Abstract
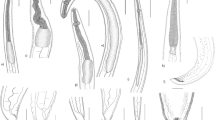
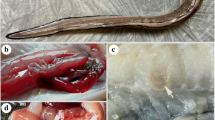
The occurrence of Genus Anisakis nematode larvae in marine fishes and cephalopods is epidemiologically important because Anisakis simplex larval stage can cause a clinical disease in humans when infected hosts are consumed raw. Common squid (Todarodes pacificus) from Korean waters were investigated for anisakid nematodes infection during 2009∼2011. In total, 1,556 larvae were collected from 615 common squids and 732 of them were subsequently identified by PCR-RFLP analysis of ITS rDNA. Depending on the sampling locations, the nematode larvae from common squid showed different prevalence, intensity and species distribution. A high prevalence (P) and mean intensity (MI) of infection were observed in the Yellow Sea (n = 250, P = 86.0%, MI = 5.99 larvae/host) and the southern sea of Korea (n = 126, P = 57.1%, MI = 3.36 larvae/host). Anisakis pegreffii was dominantly found in common squid from the southern sea (127/ 140, 90.7%) and the Yellow Sea (561/565, 98.9%). In contrast, the P and MI of infection were relatively low in the East Sea (n = 239, P = 8.37%, MI = 1.25 larvae/host). A. pegreffii was not found from the East Sea and 52.0% (13/25) of the nematodes were identified as A. simplex. Most of them were found in the body cavity or digestive tract of common squid, which are rarely consumed raw by humans. Considering the differenences in anisakid nematode species distribution and their microhabitat in common squid, it remains unclear whether common squid plays an important role in the epidemiology of human anisakis infection in Korea. Further extensive identification of anisakid nematodes in common squid, with geographical and seasonal information will be necessary.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe N, Ohya N, Yanagiguchi R (2005) Molecular characterization of Anisakis pegreffii larvae in Pacific cod in Japan. J Helminthol 79:303–306
Abollo E, Gestal C, Pascual S (2001) Anisakis infestation in marine fish and cephalopods in Galician waters: an update perspective. Parasitol Res 87:492–499
Abollo E, Paggi L, Pascual S, D’Amelio S (2003) Occurrence of recombinant genotypes of Anisakis simplex s.s. and Anisakis pegreffii (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in an area of sympatry. Infect Genet Evol 3:175–181
Audicana MT, Kennedy MW (2008) Anisakis simplex: from obscure infectious worm to inducer of immune hypersensitivity. Clin Microbiol Rev 21:360–379
Bower SM, Margolis L (1991) Potential use of helminth parasites in stock identification of flying squid, Ommastrephes bartrami, in North Pacific waters. Can J Zool 69:1124–1126
Bower JR, Miyhara K (2005) The diamond squid (Thysanoteuthis rhombus): a review of the fishery and recent research in Japan. Fish Res 73:1–11
Boyle P, Rodhouse P (2005) Cephalopods: ecology and fisheries. Blackwell Publishing, London, pp 222–296
Bush AO, Lafferty KD, Lotz JM, Shostak AW (1997) Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J Parasitol 83:575–583
Chai JY, Chu YM, Sohn WM, Lee SH (1986) Larval anisakids collected from the yellow corvina in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 24:1–11
Cho MH, Lee SJ, Joung HC, Kang JW, Lee KW, Kim YD, Cheon GJ (2012) A case of gastric and colonic submucosal tumors after the removal of 51 Anisakis larvae. Korean J Med 82: 453–458
Choi SH, Kim J, Jo JO, Cho MK, Yu HS, Cha HJ, Ock MS (2011) Anisakis simplex larvae: infection status in marine fish and cephalopods purchased from the Cooperative Fish Market in Busan, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 49:39–44
Chun KS, Kim SW (1995) Infection status of Todarodes pacificus (Mollusca:Cephalopoda) with Anisakid larvae in the South Sea, Korea. J Korean Soc Oceanogr 30:197–202
Chun KS, Kim SW (1996) Infection status of Todarodes pacificus (Mollusca:Cephalopoda) with Anisakid larvae in the markets from Jumunjin. J Korean Soc Oceanogr 31:55–57
D’Amelio S, Mathiopoulos KD, Santos CP, Pugachev ON, Webb SC, Picanco M, Paggi L (2000) Genetic markers in ribosomal DNA for the identification of members of the genus Anisakis (Nematoda: Ascaridoidea) defined by polymerase chain reactionbase restriction fragment length polymorphism. Int J Parasitol 30:223–226
Du C, Zhang L, Shi M, Ming Z, Hu M, Gasser RB (2010) Elucidating the identity of Anisakis larvae from a broad range of marine fishes from the Yellow Sea, China, using a combined electrophoretic-sequencing approach. Electrophoresis 31:654–658
Hibi Y, Ogata J, MImuro A, Ito K, Hakamada Y (2009) A case of small intestinal intussusceptions caused by anisakidosis. Japanese J Gastroenterol Surg 42:669–673 (In Japanese)
Hochberg NS, Hamer DH (2010) Anisakidosis: perils of the deep. Clin Inf Dis 50:806–812
Im KI, Yong TS, Shin HJ, Kim BH, Moon SI (1990) Gastric anisakiasis in Korea, with review of 47 cases. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 21:1–7
Im KI, Shin HJ, Kim BH, Moon SI (1995) Gastric anisakiasis cases in Cheju-do, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 33:179–186 (In Korean)
Jang GL, Chung JY, Kim WK, Kim KS, Kim JG, Kim YJ, Park BK, Hwang SS, Kang MK (1989) Clinical observation of 12 cases of gastric anisakiasis. Korean J Int Med 37:403–410 (In Korean)
Kim CH, Chung BS, Moon YI, Chun SH (1971) A case report on human infection with Anisakis sp. in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 9:39–43 (In Korean)
Lee MW, Cheon DS, Choi CS (2009) Molecular genotyping of Anisakis species from Korea sea fish by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP). Food Control 20:623–626
Mattiucci S, Nascetti G (2008) Advances and trends in the molecular systematics of Anisakid nematodes, with implications for their evolutionary ecology and host-parasite co-evolutionary processes. Adv Parasitol 66:47–248
Nadler SA, Hudspeth DSS (2000) Phylogeny of the Ascaridoidea (Nematoda: Ascaridida) based on three genes and morphology: hypotheses of structural and sequence evolution. J Parasitol 86:380–393
Nagasawa K, Moravec F (1995) Larval anisakid nematodes of Japanese common squid (Todarodes pacificus) from the Sea of Japan. J Parasitol 81:69–75
Nagasawa K, Moravec F (2002) Larval anisakid nematodes from four species of squid (Cephalopoda: Teuthoidea) from the central and western North Pacific Ocean. J Nat His 36:883–891
Pascual S, Gonzalez A, Arias C, Guerra A (1996) Biotic relationships of Illex coindetii and Todaropsis eblanae (Cephalopoda, Ommastrephidae) in the northeast Atlantic: Evidence from parasites. Sarsia 81:265–274
Pascual S, Hochberg FG (1996) Marine parasites as biological tags of cephalopod hosts. Parasitol Today 12:324–327
Pontes T, D’Amelio S, Costa G, Paggi L (2005) Molecular characterization of larval Anisakid nematodes from marine fishes of Madeira by a PCR-based approach, with evidence for a new species. J Parasitol 91:1430–1434
Quiazon KMA, Yoshinaga T, Ogawa K (2011) Distribution of Anisakis species larvae from fishes of the Japanese waters. Parasitol Int 60:223–226
Smith JW, Wootten R (1978) Anisakis and anisakiasis. Adv Parasitol 16:93–163
Song SB, Hwang EG (1992) Infection status of larval anisakids in Astroconger myriaster collected from the Southern Sea near Pusan. Korean J Parasitol 30:263–267 (In Korean)
Song SB, Lee SR, Chung HH and Han NS (1995) Infection status of anisakid larvae in anchovies purchased from local fishery market near southern and eastern sea in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 33:95–99 (In Korean)
Suzuki J, Murata R, Hosaka M, Araki J (2010) Risk factors for human Anisakis infection and association between the geographic origins of Scomber japonicus and anisakid nematodes. Int J Food Microbiol 137:88–93
Takahara H, Sakurai Y (2010) Infection of the Japanese common squid, Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda:Ommastrephidae) by larval anisakid nematodes. Fish Res 106:156–159
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1569
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: 362 improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment 363 through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and 364 weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Umehara A, Kawakami Y, Matsui T, Araki J, Uchida A (2006) Molecular identification of Anisakis simplex sensu stricto and Anisakis pegreffii (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from fish and cetacean in Japanese waters. Parasitol Int 55:267–271
Umehara A, Kawakami Y, Araki J, Uchida A (2007) Molecular identification of the etiological agent of the human anisakiasis in Japan. Parasitol Int 56:211–215
Umehara A, Kawakami Y, Ooi HK, Uchida A, Ohmae H, Sugiyama H (2010) Molecular identification of Anisakis type I larvae isolated from hairtail fish off the coasts of Taiwan and Japan. Int J Food Microbiol 143:161–165
Wasko AP, Martins C, Oliveira C, Foresti F (2003) Non-destructive genetic sampling in fish. An improved method for DNA extraction from fish fins and scales. Hereditas 138:161–165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Setyobudi, E., Jeon, CH., Choi, K. et al. Molecular identification of anisakid nematodes third stage larvae isolated from common squid (Todarodes pacificus) in Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 48, 197–205 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-013-0016-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-013-0016-z