Abstract
Background
Nematodes of the family Anisakidae are parasites of many fishes and aquatic invertebrates which act as intermediate or paratenic hosts, while mammals and fish-eating birds are definitive hosts. Infective L3 larvae may be incidentally taken by human through eating raw or undercooked fish meat, causing anisakidosis. The main purpose of this study is to provide a basis for the future investigations to discover the genetic diversity of this widely distributed parasite nematodes of fishes and fish eating animals and their effect on fisheries and public health in Egypt and worldwide.
Results
One thousand, one hundred and fifteen specimens belong to nine fish species were collected from Lake Nasser, Egypt, and examined for infection with Anisakid larvae. Four fish species (Oreochromis niloticus, Tilapia galilaea, Lates niloticus, and Hydrocynus forskahlii) were found infected with third stage larvae of Contracaecum spp. No other Anisakid nematodes were detected. Larvae were found in the body cavity adhering to mesenteries by a thin membrane, except in Oreochromis niloticus and Tilapia galilaea were found free in branchial chambers. The highest prevalence was recorded in L. niloticus (100%) and H. forskahlii (82%). The mean intensity of infections were 0.17–4.12 and 5.1–10.3 in L. niloticus and H. forskahlii respectively. For further identification, the internal transcribed spacers (ITS-1 and ITS-2) of nuclear ribosomal DNA from isolated larvae (n = 54) were amplified by PCR, followed by single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis which revealed five possible profiles.
Conclusion
Light and scanning electron microscope studies revealed that all anisakid larvae in the present study showed the most typical features of the genus Contracaecum. The sequencing (n = 28) and sequence and phylogenetic analyses showed that the present nematode larvae are likely belonging to C. multipapillatum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Parasites usually influence the quality and marketing of commercially produced fish and may contribute to high fish mortalities and economic losses or threaten the abundance and diversity of fish species, accordingly, raising a lot of public health concerns, particularly in regions where raw or smoked fish are eaten (Adams, Murrell, & Cross, 1997; Paperna, 1996; Barson, 2004).
Nematodes of the family Anisakidae are parasites of many fishes and aquatic invertebrates which acting as intermediate or paratenic hosts, while mammals and fish-eating birds are definitive hosts. The most widespread genera are Anisakis, Pseudoterranova, and Contracaecum which have similar life cycles. Third stage larvae (L3) of Contracaecum (Railliet et Henry, 1912) were found usually in the body cavity, branchial chambers, and mesenteries of the fish while the adults were found in the gut of the fish-eating birds as mentioned by Whitfield and Heeg (1977). It was reported in Cichlids and Catfish in different African countries, such as Egypt (Amin, 1978), East Africa (Aloo, 2001) and South Africa (Boomker, 1982, 1994; Van As & Basson, 1984). These larvae were the most prevalent nematode parasite identified from the mesenteries of Clarias gariepinus, Barbus acutirostris, B. tsanensis, and B. brevicephalus and from the pericardial cavity of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) captured from Lake Tana Ethiopia (Yimer & Enyew, 2003). Kaddumukasa, Kaddu, and Makanga (2006) investigated the positive correlation between intensity of infection and length of Nile tilapia, O. niloticus, in Lake Wamala. The high spread of Contracaecum in fish might influence their health; subsequently, it can affect the commercial value of fish, particularly when it was found in the musculature, and thus represent some economic loss for fisheries industry (Angot & Brasseur, 1995). At the point when in the stomach of the definitive host, L3 molts to become L4 and both the larvae and the adults may influence the host health negatively (Martins, Onaka, & Fenerick Jr., 2005; Girişgin, Alasonyalilar-Demirer, & Girişgin, 2012). In case of the larvae are incidentally taken by human through eating raw or undercooked fish meat, they may cause anisakidosis, a zoonotic infection causing stomach pains, fever, diarrhea, and vomiting (Sakanari & McKerrow, 1989; Kaneko, 1991; Arslan, Dinçoğlu, & Güven, 1995; Audicana, Ansotegui, de Corres, & Kennedy, 2002; Palm, 2004; Shamsi & Butcher, 2011).
The identification of Contracaecum spp. from various host groups attracted attention of scientists in different geographical parts of the world using both light and scanning electron microscopy for morphological examination, as well as the evaluation of genetic markers as the ribosomal internal transcribed spacers (ITS-1 and ITS-2) for the molecular characterization (Nadler, D'Amelio, Dailey, Paggi, Siu, et al., 2005; D'Amelio, Barros, Ingrosso, Fauquier, Russo, et al., 2007; Shamsi, Gasser, Beveridge, & Shabani, 2008; Shamsi, Norman, Gasser, & Beveridge, 2009; Shamsi, Gasser, & Beveridge, 2011; Garbin, Mattiucci, Paoletti, González-Acuña, & Nascetti, 2011; Garbin, Mattiucci, Paoletti, Diaz, Nascetti, et al., 2013; Jabbar, Fong, Kok, Lopata, Gasser, et al., 2013; Borges, Santos, Brandã, Santos, Miranda, et al., 2014).
The Fishes are an important source of protein for humans and other animals. The fish industry likewise provides livelihood chances to numerous individuals, as well as income at household and national levels (FAO, 1996).
Lake Nasser is a reservoir constructed by the High Dam in southern part in Egypt and extends to the second cataract in Sudan. It is about 480 km long, 300 km in Egypt (Lake Nasser), and 180 km in Sudan (Lake Nubia). Lake Nasser is considered as important source of fish and of considerable economic potential in Egypt. Its estimated commercial value of the fishery (including both fresh and salted fish) is around US $17 million (Béné, Bandi, & Durville, 2008).
Fifty-seven species of fish belonging to 16 families were recorded in Lake Nasser. Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus), Nile perch (Lates niloticus), Tiger fish (Hydrocynus forskahlii), and Alestes spp. are the most common species and important for the fishery (Latif, 1974; Rashid, 1995). While Tilapia and Nile perch are landed fresh, Tiger fish and Alestes are usually processed before being sold as salted fish (Bishai, Abdel-Malek, & Khalil, 2000).
However, the parasitic fauna of fishes from different inland water in Egypt were studied by several investigators; only few published data based on morphological characteristics were performed on helminth infections in Lake Nasser (Saoud & Wannas, 1984; Al-Bassel, 1992; Saad, 2007; Ezzat, ElKorashey, & Sherif, 2012). Thus, our knowledge about the prevalence, abundance, and the genetic diversity of nematodes of fishes is still limited. The present investigation is the first study to use an integrated molecular and morphological approach toward identification and detailed description of socioeconomically important anisakid nematodes from four infected out of nine examined species of fishes in Lake Nasser, Egypt.
Methods
Parasite
Guidelines and rules of Aswan University were followed in terms of dealing with and use of animals. Approvals from the committee of Graduate Studies and from the College Council were taken before starting the study.
During 2 years, from November 2013 to October 2015,1115 fish specimens were collected from Lake Nasser, Egypt, and examined for infection with anisakid larvae. These fishes were Oreochromis niloticus (n = 73); Tilapia galilaea (n = 712); Lates niloticus (n = 85); Synodontis frontosus (n = 40); Mormyrus caschive (n = 53); Chrysichthys auratus (n = 43); Hydrocynus forskahlii (n = 35); Alestes baremose (n = 44); and Lebeo niloticus (n = 30). They were caught from 6 different localities (Khors) of the Lake, Allaqi, Dehmet, Khor Ghazal, Khor Maria, Khor Galal, and Wady abyad. Then, they were immediately transported to the laboratory for parasite examinations. Subsequently, they were dissected and the alimentary tract, liver, and gills were taken out and examined in physiological saline. Also, the body cavity was examined for investigation of nematode infection. The worms were collected and washed extensively with physiological saline. The prevalence and intensity were calculated for each fish species.
Morphological identification
Each individual nematode was divided into three pieces. Small pieces of the middle parts were kept in − 20 in 70% ethanol for molecular studies, while the anterior and posterior parts fixed in hot 70% ethanol (60–70 °C) for relaxing their bodies, and then preserved in 70% ethanol with few drops of glycerin to avoid distortion of the outer layer of the cuticle. Before light microscopic study, worms were cleared in Lactophenol for 24 h. All measurements were made specifically with an eyepiece micrometer and given in millimeters, unless mentioned otherwise. The photomicrographs were taken for the obtained nematodes using Olympus light microscope attached with a camera model HBS (HB2) and digital microscope model Olympus CX41. Identifications were based on key features and descriptions (Yamaguti, 1961; Nadler & Hudspeth, 1998; Anderson, 2000; Martins et al., 2005; Olivero-Verbel, Baldiris-Avila, Guette-Fernandez, Benavides-Alvarez, Mercado-Camargo, et al., 2006). For the scanning electron microscope (SEM) examinations, specimens were fixed in 5% glutaraldehyde solution for 24 h and then washed five times in Sodium cacodylate buffer solution (15 min each). Post-fixation, specimens were rinsed in 1% of osmic acid for 2 h. After washing, three changes in Sodium cacodylate buffer solution (15 min each) took place, and then the specimens were dehydrated in ascending grade of alcohols; 30, 50, 70, 90, and 100% alcohol for 30 min each. Then, the specimens were dried to acritical point as a result of exposure to 25 °C. Subsequently, samples were placed on holder and were coated by a very thin layer of gold (thickness of 150–200 Angstroms). Finally, the specimens were examined by scanning the electron microscope type JSM 5400 LV: Jeol.
Molecular characterization
Genomic DNA isolation, PCR, and sequencing
Genomic DNA was isolated from individual larvae (n = 54), as described before (Younis, Geisinger, Ajonina-Ekoti, Soblik, Steen, et al., 2011) with slight modifications. In brief, the individual parasite materials were digested for 3–4 h at 56 °C with proteinase K in ALT buffer (Dneasy kit, Qiagen) under a constant agitation. gDNA extracted with the standard phenol⁄chloroform method and treated with RNase A was then precipitated with 5.2 M ammonium acetate and dissolved in 20–30 μl HPLC water. Concentrations were determined by spectrophotometry.
The specific primer sets SS1/NC13R and SS2/NC2 were used to amplify the two nuclear ribosomal markers ITS-1 and ITS-2 respectively, under the same conditions as described previously (Zhang, Hu, Shamsi, Beveridge, Li, et al., 2007). The negative control (gDNA from intact fish muscles and non-DNA) samples were used. The PCR products were analyzed by 1% w/v agarose gel, stained with ethidium bromide and photographed using a gel documentation system, were then purified using QIAquick® PCR purification kit (Qiagen), according to the manufacturer’s protocols. The resulted products were sequenced by a dideoxy termination method using an applied Biosystems 373 DNA sequencer (LGC Genomics GmbH, Germany) in the two directions (forward and reverse) by the same PCR-used primers.
Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)
All amplicons (ITS-1 and ITS-2) were subjected to SSCP analysis (Gasser, Hu, Chilton, Campbell, Jex, et al., 2006) to screen nucleotide sequence variation among amplicons. In details, 5 μl of individual amplicons were mixed with 10 μl of loading buffer (75% formamide, 2.5 mM Tris, 0.0075 bromophenol blue, 0.0075% xylene cyanol, 15% glycerol, 15 mM EDTA), denaturated at 96 °C for 15 min and snapped cooling on a freeze block (− 20 °C) for 5 min. Individual samples (15 μl) were loaded into the wells of a 10% acrylamide/bis gel (29:1), containing 7% glycerol, and 1X TBE buffer and casted in mini protein tetra vertical chamber (Bio-Rad). Gels were subjected to electrophoresis for 7 h at constant power (70 V) and temperature 8 °C in a pre-cooled 1XTBE. The gels were then stained with ethidium bromide (1 μg/ml in 1XTBE buffer for 15 min), de-stained in 1XTBE for 10 min and photographed by an ultraviolet transilluminator.
Computer-based sequence analysis
For each sequence, the NCBI Blast program was used for homology search (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). After that, each sequence (forward) was compared to its complement (reverse) and then adjusted manually to get one sequence. Subsequently, the resulted sequences were aligned to each other and to the most homologous sequences in the database using CLUSTALW multiple sequence alignment program. The phylogenetic trees were constructed using online tool software Phylogeny.fr program (Dereeper, Guignon, Blanc, Audic, Buffet, et al., 2008).
Results
Morphological identification
Morphological examinations and measurements showed that all the nematodes larvae examined in the present study showed the most typical features of L3 of the genus Contracaecum with convergent shapes and morphology. Interestingly, there were no significant morphological differences of larvae among the fish species, with exception that there were two forms of L3 infected L. niloticus and H. forskahlii, short form (SF) and long form (LF).
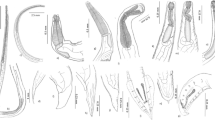
All larvae were found to share most of morphological characters with slight differences (Table 1; Figs. 1, 2, and 3). Living larvae were reddish-yellow in color. The body was long, cylindrical with rounded anterior end and tapered posterior one. Light and scanning electron microscopes data can be summarized as follows: the mouth is triangular or transverse in shape and surrounded by three lips, one dorsal and two ventrolateral; lips are provided with four papillae, two on the dorsal lip and one on each ventrolateral lip; well-defined boring tooth is located in between the ventrolateral lips; excretory pore is located anteriorly just below to the boring tooth; length of esophagus, ventricular appendix, intestinal caecum, and the ratios between each other are not the same; anal opening is located near the posterior end; the length of tail is also not equal between larvae collected from different fish species; and tail is blunt in larvae collected from Oreochromis niloticus and T. galilae, while being conical in larvae collected from other fishes and tail ending with a tapered process like spine.
Light microscopic study. a, b Anterior and posterior end of larva collected from Oreochromis niloticus; c, d anterior and posterior end of larva collected from Tilapia galilae; e, f anterior and posterior end of short form larva collected from Lates niloticus; g, h anterior and posterior end of long form larva collected from Lates niloticus; i, j anterior and posterior end of short form larva collected from Hydrocynus forskahlii; and k, l anterior and posterior end of long form larva collected from Hydrocynus forskahlii. Magnifications: a, c, e, g, i and k (×4); b and l (×40); d (×20); f, h and j (×10)
Regarding SEM study, the cuticle is striated with regular and irregular rings, which are narrower anteriorly and become wider as extended posteriorly and showing different ornamentations between larvae where cuticle of collected larvae from Oreochromis niloticus and T. galilae is striated transversely and longitudinally and forming well-defined circular ridges, which are very close anteriorly and covered with heavy mucus derived from the host (Fig. 2a, c). Larvae collected from Lates niloticus present in two sizes: short form (SF) and long form (LF). They are decorated with wavy striations in SF and net shaped in LF as shown in Fig. 4(b, c). Larvae (SF and LF) found in Hydrocynus forskahlii were striated transversely and longitudinally with overlapping strips (dendritic shape) respectively as shown in Fig. 4(d, e).
Scanning electron micrographs showing the pattern of cuticular striations in: a larva collected from Oreochromis niloticus and Tilapia galilae; b short form larva collected from Lates niloticus; c long form larva collected from Lates niloticus; d short form larva collected from Hydrocynus forskahlii; e long form larva collected from Hydrocynus forskahlii
Prevalence and infection intensity
Nine species of Lake Nasser fishes were examined for infection with Contracaecum larvae. Four fish species (Oreochromis niloticus, Tilapia galilaea, Lates niloticus, and Hydrocynus forskahlii) were found infected with L3 of Contracaecum, and the other five fish species (Synodontis frontosus, Mormyrus caschive, Chrysichthys auratus, Alestes baremose, and Lebeo niloticus) were found free in infection. Contraceacum L3 was found free in pericardial cavity and branchial chambers (O. niloticus and T. galilaea) and in the body cavity adhering to the alimentary canal (L. niloticus and H. forskahlii). The worm burden, prevalence and mean intensities per infected fish varied among different fishes (Table 2), with 100% prevalence in L. niloticus and the highest intensity in H. forskahlii. Interestingly, there were no significant differences in the data collected from different Khors of the Lake Nasser.
PCR of ITS-1 and ITS-2 and mutation scanning analysis
Following the morphological identification, the ITS-1 and ITS-2 regions were amplified by PCR from genomic DNA samples (n = 54) from individual larvae. Agarose gels analyses revealed the same size for each ITS region. Amplicons were ~ 530 bp and ~ 430 bp for the ITS-1 and ITS-2, respectively (Fig. 5a ), confirming that all sequences are of the same genus. Following, all ITS-1 and ITS-2 amplicons were analyzed using SSCP analysis to scan for sequence variability within and among individual specimens. For each ITS region, five possible profiles were observed on the SSCP gels for all 54 samples (Fig. 5b, c). Selected amplicons (n = 28) representing each possible genotype, taking fish species into consideration, were subjected to sequencing. No polymorphism was detected in any sequences that have the same SSCP profile.
Ethidium bromide-stained gel analysis of gDNA of Contracaecum L3 types. a Image of PCR products of ITS-1 and ITS-2 sequences of Contracaecum larvae in an 1.5% agarose gel under UV light. b SSCP patterns of ITS-1 sequences of Contracaecum larvae. c SSCP patterns of ITS-2 sequences of Contracaecum larvae. M: DNA ladder
Sequence and phylogenetic analyses
Alignment of resulted sequences revealed considerable variation of each ITS region, which may indicate the presence of more than one type of larvae. Scores of identities between ITS-1 sequences were ranging from 65% (between LF larvae collected from L. niloticus and H. forskahlii) to more than 99.3% (between SF larvae collected from L. niloticus and H. forskahlii), while scores of identities between ITS-2 sequences were ranging from 42% (between LF larvae collected from H. forskahlii and larvae from T. galilaea) to more than 98.7% (between larvae collected from O. niloticus and larvae from T. galilaea) (Fig. 6).
Nucleotide sequences alignment: a ITS-1 region alignment of Contracaecum larvae (sequences were deposited to the GenBank database under the accession numbers (KX580602-KX580607). b ITS-2 region alignment of Contracaecum larvae (sequences were deposited to the GenBank database under accession numbers (KX580607- KX5806013) .Samples are labeled according to host fish. Symbols: identical (asterisks; gray highlighted), no nucleotide (dashes)
The Blast analyses revealed that all sequences of both ITS-1 and ITS-2 in the present study were different from all sequences deposited in GenBank databases. ITS-1 sequences of Contracaecum larvae obtained were deposited in GenBank under accession numbers KX580602-KX580607, and ITS-2 sequences from the corresponding larvae were deposited in GenBank under accession No. KX580607-KX5806013. ITS-1 sequences obtained from larvae-infected T. galilaea showed the highest similarity (89%) to ITS-1 sequence of L3 of Contracaecum sp. 1 (Accession numbers KF990491), isolated from the body cavity and the intestines of H. forskahlii and T. zillii in Lake Turkana, Kenya (Otachi, Szostakowska, Jirsa, & Fellner-Frank, 2015). The last in turn draw an analogy (89%) to the Contracaecum multipapillatum (von Drasche, 1882) from the Australian pelican Pelecanus conspicillatus (Accession numbers AM940056) (Shamsi et al., 2008). In addition, ITS-2 from the same larvae showed the highest similarity (86%) to three ITS-2 sequences of Contracaecum L3 (Accession numbers FM210437- FM210438- FM210439) from Iranian fish (recorded by Shamsi in 2008 to the GenBank). Similarly, sequences of ITS-1 and ITS-2 of L3 from O. niloticus showed 99 and 86% similarity to Contracaecum multipapillatum (Accession numbers KF990491) and to Contracaecum L3 (Accession numbers FM210437-FM210439) respectively. In H. forskahlii, two forms (differ in size) of larvae were found, SF and LF. The last is morphologically similar to all other larvae found in other fishes. ITS-1 of SF larvae collected from H. forskahlii showed the highest similarity (97%) to three ITS-1 sequences (Accession numbers FM210433- FM210434- FM210435) from C. multipapillatum L3 which were collected from intestine and body cavity of barboid fishes in Parishan Lake, Iran (Shamsi & Aghazadeh-Meshgi, 2011). Further, ITS-2 of the same larvae (SF L3 from H. forskahlii) showed the highest similarity (98%) to the previously abovementioned three ITS-2 sequences of Contracaecum L3 (Accession numbers FM210437-FM210438-FM210439). Also, ITS-1 of LF larvae collected from H. forskahlii showed the highest similarity (78%) to the three abovementioned ITS-1 sequences of C. multipapillatum L3 (Accession numbers FM210433- FM210434- FM210435). Differently, ITS-2 sequence of the same larvae (LF L3 from H. forskahlii) showed the highest similarity (92%) to 18S- 5,8S-, 28S-rDNA-cluster of Contracaecum osculatum (Rudolphi, 1802) larvae (Accession numbers KM273050) in cod (Gadus morhua) from the Baltic Sea (Mehrdana, Bahlool, Skov, Marana, Sindberg, et al., 2014). Moreover, L. niloticus had SF and LF larvae. ITS-1 of SF larvae collected from L. niloticus showed the highest similarity (98%) to the three abovementioned ITS-1 sequences of C. multipapillatum L3 (Accession numbers FM210433- FM210434- FM210435). Also, ITS-2 of the same larvae (SF L3 from L. niloticus) showed the highest similarity (98%) to the abovementioned three ITS-2 sequences of Contracaecum L3 (Accession numbers FM210437-FM210438-FM210439). Finally, ITS-1 of LF larvae collected from L. niloticus showed the highest similarity (92%) to the three abovementioned ITS-1 sequences of C. multipapillatum L3 (Accession numbers FM210433- FM210434- FM210435). In addition, ITS-2 of SF L3 from L. niloticus showed the highest similarity to the abovementioned three ITS-2 sequences of Contracaecum L3 (Accession numbers FM210437-FM210438-FM210439).
Phylogenetic analysis for both ITS-1 and ITS-2 sequences produced nearly similar results, of which the first is displayed in Fig. 7. The identities and phylogenetic distances of the selected and most related ITS sequences showed nematode larvae investigated in this study are closely related to C. multipapillatum and likely are of different sub-species.
Phylogenetic tree of the aligned 15 ITS-1 sequences from Contracaecum larvae including 6 ITS-1 sequences, identified in this study, using the Phylogeny.fr program (http://www.phylogeny.fr/). Bootstrap support values are shown on the branches. The compared sequences are represented by accession numbers
Discussion
The present investigation is the first study to use integrated molecular and morphological approaches toward characterization of larval anisakid nematodes from four infected out of nine examined species of fishes in Lake Nasser, Egypt.
Based on morphological characteristics, all anisakid larvae collected from O. niloticus, Tilapia galilaea, Lates niloticus, and Hydrocynus forskahlii fishes in present study are belonging to the genus Contracaecum. They were found in the body cavity adhering to the mesentery by a thin membrane, except in O. niloticus and Tilapia galilaea were found free in pericardial cavity and gills. It was noticed that the parasitic fauna of Lake Nasser is changeable and there was a peak of infection by this larvae in fish species. Al-Bassel (1990) found the juveniles of Contracaecum sp. in the abdominal and branchial cavities of a variety of Lake Nasser fish species, such as Clarias gariepinus, Barbus bynni, Lates niloticus, Synodontis schall, Sarotherodonl galilaeus, and Mormyrus kannume. Garo (1993) reported that such juveniles were found in the branchial cavity and mainly in the sinus venosus of 51.6% of Serotherodon galilaeus fish from Lake Nasser. This fluctuation in the parasitic fauna of Lake Nasser may be a result of the change of water level, temperature degrees of the Lake, and the intensity of migratory birds. It may also be owing to the increasing numbers of intermediate and paratenic hosts and the change of the habitat of these hosts. The reports of Skov, Kania, Olsen, Lauridsen, and Buchmann (2009) and Mathenge (2010) proved that the infection in wild fish was higher than farmed fish due to the high abundance of definitive piscivorous birds in the wild regions; also, the prevalence and intensity in Catfish were higher than in Tilapia; this may be according to the feeding habits of Tilapia, which is herbivores and is less likely to get infected directly, while Catfish are omnivorous that will feed on all intermediate hosts (Malvestuto & Ogambo-Ongoma, 1978). These are compatible with the present study in that the highest prevalence and intensity were recorded in L. niloticus which represented 100%, followed by H. forskahlii, which have a prevalence of 82%, and the lowest were in O. niloticus and T. galilaea that recorded prevalence of 35.6 and 0.14% respectively.
Human anisakidosis (previously known as anisakiasis) is a disease that became of major health and economic importance. Humans were considered accidental hosts in the life cycle, as a result of consumption of raw fish, and these nematodes never develop inside the alimentary canal of human and may penetrate the tract and associated organs with severe pathological consequences. This disease was recorded in Egypt by Cocheton, Cabout, and Lecomte (1991). Early evisceration is recommended to avoid anisakidosis disease, due to the movement of the larvae from the digestive tract into muscles within a few days (Declerck, 1988). Also, freezing at − 20 °C for 3 days or heating to 70 °C because the larvae can survive at 50 °C. Sakanari and McKerrow (1989) indicated that larvae resist salting, smoking, and 51 days in vinegar. According to the US Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) agency, all fish products not intended for cooking or processing at temperature > 60 °C should be deep frozen at − 35 °C for > 15 h, or at − 23 °C for a minimum period of 7 days (Deardorff, Kayes, & Fukumura, 1991). Interestingly, C. magnipapillatum was redescribed from cormorants in Wadi Al-Raiyan lake area, Fayoum, Egypt, by Al-Bassel, 2006. In the present study, Hydrocynus forskahlii was the most Egyptian traditional salted fish (local name is Kalb-El Samak). This fish was exposed to direct sun in open air for about 24 h. The larger sized fish were gutted before being salted while small fishes were salted as a whole. Contracaecum larvae infected this fish by a prevalence of 82% and this may affect the human health in Egypt.
The SSCP analysis of ITS-1 and ITS-2 revealed five possible profiles for each. The sequence and phylogenetic analyses showed that the nematode larvae investigated in this study are closely related to C. multipapillatum, which is a species complex and it was shown that it consists of at least 4 distinct species found in the USA, Europe, and Australia (Nadler, D’Amelio, Fagerholm, Berland, & Paggi, 2000; Mattiucci, Turchetto, Bragantini, & Nascetti, 2002; D'Amelio et al., 2007; Shamsi et al., 2008).
Conclusion
It seems that Contracaecum larvae in Lake Nasser are belonging to C. multipapillatum complex and differ from each other in the sub-species level, with the possibility of the presence of at least one new species. It is necessary to complete the life cycles of different larvae of Contracaecum in the laboratory (running experiments) and examine adult worms using detailed morphological examination and molecular biology with complete ITS sequences and additional genetic markers.
Abbreviations
- a.:
-
Anus
- B.T:
-
Boring tooth
- Cut.r.:
-
Cuticle ridges
- DL:
-
Dorsal lip
- ex.p.:
-
Excretory pore
- Int. c.:
-
Intestinal caecum
- ITS:
-
Internal transcribed spacer
- LF:
-
Long form
- m.o.:
-
Mouth opening
- Oes.:
-
Esophagus
- p.:
-
Papillae
- r.:
-
Rectum
- SF:
-
Short form
- t.:
-
Tail
- t.p.:
-
Tapered process
- v.:
-
Ventriculus
- v.a.:
-
Ventricular appendages
- VL:
-
Ventral lip
References
Adams, A. M., Murrell, K. D., & Cross, J. H. (1997). The parasites of fish and risks to public health. Revue Scientifique et Technique-Office International des Epizooties, 16, 652–660.
Al-Bassel, D. A. (1990). Studies on the helminth parasites of some fishes from inland water in Egypt, PhD thesis (). Cairo: Cairo University Cited from Al-Bassel 2003.
Al-Bassel, D. A. (1992). A general survey of helminth parasites infecting the common fishes in some inland water in Egypt. Proceedings of the Zoological Society, 23, 227–241.
Al-Bassel, D. A. (2006). Scanning electron microscopic studies on Contracaecum magnipapillatum (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from cormorants in Wadi Al-Raiyan lake area, Fayoum. Journal-Egyptian German Society Of Zoology, 49(D), 39–48.
Aloo, P. A. (2001). Occurrence of larval Contracaecum (Nematoda: Heterocheilidae) in three teleostean species from Lake Naivasha, Kenya. East African. Journal of Science, 3, 1–12.
Amin, O. M. (1978). Intestinal helminths of some Nile fishes near Cairo, Egypt, with re-descriptions of Camallanus kirandensis Baylis, 1928 (Nematoda) and Bothriocephalus aegyptiacus Rysavy and Moravec, 1975 (Cestoda). Journal of Parasitology, 64, 93–101.
Anderson, R. C. (2000). Nematode parasites of vertebrates: Their development and transmission, (2nd ed., p. 650). Wallingford: CABI Publishing, CAB International.
Angot, V., & Brasseur, P. (1995). Anisakid larvae and their incidence on fish quality. Veterinary Medicine Review, 146, 791–804.
Arslan, A., Dinçoğlu, A., & Güven, A. (1995). The zoonoses produced by the sea foods consumption in humans. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg, 1, 103–107.
Audicana, M. T., Ansotegui, I. J., de Corres, L. F., & Kennedy, M. W. (2002). Anisakis simplex: Dangerous—Dead and alive? Trends in Parasitology, 18, 20–25.
Barson, M. (2004). The occurrence of Contracaecum sp. larvae (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in the catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell) from Lake Chivero, Zimbabwe. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 71, 35–39.
Béné, C., Bandi, B., & Durville, F. (2008). Liberalization reform, ‘neo-centralism’ and black market: The political diseconomy of Lake Nasser fishery development. Water Alternatives, 1, 219–235.
Bishai, H. M., Abdel-Malek, S. A., & Khalil, M. T. (2000). Lake Nasser. Publication of National Biodiversity Unit – No, (p. 11).
Boomker, J. (1982). Parasites of South African freshwater fish. I. Some nematodes of the catfish [Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822)] from the Hartbeespoort Dam. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 49, 41–51.
Boomker, J. (1994). Parasites of South African freshwater fish. VII. Nematodes of some scaled fishes from the Hartbeespoort Dam, Transvaal. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 61, 197–199.
Borges, J. N., Santos, H. L. C., Brandã, M. L., Santos, E. G. N., Miranda, D. F., Balthazar, D. A., … Santos, C. P. (2014). Molecular and morphological characterization of Contracaecum pelagicum (Nematoda) parasitizing Spheniscus magellanicus (Chordata) from Brazilian waters. Braz. J. Vet. Parasitol, 23, 74–79. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-29612014010.
Cocheton, J.J., Cabout, I., Lecomte, I., (1991). Anisakiasis and anisakid infection. Annls Med. int. 142: 121–130.
D'Amelio, S., Barros, N. B., Ingrosso, S., Fauquier, D. A., Russo, R., & Paggi, L. (2007). Genetic characterization of members of the genus Contracaecum (nematoda: Anisakidae) from fish-eating birds from west-central florida, USA, with evidence of new species. Parasitology, 134, 1041–1051. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118200700251X.
Deardorff, T. L., Kayes, S. G., & Fukumura, T. (1991). Human anisakiasis transmitted by marine food products. Hawaii Medical Journal, 50, 9–16.
Declerck, D., (1988). Presence of Anisakis simplex larvae in herring (Clupea harangus). Rev. Agric. 41: 971–980.
Dereeper, A., Guignon, V., Blanc, G., Audic, S., Buffet, S., Chevenet, F., … Gascuel, O. (2008). Phylogeny.fr: Robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, 465–469. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn180.
Drasche, R., (1882). Helminthological notes. Verh Zool-Bot Ges Wien 32:139–142.
Ezzat, S. M., ElKorashey, R. M., & Sherif, M. M. (2012). The economical value of Nile Tilapia fish “Oreochromis niloticus” in relation to water quality of Lake Nasser, Egypt. Journal of American Science, 8, 234–247.
FAO, (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) (1996). Fisheries and aquaculture in sub-saharan Africa: Situation and outlook in 1996. Rome: FAO fisheries circular No. 922FIPP/C922.
Garbin, L., Mattiucci, S., Paoletti, M., Diaz, J. I., Nascetti, G., & Navone, G. T. (2013). Molecular identification and larval morphological description of Contracaecum pelagicum (Nematoda: Anisakidae) from the Anchovy Engraulisanchoita (Engraulidae) and fish-eating birds from the Argentine North Patagonian Sea. Parasitology International, 62, 309–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2013.03.001.
Garbin, L. E., Mattiucci, S., Paoletti, M., González-Acuña, D., & Nascetti, G. (2011). Genetic and morphological evidences for the existence of a new species of Contracaecum (Nematoda: Anisakidae) parasite of Phalacrocorax brasilianus (Gmelin) from Chile and its genetic relationships with congeners from fish-eating birds. Journal of Parasitology, 97, 476–492. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-2450.1.
Garo, K. V. (1993). Studies on some parasitic nematodes infecting some locally consumed fish in Egypt, Ph.D. thesis, Fac. Of Sci (). Cairo: Cairo Univ.
Gasser, R. B., Hu, M., Chilton, N. B., Campbell, B. E., Jex, A. J., Otranto, D., … Zhu, X. (2006). Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) for the analysis of genetic variation. Nature Protocols, 1, 3121–3128. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.485.
Girişgin, A. O., Alasonyalilar-Demirer, A., & Girişgin, O. A. (2012). Case of Contracaecum sp. (Ascaridida: Anisakidae) infection in Dalmatian Pelican (Pelecanu scrispus). Kafkas Univ Vet FakDerg, 18(Suppl-A), A227–A229.
Jabbar, A., Fong, R. W., Kok, K. X., Lopata, A. L., Gasser, R. B., & Beveridge, I. (2013). Molecular characterization of anisakid nematode larvae from 13 species of fish from Western Australia. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 161, 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.12.012.
Kaddumukasa, M., Kaddu, J. B., & Makanga, B. (2006). Occurrence of nematodes in the Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linne) in Lake Wamala, Uganda. Uganda Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 12, 1–6.
Kaneko, J. J. (1991). Parasite hazards of public health significance to U.S. consumers of raw fish. IAAAM Proc, 22, 130–134.
Latif, A. F. A. (1974). Fisheries of Lake Nasser. Aswan: Aswan Regional Planning, Lake Nasser Development Center.
Malvestuto, S. P., & Ogambo-Ongoma, A. (1978). Observations of the infection of Tilapia leucosticta (Pisces: Cichlidae) with Contracaecum (Nematoda: Heterocheilidae) in Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Journal of Parasitology, 64, 383–384.
Martins, M. L., Onaka, E. M., & Fenerick Jr., J. (2005). Larval Contracaecum sp. (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in Hoplias malabaricus and Hoplerythrin usunitaeniatus (Osteichthyes: Erythrinidae) of economic importance in occidental marshlands of Maranha˜o, Brazil. Veterinary Parasitology, 127, 51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.09.026.
Mathenge, C. G. (2010). Prevalence, intensity and pathological lesions associated with helminth infections in farmed and wild fish in upper Tana river basin, Kenya, MSc. Thesis (). Nairobi: College of Agriculture and Veterinary Science, University of Nairobi.
Mattiucci, S., Turchetto, M., Bragantini, F., & Nascetti, G. (2002). On the occurrence of the sibling species of Contracaecum rudolphii Complex (Nematoda:Anisakidae) in cormorants (Phalacrocorax carbo sinensis) from Venice and Caorle lagoons: Genetic markers and ecological studies. Parassitologia, 44, 105.
Mehrdana, F., Bahlool, Q. Z., Skov, J., Marana, M. H., Sindberg, D., Mundeling, M., … Buchmann, K. (2014). Occurrence of zoonotic nematodes Pseudoterranova decipiens, Contracaecum osculatum and Anisakis simplex in cod (Gadusmorhua) from the Baltic Sea. Veterinary Parasitology, 205, 581–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.08.027.
Nadler, S. A., D’Amelio, S., Fagerholm, H. P., Berland, B., & Paggi, L. (2000). Phylogenetic relationships among species of Contracaecum and Phocascaris (Nematoda, Ascaridoida) based on nuclear rDNA. Parasitology, 121, 455–463.
Nadler, S. A., D'Amelio, S., Dailey, M. D., Paggi, L., Siu, S., & Sakanari, J. A. (2005). Molecular phylogenetics and diagnosis of Anisakis, Pseudoterranova, and Contracaecum from northern Pacific marine mammals. The Journal of Parasitology, 91, 1413–1429.
Nadler, S. A., & Hudspeth, D. S. (1998). Ribosomal DNA and phylogeny of the Ascaridoidea (Nemata: Secernentea): Implications for morphological evolution and classification. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 10, 221–236. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.1998.0514.
Olivero-Verbel, J., Baldiris-Avila, R., Guette-Fernandez, J., Benavides-Alvarez, A., Mercado-Camargo, J., & Arroyo-Salgado, B. (2006). Contracaecum sp. infection in Hoplias malabaricus (moncholo) from rivers and marshes of Colombia. Veterinary Parasitology, 140, 90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.03.014.
Otachi, E. O., Szostakowska, B., Jirsa, F., & Fellner-Frank, C. (2015). Parasite communities of the elongate tigerfish Hydrocynus forskahlii (Cuvier 1819) and red belly tilapia Tilapia zillii (Gervais 1848) from Lake Turkana, Kenya: Influence of host sex and size. Acta Parasitologica, 60, 9–20. https://doi.org/10.1515/ap-2015-0002.
Palm, H. W. (2004). The Trypanorhyncha diesing, 1863. Bogor: PKSPL-IPB Press.
Paperna, I. (1996). Parasites, infections and diseases of fishes in Africa: An update. FAO/CIFA technical paper no. 31, (pp. 157–170).
Rashid, M. (1995). Some additional information on limnology and fisheries of Lakes Nasser (Egypt) and Nubia (Sudan). In R. C. M. Crul, & F. C. Roest (Eds.), Current status of fisheries and fish stocks of the four largest African reservoirs: Kainji, Kariba, Nasser/Nubia and Volta, (pp. 81–109). Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization.
Saad, A. I. (2007). A comparative study of different metacercarial infections in two freshwater fishes from Lake Nasser, Nile River and hatcheries at Aswan –Egypt. Egyptian German Society of Zoology, 51D, 107–125.
Sakanari, J. A., & McKerrow, J. H. (1989). Anisakiasis. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2, 278–284.
Saoud, M. F., & Wannas, M. Q. (1984). A qualitative and quantitative survey on the helminth parasites of fishes from the Aswan high dam lake in Egypt. Qatar Univ. Sci. Bull., 4, 129–142.
Shamsi, S., & Aghazadeh-Meshgi, M. (2011). Morphological and genetic characterisation of selected Contracaecum (Nematoda: Anisakidae) larvae in Iran. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences, 10, 356–361.
Shamsi, S., & Butcher, A. R. (2011). The first report of human anisakidosis in Australia. Medical Journal of Australia, 194, 199–200.
Shamsi, S., Gasser, R., Beveridge, I., & Shabani, A. A. (2008). Contracaecum pyripapillatum n. sp. and a description of C. multipapillatum (von Drasche, 1882) from the Australian pelican, pelecanus conspicillatus. Parasitology Research, 103, 1031–1039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1088-z.
Shamsi, S., Gasser, R. B., & Beveridge, I. (2011). Mutation scanning-coupled sequencing of nuclear ribosomal DNA spacers as a tool for the specific identification of different Contracaecum (nematoda: Anisakidae) larval types. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 25, 13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2010.09.003.
Shamsi, S., Norman, R., Gasser, R., & Beveridge, I. (2009). Genetic and morphological evidences for the existence of sibling species within Contracaecum rudolphii (hartwich, 1964) (nematoda: Anisakidae) in Australia. Parasitology Research, 105, 529–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1424-y.
Skov, J., Kania, P. W., Olsen, M. M., Lauridsen, J. H., & Buchmann, K. (2009). Nematode infections of maricultured and wild fishes in Danish waters: A comparative study. Aquaculture, 298, 24–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.09.024.
Van As, J. G., & Basson, L. (1984). Checklist of freshwater fish parasites from southern Africa. South African Journal of Wildlife Research, 14, 49–61.
Whitfield, A. K., & Heeg, J. (1977). On the life cycles of the cestode Ptychobothrium belones and nematodes of the genus Contracaecum from Lake St. Lucia, Zululand. South African Journal of Science, 73, 121–122.
Yamaguti, S. (1961). Systema Helminthum, Vol. 3. The nematodes of vertebrates, part I and II, (p. 1575). New York, London: Interscience Publishers, Inc.
Yimer, E., & Enyew, M. (2003). Parasites of fish at Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Ethiopian Journal of Science, 26, 31–36. https://doi.org/10.4314/sinet.v26i1.18197.
Younis, A. E., Geisinger, F., Ajonina-Ekoti, I., Soblik, H., Steen, H., Mitreva, M., … Brattig, N. W. (2011). Stage-specific excretory–secretory small heat shock proteins from the parasitic nematode Strongyloides ratti—Putative links to host’s intestinal mucosal defense system. FEBS Journal, 278, 3319–3336. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08248.x.
Zhang, L., Hu, M., Shamsi, S., Beveridge, I., Li, H., Xu, Z., … Gasser, R. B. (2007). The specific identification of anisakid larvae from fishes from the Yellow Sea, China, using mutation scanning-coupled sequence analysis of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 21, 386–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2007.05.004.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank PD. Dr. Norbert Brattig and PD. Dr. Klaus Erttmann (Tropical Medicine Section, Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine, Hamburg, Germany) for providing their laboratory facilities during the preparatory experiment in this work.
Funding
There are no external sources of funding for this work except from the institutions to which they were affiliated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This work is part of the doctoral thesis of JR. She has done most of the experiments. AY is assistant supervisor who has done the practical part of molecular biology, data analyses and subsequent interpretations. AS is the main supervisor who prepared the research plan and contributed to the explanation of the morphological part. All coauthors contributed in the writing and revision of this manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Younis, A.E., Saad, A.I. & Rabei, J.M. The occurrence of Contracaecum sp. larvae (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in four teleostean species from Lake Nasser, Egypt: morphological and molecular studies. JoBAZ 78, 9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41936-017-0012-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41936-017-0012-4