Abstract
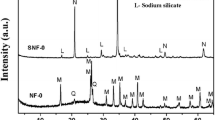
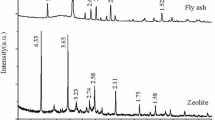
A novel microwave digestion and alkali fusion assisted hydrothermal method was proposed to synthesize zeolite from coal fly ash and the zeolite product was studied for removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solution through batch experiments. The adsorbent was characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, surface area analyzer and zeta potential measurement. The results show that the synthetic zeolite was identified as faujasite. The optimum conditions for removal of Cd(II) are found to be: adsorbent dose of 0.5 g/L, pH 6, contact time of 90 min and initial concentration of 20 mg/L, the removal rate of Cd(II) is 98.55%. The experimental kinetic data agree well with the pseudo second-order equation; the Langmuir isotherm model is found to be more suitable to explicate the experimental equilibrium isotherm results than Freundlich, Dubinin-Radushkevich and Temkin models, and the maximum adsorption capacity of Cd(II) is found to be 86.96 mg/g. The thermodynamic parameters such as ΔGΘ, ΔHΘ and ΔSΘ were evaluated and the results show that the adsorption of Cd(II) onto the as-synthesized zeolite is spontaneous, endothermic and feasible under studied conditions.
摘要
针对传统水热法合成沸石存在碱熔温度高、 反应时间长的问题, 提出了一种新的粉煤灰微波碱熔辅助水热合成沸石的方法, 并将沸石产品用于吸附水溶液中的 Cd(II)。 其合成工艺是将粉煤灰与氢氧化钠混合物置于微波箱式高温反应器中以 450 °C 反应 15 min, 碱熔产物加水在常温下磁力搅拌 4 h, 再在 90 °C 下静置 12 h, 过滤、 洗涤、 干燥得到沸石产品。 采用 X 射线衍射分析、 扫描电镜分析、 红外光谱分析、 比表面积分析和 zeta 电位分析表征吸附剂。 结果表明: 合成的沸石为八面沸石, 含量约为 93%, 比表面积为 75.72 m2/g, pHzpc 为 3.80。 从水溶液中去除 Cd(II), 优化的吸附剂用量为 0.5 g/L, pH 6, 吸附时间为 90 min, 初始浓度为 20 mg/L。 在此条件下, Cd(II)的去除率达 98.55%。 Cd(II)在沸石表面的吸附符合伪二级动力学模型, Langmuir 等温吸附模型比 Freundlich 模型、 Dubinin-Radushkevich 模型和 Temkin 模型更适合于描述等温吸附过程, 最大的 Cd(II)吸附量为 86.96 mg/g。 热力学计算表明: Cd(II)在合成沸石表面的吸附为自发、 吸热过程。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SUN Wei-ling, JIANG Bo-feng, WANG Fei, XU Nan. Effect of carbon nanotubes on Cd(II) adsorption by sediments [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 264: 645–653.
MUBARAK N M, SAHU J N, ABDULLAH E C, JAYAKUMAR N S, GANESAN P. Microwave assisted multiwall carbon nanotubes enhancing Cd(II) adsorption capacity in aqueous media [J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2014, 24: 24–33.
FU Feng-lian, XIE Li-ping, TANG Bing, WANG Qi, JIANG Shu-xian. Application of a novel strategy-advanced Fenton-chemical precipitation to the treatment of strong stability chelated heavy metal containing wastewater [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 189–190: 283–287.
ZEWAIL T M, YOUSEF N S. Kinetic study of heavy metal ions removal by ion exchange in batch conical air spouted bed [J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2015, 54(1): 83–90.
HUNSOM M, PRUKSATHORN K, DAMRONGLERD S, VERGNES H, DUVERNEUIL P. Electrochemical treatment of heavy metals (Cu2+, Cr6+, Ni2+) from industrial effluent and modeling of copper reduction [J]. Water Research, 2005, 39(4): 610–616.
BESSBOUSSE H, RHLALOU T, VERCHERE J F, LEBRUN L. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by filtration with a novel complexing membrane containing poly(ethyleneimine) in a poly(vinyl alcohol) matrix [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 307(2): 249–259.
OZAKI H, SHARMA K, SAKTAYWIN W. Performance of an ultra-low-pressure reverse osmosis membrane (ULPROM) for separating heavy metal: Effects of interference parameters [J]. Desalination, 2002, 144(1–3): 287–294.
JAVADIAN H, GHORBANI F, TAYEBI H, ASI S H. Study of the adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solution using zeolite-based geopolymer, synthesized from coal fly ash; kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 8(6): 837–849.
ANIRUDHAN T S, SREEKUMARI S S. Adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions from industrial effluents using activated carbon derived from waste coconut buttons [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(12): 1989–1998.
GOUDA A A, AL GHANNAM S M. Impregnated multiwalled carbon nanotubes as efficient sorbent for the solid phase extraction of trace amounts of heavy metal ions in food and water samples [J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 202: 409–416.
LASHEEN M R, EL-SHERIF I Y, TAWFIK M E, EI-WAKEEL S T, EI-SHAHAT M F. Preparation and adsorption properties of nano magnetite chitosan films for heavy metal ions from aqueous solution [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2016, 80: 344–350.
VISA M. Synthesis and characterization of new zeolite materials obtained from fly ash for heavy metals removal in advanced wastewater treatment [J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 294: 338–347.
WANG Jian-cheng, LI De-kui, JU Feng-long, HAN Li-na, CHANG Li-ping, BAO Wei-ren. Supercritical hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash for mercury removal from coal derived gas [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2015, 136: 96–105.
IZIDORO J D C, FUNGARO D A, ABBOTT J E, WANG Shao-bing. Synthesis of zeolites X and A from fly ashes for cadmium and zinc removal from aqueous solutions in single and binary ion systems [J]. Fuel, 2013, 103(1): 827–834.
KOSHY N, SINGH D N. Fly ash zeolites for water treatment applications [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016, 4(2): 1460–1472.
NASCIMENTO M, SOARES P S M, SOUZA V P D. Adsorption of heavy metal cations using coal fly ash modified by hydrothermal method [J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(9): 1714–1719.
ZHANG Bao-ping, CHEN Yun-lin, WEI Lin, ZU Zhi-nan. Preparation of molecular sieve X from coal fly ash for the adsorption of volatile organic compounds [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 156(8): 36–39.
KOUKOUZAS N, VASILATOS C, ITSKOS G, MITSIS I. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using CFB-coal fly ash zeolitic materials [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 173(1–3): 581–588.
INADA M, TSUJIMOTO H, EGUCHI Y, ENOMOTO N, HOJO J. Microwave-assisted zeolite synthesis from coal fly ash in hydrothermal process [J]. Fuel, 2005, 84(12, 13): 1482–1486.
TANAKA H, FUJII A, FUJIMOTO S, TANAKA Y. Microwave-assisted two-step process for the synthesis of a single-phase Na-A zeolite from coal fly ash [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2008, 19(1): 83–94.
FUKUI K, KANAYAMA K, YAMAMOTO T, YOSHIDA H. Effects of microwave irradiation on the crystalline phase of zeolite synthesized from fly ash by hydrothermal treatment [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2007, 18(4): 381–393.
ITSKOS G, KOUTSIANOS A, KOUKOUZAS N, VASILATOS C. Zeolite development from fly ash and utilization in lignite mine-water treatment [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2015, 139: 43–50.
HOLLMAN G G, STEEBRUGGEN G, JANSSENJURKOVICOVA M. A two-step process for the synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash [J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(10): 1225–1230.
BUKHARI S S, BEHIN J, KAZEMIAN H, ROHANI S. Conversion of coal fly ash to zeolite utilizing microwave and ultrasound energies: A review [J]. Fuel, 2015, 140: 250–266.
CUI Xing-yu, ZHANG Xu-ning, CHEN Sun-wei, FAN Bin-bin, MA Jing-hong, LI Rui-feng. Synthesis of zeolite 4A from coal fly ash [J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2012, 43(5): 539–543. (in Chinese)
ONUTAI S, JIEMSIRILERS S, THAVORNITI P, KOBAYASHI T. Fast microwave syntheses of fly ash based porous geopolymers in the presence of high alkali concentration [J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(8): 9866–9874.
LIU Yi, YAN Chun-jie, QIU Xiu-mei, LI Dan, WANG Hong-quan, ALSHAMERI A. Preparation of faujasite block from fly ash-based geopolymer via in-situ hydrothermal method [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2016, 59: 433–439.
THUADAIJ P, NUNTIYA A. Preparation and characterization of faujasite using fly ash and amorphous silica from rice husk ash [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 32: 1026–1032.
LEOFANTI G, PADOVAN M, TOZZOLA G, VENTURELLI B. Surface area and pore texture of catalysts [J]. Catalysis Today, 1998, 41(1–3): 207–219.
LIU Hai-cheng, CHEN Wei, CUI Biao, LIU Cheng. Enhanced atrazine adsorption from aqueous solution using chitosan-modified sepiolite [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(11): 4168–4176.
CHEN Wei, LIU Hai-cheng, Adsorption of sulfate in aqueous solutions by organo-nano-clay: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetic studies [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(5): 1974–1981.
MIRETZKY P, MUNOZ C. Enhanced metal removal from aqueous solution by Fenton activated macrophyte biomass [J]. Desalination, 2011, 271(1–3): 20–28.
LI Xin, WANG Guang-zhi, LI Wei-guang, WANG Ping, SU Cheng-yuan. Adsorption of acid and basic dyes by sludge-based activated carbon: Isotherm and kinetic studies [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(1): 103–113.
HRITCU D, HUMELNICU D, DODI G, POPA M I. Magnetic chitosan composite particles: Evaluation of thorium and uranyl ion adsorption from aqueous solutions [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2012, 87(2): 1185–1191.
WANG Yan, TANG Xiao-wu, WANG Heng-yu. Characteristics and mechanisms of Ni(II) removal from aqueous solution by Chinese loess [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(11): 4184–4192.
LIN Li-dan, LIN Yan, Li Chun-jie, WU De-yi, KONG Hai-nan. Synthesis of zeolite/hydrous metal oxide composites from coal fly ash as efficient adsorbents for removal of methylene blue from water [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 148(1): 32–40.
FERNANDES A N, ALMEIDA C A P, DEBACHER N A, SIERRA M M D S. Isotherm and thermodynamic data of adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto peat [J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2010, 982(1–3): 62–65.
TAAMNEH Y, SHARADQAH S. The removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using natural Jordanian zeolite [J]. Applied Water Science, 2017: 7(4): 2021–2028.
VISA M. Synthesis and characterization of new zeolite materials obtained from fly ash for heavy metals removal in advanced wastewater treatment [J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 294: 338–347.
CHEN Ju. Evaluation of synthesized fly ash-zeolite pellets as potential adsorbents for Cd(II) ion in wastewater [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2010. (in Chinese)
HE Kuang, CHEN Yuan-cai, TANG Zheng-hua, HU Yong-you. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by zeolite synthesized from fly ash [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(3): 2778–2788.
YANG Wen-huan, CHEN A-hui, LI Wei-ping, ZHANG Xue-feng, GUO Jun-wen. Synthesization of fly-ash zeolite by alkali fusion- microwave crystallization process and adsorption to Cd(II) [J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2015, 35(5): 547–551. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(2013BAC15B01, 2013BAB07B03) supported by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China; Project(Qian Ke He JZ [2014] 2009) supported by the Key Foundation of Science and Technology of Guizhou Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Xb., Ye, Jj., Liu, Zh. et al. Microwave digestion and alkali fusion assisted hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite from coal fly ash for enhanced adsorption of Cd(II) in aqueous solution. J. Cent. South Univ. 25, 9–20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3712-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3712-0