahmanyar D, Razmjooy N (2020) A new optimal energy management strategy based on improved multi-objective antlion optimization algorithm: applications in smart home. SN Appl Sci 2 (12):1–17
Raychowdhury A (2007) Designing low-power and high-performance digital circuits with carbon nanotube transistors. Ph.D. thesis, Purdue University
Samal A, Tripathi SL, Mohapatra SK (2020) A journey from bulk mosfet to 3 nm and beyond. Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Materials: 1–13
Sirugudi H, Gadgil S, Vudadha C (2020) A novel low power ternary multiplier design using cnfets. In: 2020 33rd International conference on VLSI design and 2020 19th International conference on embedded systems (VLSID). IEEE, pp 25–30
Soref R (2010) Silicon photonics: a review of recent literature. Silicon 2(1):1–6
Thai TT, Yang L, DeJean GR, Tentzeris MM (2011) Nanotechnology enables wireless gas sensing. IEEE Microw Mag 12(4):84–95
Vandana B, Kumar DJ, Mohapatra SK, Lata TS (2018) Impact of channel engineering (si1-0.25 ge0. 25) technique on gm (transconductance) and its higher order derivatives of 3d conventional and wavy junctionless finfets (jlt). Facta universitatis-series: Electronics and Energetics 31(2):257– 265
Xuan CT, Thuy NT, Luyen TT, Huyen TT, Tuan MA (2017) Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor for dna sensing. J Electron Mater 46(6):3507–3511
Yan X, Xiao Y, Li Z (2006) Effects of intertube coupling and tube chirality on thermal transport of carbon nanotubes. J Appl Phys 99(12):124305
Yang K, Yi Z, Jing Q, Yue R, Jiang W, Lin D (2013) Sonication-assisted dispersion of carbon nanotubes in aqueous solutions of the anionic surfactant sdbs: The role of sonication energy. Chin Sci Bull 58(17):2082–2090
Yang Q, Scott D, Chung T, Stillman G (2000) Optimization of emitter cap growth conditions for ingap/gaas hbts with high current gain by lp-mocvd. J Electron Mater 29(1):75–79
Yoon Y, Fodor J, Guo J (2007) A computational study of vertical partial-gate carbon-nanotube fets. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 55(1):283–288
Zanchetta S, Todon A, Abramo A, Selmi L, Sangiorgi E (2002) Analytical and numerical study of the impact of halos on short channel and hot carrier effects in scaled mosfets. Solid-State Electron 46 (3):429–434
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both the authors have equal contribution in formulating the problems and getting the solution.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
I confirm for the following
1. No financial support from any institution or authors.
2. No conflicts of interest.
3. No research involving animals.
4. No research involving humans as subjects.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, G., Agrawal, S. Ant Lion Optimizer for Suppression of Ambipolar Conduction in Schottky Barrier Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors. Silicon 14, 5809–5817 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01353-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01353-4