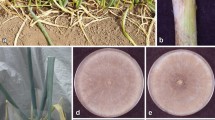
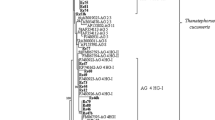
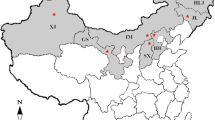
Abstract
During surveys conducted in 2010–2012 Rhizoctonia symptoms were observed on 30 ornamental species in different nurseries located in eastern Sicily (Southern Italy). Eighty-eight isolates of Rhizoctonia spp. were obtained from symptomatic leaves, roots and stems. Fifty-six of the isolates were binucleate and 32 were multinucleate Rhizoctonia. Characterisation of anastomosis groups (AGs) was performed using morphological characteristics and sequence analysis of the internal transcribed spacer of ribosomal DNA ( rDNA-ITS) region. Most isolates collected were Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 HG-I (35.2% of all isolates) and one isolate was AG-2-2 IIIB. The binucleate isolates belonged to AG-R (27.3%), AG-A (21.6%), AG-G (12.5%), AG-V (1.1%) and AG-Fb (1.1%). The pathogenicity of 38 representative isolates collected from each host was tested on seedlings or cuttings grown in a growth chamber. All R. solani AG-4 HG-I isolates, most of the binucleate AG-R, AG-A and AG-G and AG-V were pathogenic and reproduced symptoms identical to that observed in nurseries, while binucleate AG-Fb and R. solani AG-2-2 IIIB isolates were nonpathogenic. This is the first report of the occurrence of Rhizoctonia species on some ornamental plants and the first report of binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-R and AG-V in Europe.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiello, D., Castello, I., Vitale, A., Lahoz, E., Nicoletti, R., & Polizzi, G. (2008a). First report of damping-off on African daisy caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 in Italy. Plant Disease, 92, 1367.
Aiello, D., Parlavecchio, G., Vitale, A., Lahoz, E., Nicoletti, R., & Polizzi, G. (2008b). First report of damping-off caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 on Lagunaria patersonii in Italy. Plant Disease, 92, 836.
Aiello, D., Caiazzo, R., Carella, A., Lahoz, E., Nicoletti, R., Vitale, A., et al. (2009a). Characterisation of Rhizoctonia species isolated from ornamental nurseries. Journal of Plant Pathology, 91(S4), 45.
Aiello, D., Vitale, A., Lahoz, E., Nicoletti, R., & Polizzi, G. (2009b). First report of crown and root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 on orange jessamine in Italy. Plant Disease, 93, 204.
Aiello, D., Vitale, A., Hyakumachi, M., & Polizzi, G. (2012). Molecular characterisation and pathogenicity of binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-F associated to the watermelon vine decline in Italy. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 134, 161–165.
Alfieri Jr., S. A., Seymour, C. P., & Denmark, J. C. (1972). Aerial blight of Carissa grandiflora caused by Rhizoctonia solani. The Plant Disease Reporter, 56, 511–514.
Alfieri Jr., S. A., Langdon, K. R., Wehlburg, C., & Kimbrough, J. W. (1984). Index of plant diseases in Florida (revised). Florida: Division of Plant Industry, Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services.
Andersen, T. F., & Rasmussen, H. N. (1996). The mycorrhizal species of Rhizoctonia. In B. Sneh, S. Jabaji-Hare, S. Neate, & G. Dijst (Eds.), Rhizoctonia species: taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology and disease control (pp. 379–390). The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Aoyagi, T., Kageyama, K., & Hyakumachi, M. (1998). Characterisation and survival of Rhizoctonia solani AG2-2 LP associated with large patch disease of zoysia grass. Plant Disease, 82, 857–863.
Bandoni, R. J. (1979). Safranin O as a rapid stain for fungi. Mycologia, 71, 873–874.
Benson, D. M., & Cartwright, D. K. (1996). Ornamental diseases incited by Rhizoctonia spp. In S. B. Sneh, S. Jabaji-Hare, G. Neate, & Dijst (Eds.), Rhizoctonia species: taxonomy, molecular, biology, ecology, pathology, and disease control (pp. 303–314). The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Burpee, L. L., Sanders, P. L., Cole Jr., H., & Sherwood, R. T. (1980). Pathogenicity of Ceratobasidium cornigerum and related fungi representing five anastomosis groups. Phytopathology, 70, 843–846.
Carling, D. E., Rothrock, C. S., Macnish, G. C., Sweetingham, M. W., Brainard, K. A., & Winters, S. W. (1994). Characterisation of anastomosis group-11 (AG-11) of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology, 84, 1387–1393.
Carling, D. E., Pope, E. J., Brainard, K. A., & Carter, D. A. (1999). Characterisation of mycorrhizal isolates of Rhizoctonia solani from an orchid, including AG-12, a new anastomosis group. Phytopathology, 89, 942–946.
Carling, D. E., Baird, R. E., Gitaitis, R. D., Brainard, K. A., & Kuninaga, S. (2002). Characterisation of AG-13, a newly reported anastomosis group of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology, 92, 893–899.
Chase, A. R. (1991). Characterisation of Rhizoctonia species isolated from ornamentals in Florida. Plant Disease, 75, 234–238.
Collado, J., Platas, G., & Pelaez, F. (1996). Fungal endophytes in leaves, twigs, and bark of Quercus ilex from Central Spain. Nova Hedwigia, 63, 347–360.
Couch, H. B. (1995). Diseases of turfgrasses (3rd ed.). Malabar: Krieger Publishing Company.
Csinos, A. S., & Stephenson, M. G. (1999). Evaluation of fungicides and tobacco cultivar resistance to Rhizoctonia solani incited target spot, damping off and sore shin. Crop Protection, 18, 373–377.
Dmitriev, D., & Rakitov, R. (2008). Decoding of superimposed traces produced by direct sequencing of heterozygous indels. PLoS Computational Biolology, 4(7), e1000113.
Fang, X., Finnegan, P. M. & Barbetti M. J. (2013). Wide variation in virulence and genetic diversity of Binucleate Rhizoctonia isolates associated with root rot of strawberry in Western Australia. Plos One, 8, number e55877.
Farr, D. F., Bills, G. F., Chamuris, G. P., & Rossman, A. Y. (1995). Fungi on plants and plant products in the United States. Saint Paul: APS Press.
Felsenstein, J. (1985). Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 39, 783–791.
Gardes, M., & Bruns, T. D. (1993). ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes - application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Molecular Ecology, 2, 113–118.
Garibaldi, A., Minuto, A., Bertetti, D., Nicoletti, R., & Gullino, M. L. (2003). First report of web blight on yellow-sage (Lantana camara) caused by Rhizoctonia solani in Europe. Plant Disease, 87, 875.
Garibaldi, A., Bertetti, D., & Gullino, M. L. (2006). First report of leaf blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG 1B on Madagascar periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus) in Italy. Plant Disease, 90, 1361.
Garibaldi, A., Bertetti, D., & Gullino, M. L. (2009a). First report of leaf blight on Hosta fortune caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG 4 in Italy. Plant Disease, 93, 432.
Garibaldi, A., Gilardi, G., Bertetti, D., & Gullino, M. L. (2009b). First report of leaf blight on Fan columbine (Aquilegia flabellata) caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG 4 in Italy. Plant Disease, 93, 433.
Gill, J. S., Sivasithamparam, K., & Smettem, K. R. J. (2000). Soil types with different texture affects development of Rhizoctonia root rot of wheat seedlings. Plant and Soil, 221, 113–120.
Gill, J. S., Sivasithamparam, K., & Smettem, K. R. J. (2001). Effect of soil moisture at different temperatures on Rhizoctonia root rot of wheat seedlings. Plant and Soil, 231, 91–96.
Gill, J. S., Hunt, S., Sivasithamparam, K., & Smettem, K. R. J. (2004). Root growth altered by compaction of a sandy loam soil affects severity of Rhizoctonia root rot of wheat seedlings. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 44, 595.
Goll, M. B., Schade-Schutze, A., Swart, G., Oostendorp, O., Schott, J. J., Jaser, B., & Felsenstein, F. G. (2014). Survey on the prevalence of Rhizoctonia spp. in European soils and determination of the baseline sensitivity towards sedaxane. Plant Pathology, 63, 148–154.
González, D., Carling, D. E., Kuninaga, S., Vilgalys, R., & Cubeta, M. A. (2001). Ribosomal DNA systematics of Ceratobasidium and Thanatephorus with Rhizoctonia anamorphs. Mycologia, 93, 1138–1150.
Haralson, J. C., Brannen, P. M., NeSmith, D. S., & Scherm, H. (2013). Chemical control of Cylindrocladium and Rhizoctonia root rots in blueberry propagation. Crop Protection, 44, 1–5.
Harris, A. R., Schisler, D. A., Neate, S. M., & Ryder, M. H. (1994). Suppression of damping-off caused by Rhizoctonia solani, and growth promotion, in bedding plants by binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 26, 263–268.
Holcomb, G. E., & Carling, D. E. (2002). First report of web blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani on Catharanthus roseus in Louisiana. Plant Disease, 86, 1272.
Hua, G. K. H., Bertier, L., Soltaninejad, S., & Hofte, M. (2014). Cropping Systems and Cultural Practices Determine the Rhizoctonia Anastomosis Groups Associated with Brassica spp. in Vietnam. PLoS ONE, 9, number e111750. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111750
Hwang, J., & Benson, D. M. (2002). Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia stem and root rot of poinsettia with Burkholderia cepacia and binucleate Rhizoctonia. Plant Disease, 86, 47–53.
Hyakumachi, M., Priyatmojo, A., Kubota, M., & Fukui, H. (2005). New anastomosis groups, AG-T and AG-U of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. causing root and stem rot of cut- flower and miniature roses. Phytopathology, 95, 784–792.
Izumitsu, K., Hatoh, K., Sumita, T., Kitade, Y., Morita, A., & Tanaka, C. (2012). Rapid and simple preparation of mushroom DNA directly from colonies and fruiting bodies for PCR. Mycoscience, 53, 396–401.
Jager, G., Velvis, H., Lamers, J. G., Mulder, A., & Roosjen, J. (1991). Control of Rhizoctonia solani in potato by biological, chemical and integrated measures. Potato Research, 34, 269–284.
Kataria, H. R., Hugelshofer, U., & Gisi, U. (1991). Sensitivity of Rhizoctonia species to different fungicides. Plant Pathology, 40, 203–211.
Kataria, H. R. & Gisi, U. (1996). Chemical control of Rhizoctonia species. In: SnehB, Jabaji-Hare S, Neate S, Dijst G, eds. Rhizoctonia species: taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology and disease control. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers. p 537–547.
Khan, F. U., Nelson, B. D., & Helms, T. C. (2005). Greenhouse evaluation of binucleate Rhizoctonia for control of R. solani in soybean. Plant Disease, 89, 373–379.
Kimura, M. (1980). A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 16, 111–120.
Kuninaga, S., & Yokosawa, R. (1984). DNA base sequence homology in Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. IV. Genetic relatedness within AG-4. Annals of the Phytopathological Society of Japan, 50, 322–330.
Kuramae, E. E., Buzeto, A. L., Nakatani, A. K., & Souza, N. L. (2007). rDNA-based characterisation of a new binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. causing root rot on kale in Brazil. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 119, 469–475.
Leiner, R. H., & Carling, D. E. (1994). Characterization of Waitea circinata (Rhizoctonia) isolated from agricultural soils in Alaska. Plant Disease, 78, 385–388.
Manici, L., & Bonora, P. (2007). Molecular genetic variability of Italian binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. isolates from strawberry. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 118, 31–42.
Martin, F. N. (2000). Rhizoctonia spp. recovered from strawberry roots in central coastal California. Phytopathology, 90, 345–353.
Mulenko, W., Majewski, T., & Ruszkiewicz-Michalska, M. (2008). A preliminary checklist of micromycetes in Poland. In W. Mułenko, T. Majewski, & M. Ruszkiewicz-Michalska (Eds.), A preliminary checklist of micromycetes in Poland (p. 752). Polish Academy of Sciences: Institute of Botany.
Muzhinji, N., Truter, M., Woodhall, J. W., & Van der Waals, J. E. (2015). Anastomosis groups and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani and Binucleate Rhizoctonia from potato in South Africa. Plant Disease, 99, 1790–1802.
Naito, S. (2004). Rhizoctonia diseases: taxonomy and population biology (pp. 18–31). Japan-Argentina Joint Study, Buenos Aires, Argentina: Proceeding of the International Seminar on Biological Control of Soilborne Plant Diseases.
Nadarajah, K., Omar, N. S., Rosli, M. M., & Tze, O. S. (2014). Molecular Characterization and Screening for Sheath Blight Resistance Using Malaysian Isolates of Rhizoctonia solani. BioMed Research International. doi:10.1155/2014/434257
Ogoshi, A. (1975). Grouping of Rhizoctonia solani Kühn and their perfect stages. Review of Plant Protection Research, 8, 93–103.
Ogoshi, A. (1987). Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intraspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. In R. J. Cook (Ed.), Annual Review of Phytopathology (p. 25). Palo Alto: Annual Reviews Inc..
Ogoshi, A. (1996). Introduction – the genus Rhizoctonia. In B. Sneh, S. Jabaji-Hare, S. Neate, & G. Dijst (Eds.), Rhizoctonia species: taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology, and disease control (pp. 1–9). The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publisher.
Ogoshi, A., Oniki, M., Araki, T., & Ui, T. (1983). Studies on the anastomosis groups of binucleate Rhizoctonia and their perfect states. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture , 61, 244–260.Hokkaido University
Ohkura, M., Abawi, G. S., Smart, C. D., & Hodge, K. T. (2009). Diversity and aggressiveness of Rhizoctonia solani and Rhizoctonia-like fungi on vegetables in New York. Plant Disease, 93, 615–624.
Polizzi, G., Aiello, D., Castello, I., & Vitale, A. (2009a). First report of crown and root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 on Coprosma repens and C. lucida in Italy. Plant Disease, 93, 972.
Polizzi, G., Aiello, D., Vitale, A., Kato, M., & Hyakumachi, M. (2009b). First report of crown and root rot caused by binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-A on Dodonaea viscosa in Italy. Plant Disease, 93, 1347.
Polizzi, G., Aiello, D., Vitale, A., Lahoz, E., Nicoletti, R., & Hyakumachi, M. (2009c). First report of crown rot, stem rot, and root rot caused by binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-G on Viburnum tinus in Italy. Plant Disease, 93, 433.
Polizzi, G., Aiello, D., Castello, I., Guarnaccia, V., & Vitale, A. (2010a). First report of damping-off caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 on Mediterranean fan palm in Italy. Plant Disease, 94, 125.
Polizzi, G., Aiello, D., Castello, I., Guarnaccia, V., & Vitale, A. (2010b). First report of crown rot and stem rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 on marmalade bush in Italy. Plant Disease, 94, 486.
Polizzi, G., Aiello, D., Castello, I., Vitale, A., Kato, M., & Hyakumachi, M. (2010c). First report of crown and root rot caused by binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-A on Thryptomene saxicola in Italy. Plant Disease, 94, 275.
Polizzi, G., Aiello, D., Guarnaccia, V., Panebianco, A., & Formica, P. T. (2011a). First report of crown and root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 on banana passionflower (Passiflora mollissima) in Italy. Plant Disease, 95, 1194.
Polizzi, G., Aiello, D., Vitale, A., Guarnaccia, V., Panebianco, A., & Cirvilleri, G. (2011b). First report of damping-off caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 on pink ipê (Tabebuia impetiginosa) in Italy. Plant Disease, 95, 78.
Pope, E. J., & Carter, D. A. (2001). Phylogenetic placement and host specificity of mycorrhizal isolates belonging to AG-6 and AG-12 in the Rhizoctonia solani species complex. Mycologia, 93,712–719.
Priyatmojo, A., Escopalao, V. E., Tangonan, N. G., Pascual, C. B., Suga, H., Kageyama, K., et al. (2001). Characterisation of a new subgroup of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 1 (AG-1 ID), causal agent of a necrotic leaf spot on coffee. Phytopathology, 91, 1054–1061.
Rinehart, T. A., Copes, W. E., Toda, T., & Cubeta, M. A. (2007). Genetic characterisation of binucleate Rhizoctonia species causing web blight on azalea in Mississippi and Alabama. Plant Disease, 91, 616–623.
Saitou, N., & Nei, M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 4, 406–425.
Schroeder, K. L., & Paulitz, T. C. (2008). Effect of inoculum density and soil tillage on the development and severity of Rhizoctonia root rot. Phytopathology, 98, 304–314.
Sharon, M., Kuninaga, S., Hyakumachi, M., & Sneh, B. (2006). The advancing identification and classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using molecular and biotechnological methods compared with the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience, 47, 299–316.
Sharon, M., Kuninaga, S., Hyakumachi, M., Naito, S., & Sneh, B. (2008). Classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using rDNA-ITS sequence analysis supports the genetic basis of the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience, 49, 93–114.
Sneh, B. (1998). Use of non-pathogenic or hypovirulent fungal strains to protect plants against closely related fungal pathogens. Biotechnology Advances, 16, 1–32.
Sneh, B., Burpee, L., & Ogoshi, A. (1991). Identification of Rhizoctonia species. The APS: St. Paul, Press.
Sneh, B., Burpee, L., & Ogoshi, A. (1998). Identification of Rhizoctonia species. St. Paul: The APS.
Stevens Johnk, J., & Jones, R. K. (2001). Differentiation of three homogeneous groups of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 4 by analysis of fatty acids. Phytopathology, 91, 821–830.
Strausbaugh, C. A., Eujayl, I. A., Panella, L. W., & Hanson L. E. (2011). Virulence, distribution, and diversity of Rhizoctonia solani from sugar beet in Idaho and Oregon. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 33, 210–226.
Sumner, D. R. (1985). Virulence of anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani and Rhizoctonia-like fungi on selected germ plasm of snap bean, lima bean, and cowpea. Plant Disease, 69, 25–27.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., & Kumar, S. (2013). MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725–2729.
Toda, T., Mushika, T., Hayakawa, T., Tanaka, A., Tani, T., & Hyakumachi, M. (2005). Brown-ring-patch disease: a new disease on bentgrass caused by Waitea circinata Var. circinata. Plant Disease, 89, 536–542.
Ueyama, I., Araki, Y., Kurogochi, S., Yoneyama, K., & Yamaguchi, I. (1990). Mode of action of the phenyl urea fungicide pencycuron in Rhizoctonia solani. Pesticide Science, 30, 363–365.
Virgen-Calleros, G., Olalde-Portugal, V., & Carling, D. E. (2000). Anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani on potato in Central Mexico and potential for biological and chemical control. American Journal of Potato Research, 77, 219–224.
Yang, G. (2013). Identification of AG-V, a new anastomosis group of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. from taro and ginger in yunnan province. 5th International Symposium on Rhizoctonia, Zhengzhou, China, August 21–24.
Yang, Y. G., & Wu, X. H. (2013). First report of potato stem canker caused by binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-A in Jilin Province. China Plant Disease, 97, 1246.
Yang, G. H., Naito, S., Ogoshi, A., & Dong, W. H. (2006). Identification, isolation frequency and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. causing the wire stem of red birch in China. Journal of Phytopathology, 154, 80–83.
Yang, Y. G., Zhao, C., Guo, Z. J., & Wu, X. H. (2015). Characterisation of a new anastomosis group (AG-W) of binucleate Rhizoctonia, causal agent for potato stem canker. Plant Disease, 99(12), 1757–1763.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by MIUR project number PON01_01611 (SO.PRO.ME: Sustainable production of potted plants in Mediterranean environment). The authors thank Prof. Masao Arakawa (Faculty of Agriculture, Meijo University, Japan) for his contribution in the molecular characterisation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aiello, D., Guarnaccia, V., Formica, P.T. et al. Occurrence and characterisation of Rhizoctonia species causing diseases of ornamental plants in Italy. Eur J Plant Pathol 148, 967–982 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1150-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1150-8