Abstract
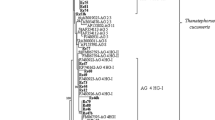
A total of 30 Rhizoctonia isolates were collected from plants with Rhizoctonia-like symptoms in kale growing areas in Ordu province during the 2014–2015 growing seasons. All the isolates were identified using nuclear staining tecnique and the nucleotide sequence analysis of the nuclear rDNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS)1–5.8S-ITS2 region. The most prevalent anastomosis group (AG) was AG 2–1 (36.67% of isolates), followed by AG-A (30%), AG 4 HG-I (10%), AG 5 (6.67%), AG-Fb (6.67%), AG-E (6.67%) and AG-K (3.33%). Cultural characteristics showed that randomly selected RsCB-13 (AG 2–1), RsCB-20 (AG 4 HG-I), RsCB-21 (AG 5), RCB-16 (AG-A), RCB-7 (AG-E), RCB-22 (AG-Fb) and RCB-26 (AG-K) isolates representing each AG had greyed-yellow, brown, white-orange and greyed-orange colony colors, and optimum growth temperatures of the isolates ranged from 25.21 to 27.67 °C. Pathogenicity tests on the seedlings of kale cv. Arzuman revealed generally significant virulence differences between AG 2–1 and AG 4 HG-I isolates, and other Rhizoctonia isolates (P < 0.05). In addition, with the exception of several AG 2–1 isolates, the isolates of both groups caused severe root and stem rot and seedling deaths, unlike the relatively low and moderate virulent AG 5, AG-E, AG-Fb and AG-K isolates. However, AG-A had very low virulence and did not affect plant growth parameters such as plant height, shoot and root dry weights and root length while the isolates of all other groups generally reduced these parameters compared to control plants (P < 0.05). To our knowledge, this is the first study reporting AGs of Rhizoctonia isolates causing root and stem rot on kale plants in Turkey and in the world.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiello, D., Guarnaccia, V., Formica, P. T., Hyakumachi, M., & Polizzi, G. (2017). Occurrence and characterisation of Rhizoctonia species causing diseases of ornamental plants in Italy. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 148, 967–982.
Aoyagi, T., Kageyama, K., & Hyakumachi, M. (1998). Characterization and survival of Rhizoctonia solani AG 2–2 LP associated with large patch disease of zoysia grass. Plant Disease, 82, 857–863.
Ball, G. J. (1990). Grower talks on plugs. Growertalks magazine, George J. Ball Publishing, Geneva, III.
Bandoni, R. J. (1979). Safranin-O as a rapid nuclear stain for fungi. Mycologia, 63, 873–874.
Belka, M., & Manka, M. (2014). Characteristics and diversity of Rhizoctonia spp. population in soil of selected forest bare-root nurseries in Poland. Acta Mycology, 49(2), 279–290.
Brayford, D. (1993). Cylindrocarpon. In L. L. Singleton, J. D. Mihail, & C. M. Rush (Eds.), Methods for research on soilborne phytopathogenic fungi (p. 265). St. Paul: APS Press.
Broders, K. D., Parker, M. L., Melzer, M. S., & Boland, G. J. (2014). Phylogenetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani associated with canola and wheat in Alberta, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan. Plant Disease, 98, 1695–1701.
Budge, G. E., Shaw, M. W., Lambourne, C., Jennings, P., Clayburn, R., Boonham, N., & McPherson, M. (2009). Characterization and origin of infection of Rhizoctonia solani associated with Brassica oleracea crops in the UK. Plant Pathology, 58, 1059–1070.
Carling, D. E., Kuninaga, S., & Brainard, K. A. (2002). Hyphal anastomosis reactions, rDNA-internal transcribed spacer sequences, and virulence levels among subsets of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 2 (AG 2) and AG BI. Phytopathology, 92, 43–50.
Çebi Kılıçoğlu, M., & Özkoç, I. (2013). Phylogenetic analysis of Rhizoctonia solani AG 4 isolates from common beans in Black Sea coastal region, Turkey, based on ITS-5.8S rDNA. Turkish Journal of Biology, 37, 18–24.
Dong, W., Li, Y., Duan, C., Li, X., Naito, S., Conner, R. L., Yang, G., & Li, C. (2017). Identification of AG-V, a new anastomosis group of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. from taro and ginger in Yunnan province. European Journal of Plant Pathology 148(4), 895–906.
Erper, I., Karaca, G. H., Türkkan, M., & Özkoç, I. (2006). Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. from onion in Amasya, Turkey. Journal of Phytopathology, 154, 75–79.
Erper, I., Çebi Kılıçoğlu, M., Türkkan, M., & Önder, H. (2016). Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. isolated from winter squash in the Black Sea region of Turkey. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 146(3), 683–697.
Fang, X., Finnegan, P. M., & Barbetti, M. J. (2013). Wide variation in virulence and genetic diversity of binucleate Rhizoctonia isolates associated with root rot of strawberry in Western Australia. PLoS One, 8, e55877.
Godoy-Lutz, G., Kuninaga, S., Steadman, J. R., & Powers, K. (2008). Phylogenetic analysis of Rhizoctonia solani subgroups associated with web blight symptoms on common bean based on ITS-5.8S rDNA. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 74, 32–40.
Gonzalez, D., Carling, D. E., Kuninaga, S., Vilgalys, R., & Cubeta, M. A. (2001). Ribosomal DNA systematics of Ceratobasidium and Thanatephorus with Rhizoctonia anamorphs. Mycologia, 93, 1138–1150.
Hall, T. A. (1999). BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95–98.
Hyakumachi, M., Mushika, T., Ogiso, Y., Toda, T., Kageyama, K., & Tsuge, T. (1998). Characterization of a new cultural type of Rhizoctonia solani AG 2–2 isolated from warm-season turfgrasses, and its genetic differentiation from other cultural types. Plant Pathology, 47, 1–9.
Hua, G. K. H., Bertier, L., Soltaninejad, S., & Höfte, M. (2014). Cropping systems and cultural practices determine the Rhizoctonia anastomosis groups associated with Brassica spp. in Vietnam. Plos One, 9(11), e111750.
Huber, D. M., Christmas, E. P., Herr, L. J., McCay-Buis, T. S., & Baird, R. (1992). Rhizoctonia crown rot of canola in Indiana. Plant Disease, 76, 1251–1253.
Jukes, T. H., & Cantor, C. R. (1969). Evolution of protein molecules (pp. 21–132). New York: Academic Press.
Kataria, H., & Verma, P. (1992). Rhizoctonia solani damping-off and root rot in oilseed rape and canola. Crop Protection, 11, 8–13.
Keinath, A. P., & Farnham, M. W. (1997). Differential cultivars and criteria for evaluating resistance to Rhizoctonia solani in seedling Brassica oleracea. Plant Disease, 81, 946–952.
Khangura, R. K., Barbetti, M. J., & Sweetingham, M. W. (1999). Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia species on canola. Plant Disease, 83, 714–721.
Kuninaga, S., Carling, D. E., Takeuchi, T., & Yokosawa, R. (2000). Comparison of rDNA-ITS sequences between potato and tobacco strains in Rhizoctonia solani AG 3. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 66, 2–11.
Kuramae, E., Buzeto, A., Ciampi, M., & Souza, N. (2003). Identification of Rhizoctonia solani AG 1-B in lettuce, AG 4 HG-I in tomato and melon, and AG 4 HG-III in broccoli and spinach, in Brazil. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 109, 391–395.
Kuramae, E. E., Buzeto, A. L., Nakatani, A. K., & Souzar, N. L. (2007). DNA-based characterization of a new binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. causing root rot on kale in Brazil. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 119, 469–475.
Larkin, M. A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N. P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P. A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I. M., Wilm, A., Lopez, R., Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., & Higginset, D. G. (2007). Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics, 23, 2947–2948.
Misawa, T., Kubota, M., Sasaki, J., & Kuninaga, S. (2015). First report of broccoli foot rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG 2–2-IV and pathogenicity comparison of the pathogen with related pathogens. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 81, 15–23.
Misawa, T., & Aoki, M. (2017). First report of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IC causing head rot of cabbage in Japan. New Disease Reports, 36, 12.
Muzhinji, N., Truter, M., Woodhall, J. W., & van der Waals, J. E. (2015). Anastomosis groups and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani and binucleate Rhizoctonia from potato in South Africa. Plant Disease, 99, 1790–1802.
Nicoletti, R., Lahoz, E., Kanematsu, S., Naito, S., & Contillo, R. (1999). Characterization of Rhizoctonia solani isolates from tobacco fields related to anastomosis groups 2-1 and BI (AG 2–1 and AG BI). Journal of Phytopathology, 147, 71–77.
Ogoshi, A. (1975). Grouping of Rhizoctonia solani Kühn and their perfect stages. Review of Plant Protection Research, 8, 93–103.
Ogoshi, A. (1987). Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intraspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kühn. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 25(1), 125–143.
Ogoshi, A. (1996). The genus Rhizoctonia. In B. Sneh, S. Jabaji-Hare, S. Neate, & G. Dijst (Eds.), Rhizoctonia species: Taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology, and disease control (pp. 1–9). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Press.
Pannecoucque, J., Van Beneden, S., & Höfte, M. (2008). Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia isolates associated with cauliflower in Belgium. Plant Pathology, 57, 737–746.
Paulitz, T. C., Okubara, P. A., & Schillinger, W. F. (2006). First report of damping-off of canola caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG 2–1 in Washington state. Plant Disease, 90, 829–829.
Rimmer, S. R., Shattuck, V. I., & Buchwaldt, L. (2007). Compendium of brassica diseases (p. 117). New York: APS Press.
Rollins, P. A., Keinath, A. P., & Farnham, M. W. (1999). Effect of inoculum type and anastomosis group of Rhizoctonia solani causing wirestem of cabbage seedlings in a controlled environment. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 21, 119–124.
Salazar, O., Julian, M. C., & Rubio, V. (2000). Primer based on specifi c rDNAITS sequences for PCR detection of Rhizoctonia solani, R. solani AG 2 subgroups and ecological types, and binucleate Rhizoctonia. Mycological Research, 104, 281–285.
Sayama, A. (2000). Occurrence of damping-off disease caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG 2–2-IIIB on cabbage plug seedlings. Annual Report of the Society of Plant Protection of North Japan, 51, 54–57.
Sharma, M., Gupta, S. K., & Sharma, T. R. (2005). Characterization of variability in Rhizoctonia solani by using morphological and molecular markers. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 153, 449–456.
Sharon, M., Kuninaga, S., Hyakumachi, M., & Sneh, B. (2006). The advancing identification and classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using molecular and biotechnological methods compared with the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience, 47, 299–316.
Sharon, M., Freeman, S., Kuninaga, S., & Sneh, B. (2007). Genetic diversity, anastomosis groups, and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. isolates from strawberry. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 117, 247–265.
Sharon, M., Kuninaga, S., Hyakumachi, M., Naito, S., & Sneh, B. (2008). Classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using rDNA-ITS sequence analysis supports the genetic basis of the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience, 49, 93–114.
Sneh, B., Jabaji-Hare, S., Neate, S., & Dijst, G. (1996). Rhizoctonia species: Taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology and diseases control. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Press.
Stevens Johnk, J., & Jones, R. K. (2001). Differentiation of three homogeneous groups of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 4 by analysis of fatty acids. Phytopathology, 91, 821–830.
Tahvonen, R., Hollo, J., Hannukkala, A., & Kurppa, A. (1984). Rhizoctonia solani damping-off on spring turnip rape and spring rape (Brassica spp.) in Finland. Journal of Agricultural Science in Finland, 56, 143–154.
Tewoldemedhin, Y. T., Lamprecht, S. C., Mcleod, A., & Mazzola, M. (2006). Characterization of Rhizoctonia spp. recovered from crop plants used in rotational cropping systems in the Western cape province of South Africa. Plant Disease, 90, 1399–1406.
TUIK. (2018). Turkish statistical institute: Crop production statistics. Retrieved from https://biruni.tuik.gov.tr/medas (verified 11 march 2019).
Türkkan, M., Erper, I., Çebi Kılıçoğlu, M., Yazıcıoğlu, E., & Özcan, M. (2018). Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. isolated from kiwifruit in the Middle and Eastern Black Sea region of Turkey. Journal of Phytopathology, 166, 761–774.
Van, N. K., Benyon, F. H. L., Hoa, D. L., Ha, T. N., Summerell, B. A., & Burgess, L. W. (2001). First record of Rhizoctonia causing head rot of cabbage in northern Vietnam. Australasian Plant Pathology, 30, 285–286.
Verma, P. R. (1996). Oilseed rape and canola diseases incited by Rhizoctonia species. In B. Sneh, S. Jabaji-Hare, S. Neate, & G. Dijst (Eds.), Rhizoctonia species: Taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology, and disease control (pp. 249–258). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Press.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., & Taylor, J. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. Pages 315–322 in: PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications. M. A. Innis, D. H. Gelfand, J. J. Sninsky, and T. J. T. J. White, eds. Academic Press, Inc., New York.
Yang, J., Verma, P. R., & Tewari, J. P. (1992). Histopathology of resistant mustard and susceptible canola hypocotyls infected by Rhizoctonia solani. Mycological Research, 96, 171–179.
Yang, J., Kharbanda, P. D., & Wang, H. (1996). Characterization, virulence, and genetic variation of Rhizoctonia solani AG 9 in Alberta. Plant Disease, 80, 513–518.
Yang, G. H., Chen, J. Y., & Pu, W. Q. (2007). First report of head rot of cabbage and web-blight of snap bean caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG 4 HG-I. New Disease Reports, 14, 20.
Yıldırım, E., & Erper, I. (2017). Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. isolated from vegetable crops grown in greenhouses in Samsun province Turkey. Bioscience Journal, 33(2), 257–267.
Zhou, Q. X., Hwang, S. F., Fu, H. T., Strelkov, S. E., & Gossen, B. D. (2014). Genetic variation of Rhizoctonia solani isolates from canola in Alberta, Canada. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 94, 671–681.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ayşe Karataş, BSc.(Agri.), for her assistance in the survey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Türkkan, M., Kılıçoğlu, M.Ç. & Erper, I. Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia isolates collected from Brassica oleracea var. acephala in Ordu, Turkey. Phytoparasitica 48, 273–286 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-020-00793-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-020-00793-9