Abstract
Background
Obesity in the older adults is a health concern that increases the risk of several life-threatening diseases. Previous research has been revealed that alterations in the gut microbiota composition is related to obesity. So, understanding the gut microbiota changes in older adults’ obesity may help to provide promising strategies for their health management.
Objectives
Here we conducted a systematic review that investigate the alteration of gut microbiota composition in association with obesity and its indices in the older adults.
Design
Systematic review.
Setting
A comprehensive systematic search was performed through PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus and Embase databases for all relative studies up to 2023 with the main search concepts as Microbiota, Obesity and Elderly. The data about gut microbiota in association with obesity indices had been extracted.
Participants
Older adults (≥60 years).
Intervention
None.
Measurements
None.
Results
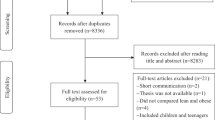
Within 10741 recordes, 11 studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in this systematic review. Most of them indicated the gut microbiota alterations in obese compared with non-obese older adults. However, the gut microbiome composition in obese older adults is affected by other underlying diseases like diabetes and metabolic syndrome. The most important taxa that had abundance alteration in association with obesity in older adults were Christensenellaceae, Porphyromonadaceae and Rikenellaceae, Akkermansia, Blautia, Prevotella, Ruminococcus, Bacteroides and Faecalibacterium.
Conclusion
The gut microbiota composition is associated with obesity in older adults. Considering the other factors affecting the composition of gut microbiota, such as age, underlying diseases and lifestyle, a more accurate conclusion about this matter requires more future studies.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability: All data generated in this study are supported by the published articles in PubMed/Medline, Web of Science, Scopus and Embase databases, and all data generated are included in this published article.
References
Chooi YC, Ding C, Magkos F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism. 2019;92:6–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.09.005.
Bluher M. Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(5):288–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0176-8.
Amin R, Kolahi AA, Sohrabi MR. Disparities in Obesity Prevalence in Iranian Adults: Cross-Sectional Study Using Data from the 2016 STEPS Survey. Obes Facts. 2021;14(3):298–305. https://doi.org/10.1159/000516115.
Vaisi-Raygani A, Mohammadi M, Jalali R, Ghobadi A, Salari N. The prevalence of obesity in older adults in Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2019;19(1):371. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-019-1396-4.
Amininezhad F, Payab M, Sharifi F, Ostovar A, Mehrdad N, Heshmat R, et al. Bone characteristics and metabolic phenotypes of obesity in an Iranian Elderly population: Bushehr Elderly Health Program (BEHP). Arch Osteoporos. 2021;16(1):92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-021-00953-2.
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA. 2012;307(5):491–7. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.39.
Inelmen EM, Sergi G, Coin A, Miotto F, Peruzza S, Enzi G. Can obesity be a risk factor in elderly people? Obes Rev. 2003;4(3):147–55. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1467-789x.2003.00107.x.
Noroozian M. The elderly population in iran: an ever growing concern in the health system. Iran J Psychiatry Behav Sci. 2012;6(2):1–6.
Wannamethee SG, Atkins JL. Muscle loss and obesity: the health implications of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society. 2015;74(4):405–12. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002966511500169X.
Xu Z, Jiang W, Huang W, Lin Y, Chan FKL, Ng SC. Gut microbiota in patients with obesity and metabolic disorders - a systematic review. Genes Nutr. 2022;17(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12263-021-00703-6.
Pinart M, Dotsch A, Schlicht K, Laudes M, Bouwman J, Forslund SK, et al. Gut Microbiome Composition in Obese and Non-Obese Persons: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2021;14(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010012.
Crovesy L, Masterson D, Rosado EL. Profile of the gut microbiota of adults with obesity: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020;74(9):1251–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-020-0607-6.
Castaner O, Goday A, Park YM, Lee SH, Magkos F, Shiow STE, et al. The Gut Microbiome Profile in Obesity: A Systematic Review. Int J Endocrinol. 2018;2018:4095789. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4095789.
Al-Assal K, Martinez AC, Torrinhas RS, Cardinelli C, Waitzberg D. Gut microbiota and obesity. Clinical Nutrition Experimental. 2018;20:60–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yclnex.2018.03.001.
Cornejo-Pareja I, Munoz-Garach A, Clemente-Postigo M, Tinahones FJ. Importance of gut microbiota in obesity. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019;72(Suppl 1):26–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0306-8.
Salazar N, Valdes-Varela L, Gonzalez S, Gueimonde M, de Los Reyes-Gavilan CG. Nutrition and the gut microbiome in the elderly. Gut microbes. 2017;8(2):82–97. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2016.1256525.
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-1.
Tavella T, Rampelli S, Guidarelli G, Bazzocchi A, Gasperini C, Pujos-Guillot E, et al. Elevated gut microbiome abundance of Christensenellaceae, Porphyromonadaceae and Rikenellaceae is associated with reduced visceral adipose tissue and healthier metabolic profile in Italian elderly. Gut microbes. 2021;13(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2021.1880221.
Atzeni A, Galie S, Muralidharan J, Babio N, Tinahones FJ, Vioque J, et al. Gut Microbiota Profile and Changes in Body Weight in Elderly Subjects with Overweight/Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Microorganisms. 2021;9(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020346.
Zhong X, Harrington JM, Millar SR, Perry IJ, O’Toole PW, Phillips CM. Gut Microbiota Associations with Metabolic Health and Obesity Status in Older Adults. Nutrients. 2020;12(8):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082364.
Shardell M, Parimi N, Langsetmo L, Tanaka T, Jiang L, Orwoll E, et al. Comparing Analytical Methods for the Gut Microbiome and Aging: Gut Microbial Communities and Body Weight in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020;75(7):1267–75. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glaa034.
Langsetmo L, Johnson A, Demmer RT, Fino N, Orwoll ES, Ensrud KE, et al. The Association between Objectively Measured Physical Activity and the Gut Microbiome among Older Community Dwelling Men. J Nutr Health Aging. 2019;23(6):538–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-019-1194-x.
Tamura M, Hoshi C, Kobori M, Takahashi S, Tomita J, Nishimura M, et al. Quercetin metabolism by fecal microbiota from healthy elderly human subjects. PLoS One. 2017;12(11):e0188271. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188271.
Lippert K, Kedenko L, Antonielli L, Kedenko I, Gemeier C, Leitner M, et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis associated with glucose metabolism disorders and the metabolic syndrome in older adults. Benef Microbes. 2017;8(4):545–56. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2016.0184.
Sepp E, Kolk H, Loivukene K, Mikelsaar M. Higher blood glucose level associated with body mass index and gut microbiota in elderly people. Microbial ecology in health and disease. 2014;25. https://doi.org/10.3402/mehd.v25.22857.
Karlsson FH, Tremaroli V, Nookaew I, Bergstrom G, Behre CJ, Fagerberg B, et al. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature. 2013;498(7452):99–103. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12198.
Claesson MJ, Jeffery IB, Conde S, Power SE, O’Connor EM, Cusack S, et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature. 2012;488(7410):178–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11319.
Mikelsaar M, Stsepetova J, Hutt P, Kolk H, Sepp E, Loivukene K, et al. Intestinal Lactobacillus sp. is associated with some cellular and metabolic characteristics of blood in elderly people. Anaerobe. 2010;16(3):240–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2010.03.001.
Badal VD, Vaccariello ED, Murray ER, Yu KE, Knight R, Jeste DV, et al. The Gut Microbiome, Aging, and Longevity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2020;12(12):3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123759.
Hasan N, Yang H. Factors affecting the composition of the gut microbiota, and its modulation. PeerJ. 2019;7:e7502. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7502.
Ejtahed HS, Angoorani P, Soroush AR, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Siadat SD, Larijani B. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in obesity: a systematic review. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2020;39(3):65–76. https://doi.org/10.12938/bmfh.2019-026.
Peters BA, Shapiro JA, Church TR, Miller G, Trinh-Shevrin C, Yuen E, et al. A taxonomic signature of obesity in a large study of American adults. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):9749. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28126-1.
Mazier W, Le Corf K, Martinez C, Tudela H, Kissi D, Kropp C, et al. A New Strain of Christensenella minuta as a Potential Biotherapy for Obesity and Associated Metabolic Diseases. Cells. 2021;10(4):823. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040823.
Biagi E, Rampelli S, Turroni S, Quercia S, Candela M, Brigidi P. The gut microbiota of centenarians: Signatures of longevity in the gut microbiota profile. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017;165(Pt B):180–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2016.12.013.
Sakamoto M, Takagaki A, Matsumoto K, Kato Y, Goto K, Benno Y. Butyricimonas synergistica gen. nov., sp. nov. and Butyricimonas virosa sp. nov., butyric acid-producing bacteria in the family ‘Porphyromonadaceae’ isolated from rat faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2009;59(Pt 7):1748–53. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.007674-0.
Shen X, Miao J, Wan Q, Wang S, Li M, Pu F, et al. Possible correlation between gut microbiota and immunity among healthy middle-aged and elderly people in southwest China. Gut Pathog. 2018;10(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13099-018-0231-3.
Ren M, Li H, Fu Z, Li Q. Succession Analysis of Gut Microbiota Structure of Participants from Long-Lived Families in Hechi, Guangxi, China. Microorganisms. 2021;9(12):2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122524.
Hall AB, Tolonen AC, Xavier RJ. Human genetic variation and the gut microbiome in disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2017;18(11):690–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2017.63.
Ozato N, Saito S, Yamaguchi T, Katashima M, Tokuda I, Sawada K, et al. Blautia genus associated with visceral fat accumulation in adults 20–76 years of age. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2019;5(1):28. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41522-019-0101-x.
Yang J, Bindels LB, Segura Munoz RR, Martinez I, Walter J, Ramer-Tait AE, et al. Disparate Metabolic Responses in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet Supplemented with Maize-Derived Non-Digestible Feruloylated Oligo- and Polysaccharides Are Linked to Changes in the Gut Microbiota. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0146144. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146144.
Liu X, Mao B, Gu J, Wu J, Cui S, Wang G, et al. Blautia-a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut microbes. 2021;13(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2021.1875796.
Geerlings SY, Kostopoulos I, de Vos WM, Belzer C. Akkermansia muciniphila in the Human Gastrointestinal Tract: When, Where, and How? Microorganisms. 2018;6(3):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030075.
Abuqwider JN, Mauriello G, Altamimi M. Akkermansia muciniphila, a New Generation of Beneficial Microbiota in Modulating Obesity: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms. 2021;9(5):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9051098.
Cani PD, Depommier C, Derrien M, Everard A, de Vos WM. Akkermansia muciniphila: paradigm for next-generation beneficial microorganisms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;19(10):625–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-022-00631-9.
Biagi E, Franceschi C, Rampelli S, Severgnini M, Ostan R, Turroni S, et al. Gut Microbiota and Extreme Longevity. Curr Biol. 2016;26(11):1480–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.04.016.
Ghosh TS, Shanahan F, O’Toole PW. The gut microbiome as a modulator of healthy ageing. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;19(9):565–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-022-00605-x.
Yang X, Zhang X, Yang W, Yu H, He Q, Xu H, et al. Gut Microbiota in Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Induced Cardiovascular Disease: Role as a Metabolic Organ. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:749125. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.749125.
Valdes AM, Walter J, Segal E, Spector TD. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ. 2018;361:k2179. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k2179.
Dziewiecka H, Buttar HS, Kasperska A, Ostapiuk-Karolczuk J, Domagalska M, Cichon J, et al. Physical activity induced alterations of gut microbiota in humans: a systematic review. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2022;14(1):122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13102-022-00513-2.
Tzemah Shahar R, Koren O, Matarasso S, Shochat T, Magzal F, Agmon M. Attributes of Physical Activity and Gut Microbiome in Adults: A Systematic Review. Int J Sports Med. 2020;41(12):801–14. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1157-9257.
Juarez-Fernandez M, Porras D, Garcia-Mediavilla MV, Roman-Saguillo S, GonzalezGallego J, Nistal E, et al. Aging, Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Diseases: Management through Physical Exercise and Nutritional Interventions. Nutrients. 2020;13(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010016.
Samper-Ternent R, Al Snih S. Obesity in Older Adults: Epidemiology and Implications for Disability and Disease. Rev Clin Gerontol. 2012;22(1):10–34. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0959259811000190.
Kociszewska D, Vlajkovic S. Age-Related Hearing Loss: The Link between Inflammaging, Immunosenescence, and Gut Dysbiosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137348.
Angoorani P, Ejtahed HS, Siadat SD, Sharifi F, Larijani B. Is There Any Link between Cognitive Impairment and Gut Microbiota? A Systematic Review. Gerontology. 2022;68(11):1201–13. https://doi.org/10.1159/000522381.
Acknowledgements
Declared none.
Funding
Funding: This study was funded by the Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (Number: 1401-3-91-1213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Additional information
Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tavassol, Z.H., Ejtahed, HS., Atlasi, R. et al. Alteration in Gut Microbiota Composition of Older Adults Is Associated with Obesity and Its Indices: A Systematic Review. J Nutr Health Aging 27, 817–823 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-023-1988-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-023-1988-8