Abstract
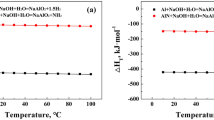
Using coal gangue (CG) as raw material, a new type of all solid-waste-based 13-X molecular sieve material was controllably prepared by alkali fusion-hydrothermal method. The synthetic molecular sieve was used as a solid adsorbent to treat Cd2+-containing wastewater, and its adsorption behavior on Cd2+ in aqueous solution was studied and analyzed. The microstructure and morphology of the molecular sieve were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and specific surface area analyzer. The results show that the synthesized 13-X molecular sieve has higher Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) specific surface area with higher crystallinity and higher adsorption capacity for the heavy metal Cd2+. The adsorption process of Cd2+ by molecular sieve conforms to the Langmuir isotherm adsorption equation and Lagergren pseudo-second-order rate equation. Combined with thermodynamic calculation, it can be concluded that the adsorption process is physically monolayer, spontaneous and exothermic. In this study, a low-cost and naturally available synthesis method of 13-X molecular sieve is reported. Combined with its adsorption mechanism for Cd2+, it provides a feasible and general method for removing heavy metal ions from coal gangue and also provides a new way for the utilization of coal gangue with high added value.
Graphical abstract

摘要
以煤矸石为原料,采用碱熔融-水热法制备了一种新型全固体废弃物基13-X分子筛材料。采用合成分子筛作为固体吸附剂处理含Cd2+废水,研究并分析了其对水溶液中Cd2+的吸附行为。采用X射线衍射、场发射扫描电镜和比表面积分析仪对分子筛的微观结构和形貌进行了研究。结果表明,合成的13-X分子筛具有较高的BET比表面积、较高的结晶度和对重金属Cd2+较高的吸附能力。分子筛对Cd2+的吸附过程符合Langmuir等温线吸附方程和Lagergren伪二级速率方程,结合热力学计算,吸附过程为物理单分子层、自发放热过程。本文报道了一种低成本、天然可得的13-X分子筛合成方法。结合其对Cd2+的吸附机理,为去除煤矸石中的重金属离子提供了一种可行、通用的方法,也为高附加值煤矸石的利用提供了新的途径。






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Narasimharao K, Lingamdinne LP, Al-Thabaiti S, Mokhtar M, Alsheshri A, Alfaifi SY, Chang YY, Koduru JR. Synthesis and characterization of hexagonal MgFe layered double hydroxide/grapheme oxide nanocomposite for efficient adsorptive removal of cadmium ion from aqueous solutions: isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanism. J Water Process Eng. 2022;47:102746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102746.
Li WD, Zeng XY, Lv GY, Liang ZH, Liu QJ, Fu WQ, Zhang JA, Feng YX, Wu HY. Fluorescent graphene oxide derived from carbonized citric acid for copper(II) ions detection. Rare Met. 2021;40(6):1443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01664-2.
Kailasa SK, Koduru JR, Thenepalli T. Fabrication of nanostructured materials with rare-earth elements for bioanalytical applications. Rare-Earth Met Recovery Green Technol Methods Appl. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38106-6_7.
Mehmood A, Mirza MA, Choudhary MA, Kim KH, Raza W, Raza N, Lee SS, Zhang M, Lee JH, Sarfraz M. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in crops in a wastewater irrigated zone and health risk assessment. Environ Res. 2019;168:382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.09.020.
Guo Y, Yang DF, Zhang Y, Wang LC, Wang K. Online estimation of SOH for lithium-ion battery based on SSA-Elman neural network. Prot Control Mod Power Syst. 2022;7(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41601-022-00261-y.
Li DZ, Yang DF, Li LW, Wang LC, Wang K. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy based on the state of health estimation for lithium-ion batteries. Energies. 2022;15(18):6665. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15186665.
Fu F, Wang Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag. 2011;92(3):407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011.
Alhan S, Nehra M, Dilbaghi N, Singhal NK, Kim KH, Kumar S. Potential use of ZnO@ activated carbon nanocomposites for the adsorptive removal of Cd2+ ions in aqueous solutions. Environ Res. 2019;173:411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.03.061.
Chen QY, Luo Z, Hills C, Xue G, Tyrer M. Precipitation of heavy metals from wastewater using simulated flue gas: sequent additions of fly ash, lime and carbon dioxide. Water Res. 2009;43(10):2605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.007.
Doula MK. Simultaneous removal of Cu, Mn and Zn from drinking water with the use of clinoptilolite and its Fe-modified form. Water Res. 2009;43(15):3659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.05.037.
Kang KC, Kim SS, Choi JW, Kwon SH. Sorption of Cu2+ and Cd2+ onto acid-and base-pretreated granular activated carbon and activated carbon fiber samples. J Ind Eng Chem. 2008;14(1):131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2007.08.007.
Nataraj SK, Hosamani KM, Aminabhavi TM. Potential application of an electrodialysis pilot plant containing ion-exchange membranes in chromium removal. Desalination. 2007;217(1–3):181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.02.012.
Hao A, Wan X, Liu X, Yu R, Shui J. Inorganic microporous membranes for hydrogen separation: challenges and solutions. Nano Res Energy. 2022;1:e9120013. https://doi.org/10.26599/NRE.2022.9120013.
Cheng N, Wang B, Wu P, Lee XQ, Xing Y, Chen M, Gao B. Adsorption of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater by modified biochar: a review. Environ Pollut. 2021;273:116448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116448.
Wang YY, Zheng KX, Zhan WH, Huang LY, Liu YD, Li T, Yang ZH, Liao Q, Chen RH, Zhang CS, Wang ZZ. Highly effective stabilization of Cd and Cu in two different soils and improvement of soil properties by multiple-modified biochar. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;207:111294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111294.
Ma CY, Du HL, Liu J, Kang L, Du X, Xi XY, Ran HP. High-temperature stability of dielectric and energy-storage properties of weakly-coupled relaxor (1–x) BaTiO3-xBi (Y1/3Ti1/2) O3 ceramics. Ceram Int. 2021;47(17):25029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.05.231.
Yang MH, Duan CX, Zeng XJ, Li JJ, Liu CY, Zeng LJ, Zhang Y, Wang K, Xi HX. Facile fabrication of nanoscale hierarchical porous zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for enhanced toluene adsorption capacity. Rare Met. 2021;40(2):471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01455-9.
Ran HP, Du HL, Ma CY, Zhao YY, Feng DN, Xu H. Effects of A/B-site Co-doping on microstructure and dielectric thermal stability of AgNbO3 ceramics. Sci Adv Mater. 2021;13(5):741. https://doi.org/10.1166/sam.2021.3943.
Feng DN, Du HL, Ran HP, Lu T, Xia SY, Xu L, Wang ZX, Ma CY. Antiferroelectric stability and energy storage properties of Co-doped AgNbO3 ceramics. J Solid State Chem. 2022;310:123081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2022.123081.
Zhang M, Yuan J. Graphene meta-aerogels: when sculpture aesthetic meets 1D/2D composite materials. Nano Res Energy. 2022;1:e9120035. https://doi.org/10.26599/NRE.2022.9120035.
Deng J, Li B, Xiao Y, Ma L, Wang CP, Bin LW, Shu CM. Combustion properties of coal gangue using thermogravimetry–Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;116:244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.01.083.
Kang L, Du HL, Deng J, Jing XR, Zhang S, Znang YJ. Synthesis and catalytic performance of a new V-doped CeO2-supported alkali-activated-steel-slag-based photocatalyst. J Wuhan Univ Technol-Mater Sci Ed. 2021;36(2):209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-021-2396-8.
Cui L, Guo YX, Wang XM, Du ZP, Cheng FQ. Dissolution kinetics of aluminum and iron from coal mining waste by hydrochloric acid. Chin J Chem Eng. 2015;23(3):590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2014.05.017.
Zhang L, Liang J, Yue L, Dong K, Li J, Zhao D, Li Z, Sun S, Luo Y, Liu Q, Cui G, Alshehri A, Guo X. Benzoate anions-intercalated NiFe-layered double hydroxide nanosheet array with enhanced stability for electrochemical seawater oxidation. Nano Res Energy. 2022;1:e9120028. https://doi.org/10.26599/NRE.2022.9120028.
Zhou WF, Du HL, Kang L, Du X, Shi YP, Qiang XJ, Li HD, Zhao J. Microstructure evolution and improved permeability of ceramic waste-based bricks. Materials. 2022;15(3):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031130.
Zhao XS, Lu GQ, Zhu HY. Effects of ageing and seeding on the formation of zeolite Y from coal fly ash. J Porous Mater. 1997;4(4):245. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009669104923.
Li HP, Cheng RQ, Liu ZL, Du CF. Waste control by waste: Fenton–like oxidation of phenol over Cu modified ZSM–5 from coal gangue. Sci Total Environ. 2019;683:638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.242.
Zhou CY, Alshameri A, Yan CJ, Qiu XM, Wang QH, Ma Y. Characteristics and evaluation of synthetic 13X zeolite from Yunnan’s natural halloysite. J Porous Mater. 2013;20(4):587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-012-9631-9.
Wajima T, Ikegami Y. Synthesis of crystalline zeolite-13X from waste porcelain using alkali fusion. Ceram Int. 2009;35(7):2983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.03.014.
Abd El-Latif MM, Ibrahim AM, Showman MS, Abdel Hamide RR. Alumina/iron oxide nano composite for cadmium ions removal from aqueous solutions. 2013;2(2):47.https://doi.org/10.4236/ijnm.2013.22007.
Ho YS, McKay G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999;34(5):451. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5.
Narasimharao K, Lingamdinne LP, Al-Thabaiti S, Mokhtar M, Alsheshri A, Alfaifi SY, Chang YY, Koduru JR. Synthesis and characterization of hexagonal MgFe layered double hydroxide/grapheme oxide nanocomposite for efficient adsorptive removal of cadmium ion from aqueous solutions: isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanism. J Water Process Eng. 2022;47:102746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102746.
Koduru JR, Lingamdinne LP, Kailasa SK, Thenepalli T, Chang YY, Yang JK. Recent strategies on adsorptive removal of precious metals and rare earths using low-cost natural adsorbents. Rare-Earth Met Recovery Green Technol Methods Appl. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38106-6_5.
Lingamdinne LP, Chang YY, Yang JK, Singh J, Cho EH, Shiratani M, Koduru JR, Attri P. Biogenic reductive preparation of magnetic inverse spinel iron oxide nanoparticles for the adsorption removal of heavy metals. Chem Eng J. 2017;307:74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.067.
Wang J, Guo X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J Hazard Mater. 2020;390:122156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127279.
Freundlich H. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z Phys Chem. 1907;57(1):385. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-1907-5723.
Lingamdinne LP, Godlaveeti SK, Angaru GKR, Chang YY, Nagireddy RR, Somala AR, Koduru JR. Highly efficient surface sequestration of Pb2+ and Cr3+ from water using a Mn3O4 anchored reduced graphene oxide: selective removal of Pb2+ from real water. Chemosphere. 2022;299:134457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134457.
Li XB, Ye JJ, Liu ZH, Qiu YQ, Li LJ, Mao S, Wang XC, Zhang Q. Microwave digestion and alkali fusion assisted hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite from coal fly ash for enhanced adsorption of Cd (II) in aqueous solution. J Cent South Univ. 2018;25(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3712-0.
Liang ZS, Gao Q, Wu ZR, Gao HY. Removal and kinetics of cadmium and copper ion adsorption in aqueous solution by zeolite NaX synthesized from coal gangue. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022;29(56):84651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21700-1.
Keochaiyom B, Wan J, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Xue WJ, Hu L, Huang C, Zhang C, Cheng M. Synthesis and application of magnetic chlorapatite nanoparticles for zinc (II), cadmium (II) and lead (II) removal from water solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;505:824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.06.056.
Phuengprasop T, Sittiwong J, Unob F. Removal of heavy metal ions by iron oxide coated sewage sludge. J Hazard Mater. 2011;186(1):502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.065.
Qi GX, Lei XF, Li L, Sun YL, Yuan C, Wang BD, Yin LD, Xu H, Wang Y. Coal fly ash-derived mesoporous calcium-silicate material (MCSM) for the efficient removal of Cd (II), Cr (III), Ni (II) and Pb (II) from acidic solutions. Procedia Environ Sci. 2016;31:567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.088.
Qiu RF, Cheng FQ, Huang HM. Removal of Cd2+ from aqueous solution using hydrothermally modified circulating fluidized bed fly ash resulting from coal gangue power plant. J Clean Prod. 2018;172:1918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.236.
Jamil TS, Ibrahim HS, Abd El-Maksoud IH, El-Wakeel ST. Application of zeolite prepared from Egyptian kaolin for removal of heavy metals: I. Optimum conditions. Desalination. 2010;258(1–3):34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.03.052.
Lei H, Hao ZD, Chen K, Chen YH, Zhang JG, Hu ZJ, Song YJ, Rao PH, Huang Q. Insight into adsorption performance and mechanism on efficient removal of methylene blue by accordion-like V2CTx MXene. J Phys Chem Lett. 2020;11(11):4253. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c00973.
Jiang L, Wen YY, Zhu ZJ, Liu XF, Shao W. A Double cross-linked strategy to construct graphene aerogels with highly efficient methylene blue adsorption performance. Chemosphere. 2021;265:129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129169.
Zhou L, Zhou HJ, Hu YX, Yan S, Yang JL. Adsorption removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using ceramic adsorbents prepared from industrial waste coal gangue. J Environ Manag. 2019;234:245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.009.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52172099), the Basic Research Plan of Natural Science of Shaanxi Province (No. 2020JQ-754), the Key Innovation Team of Shaanxi Province (No. 2014KCT-04), the Excellent Youth Science and Technology Fund Project of Xi'an University of Science and Technology (Grant No. 6310221009), the Excellent Youth Science and Technology Fund Project of Xi'an University of Science and Technology (Grant No. 6310221009), the Special Project of Shaanxi Province (No. 19JK0490) and the Study on Preparation and Properties of New Solid-Wastebased Cementitious Materials (No. 6000190120).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, L., Liu, SF., Yi, DW. et al. Renewable conversion of coal gangue to 13-X molecular sieve for Cd2+-containing wastewater adsorption performance. Rare Met. 43, 702–710 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02461-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02461-3