Abstract
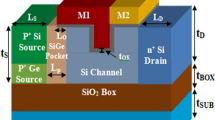
In this paper, the electrical characteristics of a low power steep-slope vertical tunnel field effect transistor (VTFET) is introduced with dual lateral channel in the source sidewall, which can considerably improve the device performance in comparison with the planar tunnel field effect transistor (TFET). The results demonstrate that unlike the conventional TFET with limited tunneling junction at the source/channel interface, the band to band tunneling area in VTFET is created along the entire length of the source region from the both sides, which amplifies the tunneling rate. The results demonstrate that on/off current ratio of 8.36e+7 and subthreshold swing (SS) of 10 mV/dec has been achieved for the VTFET in comparison with the on/off current ratio of 9.79e+5 and SS = 31 mV/dec for the planar TFET, respectively. Sensitivity analysis is conducted via calculating the standard deviation and mean value of main electrical measures as a function of various design parameters. It is indicated that gate workfunction and source doping density are critical design parameters that may fundamentally affect the efficiency of the device. An important feature of the proposed device is the insensitivity of the off-state current and subthreshold swing to the channel length scaling and drain bias, which exhibits VTFET promising potential for future low-power circuits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mukhopadhyay A, Maiti TK, Bhattacharya S, Iizuka T, Kikuchihara H, Miura-Mattausch M et al (2019) Prevention of highly power-efficient circuits due to short-channel effects in MOSFETs. IEICE. Trans. Electron. 102(6):487–494
Pourghaderi MA, Pham AT, Ilatikhameneh H, Kim J, Park HH, Jin S et al (2017) Universality of short-channel effects on ultrascaled MOSFET performance. IEEE. Electron. Device Lett. 39(2):168–171
Ahangari Z (2018) Performance investigation of a semi-junctionless type II heterojunction tunnel field effect transistor in nanoscale regime. Micro Nano Lett. 13(8):1165–1169
Bentrcia T, Djeffal F, Ferhati H, Dibi Z (2020) A comparative study on scaling capabilities of Si and SiGe nanoscale double gate tunneling FETs. Silicon 12(4):945–953
Chandan BV, Nigam K, Sharma D, Tikkiwal VA (2019) A novel methodology to suppress ambipolarity and improve the electronic characteristics of polarity-based electrically doped tunnel FET. Appl. Phys. A 125(2):81
Bagga N, Chauhan N, Gupta D, Dasgupta S (2019) A novel twofold tunnel FET with reduced miller capacitance: proposal and investigation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 66(7):3202–3208
Lu SC, Mohamed M, Zhu W (2016) Novel vertical hetero-and homo-junction tunnel field-effect transistors based on multi-layer 2D crystals. 2D Mater. 3(1):011010
Kim SW, Choi WY (2016) Hump effects of germanium/silicon heterojunction tunnel field-effect transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 63(6):2583–2588
Zhu J, Zhao Y, Huang Q, Chen C, Wu C, Jia R, Huang R (2017) Design and simulation of a novel graded-channel heterojunction tunnel FET with high ${I} _ {\scriptscriptstyle\text {ON}}/{I} _ {\scriptscriptstyle\text {OFF}} $ ratio and steep swing. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 38(9):1200–1203
Hu VPH, Wang CT (2018) Optimization of III–V heterojunction tunnel FET with non-uniform channel thickness for performance enhancement and ambipolar leakage suppression. Japan. J. Appl. Phys. 57(4S):04FD18
Sahu SA, Goswami R, Mohapatra SK (2020) Characteristic enhancement of hetero dielectric DG TFET using SiGe pocket at source/channel interface: proposal and investigation. Silicon 12(3):513–520
Loan SA, Alharbi AG, Rafat M (2018) Ambipolar leakage suppression in electron–hole bilayer TFET: investigation and analysis. J. Comput. Electron. 17(3):977–985
Alper C, Palestri P, Padilla JL, Ionescu AM (2016) The electron-hole bilayer TFET: dimensionality effects and optimization. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 63(6):2603–2609
Seo JH, Yoon YJ, Cho S, Kang IM, Lee JH (2019) Design optimization and analysis of InGaAs/InAs/InGaAs heterojunction-based electron hole bilayer tunneling FETs. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 19(10):6070–6076
Kim S, Choi WY, Park BG (2018) Vertical-structured electron-hole bilayer tunnel field-effect transistor for extremely low-power operation with high scalability. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65(5):2010–2015
Fahad MS, Srivastava A, Sharma AK, Mayberry C, Mohsin KM (2016) Silicene nanoribbon tunnel field effect transistor. ECS Trans. 75(5):175
Ni Z, Zhong H, Jiang X, Quhe R, Luo G, Wang Y, Ye M, Yang J, Shi J, Lu J (2014) Tunable band gap and doping type in silicene by surface adsorption: towards tunneling transistors. Nanoscale 6(13):7609–7618
Samipour A, Dideban D, Heidari H (2019) First principles study of the ambipolarity in a germanene nanoribbon tunneling field effect transistor. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 8(12):M111–M117
Tamersit K (2020) Performance enhancement of an ultra-scaled double-gate graphene nanoribbon tunnel field-effect transistor using channel doping engineering: quantum simulation study. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 122:153287
Kim JH, Kim S, Park BG (2019) Double-gate TFET with vertical channel sandwiched by lightly doped Si. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 66(4):1656–1661
ATLAS (2015) User Manual. Silvaco International, Santa Clara
Lin YK, Khandelwal S, Duarte JP, Chang HL, Salahuddin S, Hu C (2016) A predictive tunnel FET compact model with atomistic simulation validation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 64(2):599–605
Vandenberghe WG, Verhulst AS, Kao KH, Meyer KD, Sorée B, Magnus W, Groeseneken G (2012) A model determining optimal doping concentration and material’s band gap of tunnel field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(19):193509
Boucart K, Ionescu AM (2007) Double-gate tunnel FET with high-$\kappa $ gate dielectric. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 54(7):1725–1733
Abdi DB, Kumar MJ (2014) In-built N+ pocket pnpn tunnel field-effect transistor. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 35(12):1170–1172
Shih CH, Dang Chien N (2013) Physical operation and device design of short-channel tunnel field-effect transistors with graded silicon-germanium heterojunctions. J. Appl. Phys. 113(13):134507
Choi WY, Park BG, Lee JD, Liu TJK (2007) Tunneling field-effect transistors (TFETs) with subthreshold swing (SS) less than 60 mV/dec. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 28(8):743–745
Nagavarapu V, Jhaveri R, Woo JC (2008) The tunnel source (PNPN) n-MOSFET: a novel high performance transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 55(4):1013–1019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahangari, Z., Mahmodi, S. Design and Sensitivity Analysis of Steep-Slope Bi-Channel Vertical Tunnel Field Effect Transistor. Silicon 13, 1917–1924 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00579-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00579-y