Abstract
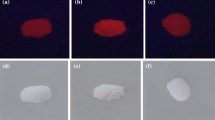
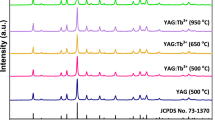
The optical and structural properties of Tb3+-doped yttrium and gadolinium oxyorthosilicate (Y2SiO5 and Gd2SiO5) phosphors were analyzed. The samples were synthesized via sol–gel combustion method using organic fuel. The phase purity and structural properties of the samples were determined via combined approach of powder X-ray diffraction, Fourier transformation infrared (FTIR) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). X-ray measurements revel monoclinic crystal lattice with P21/c symmetry for both M2SiO5 (pure host) and M2SiO5:Tb3+ (doped) silicates, irrespective of the nature of metal (Y or Gd), presence or absence of Tb3+ in lattice and change in calcination temperature up to 1050 °C. FTIR analysis was applied to confirm the bonding of prepared materials. The appearance of bands corresponding to SiO4 tetrahedra (880–1020 cm−1) suggest the layered structure and support the diffraction measurements. TEM micrographs confirm the synthesis of spherical nanoparticles with filled morphology, narrow size distribution and slightly agglomerated crystallites of the samples. The elemental composition of prepared materials was determined using energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The spectra show peaks only for elements assimilated within the host framework. The photoluminescence (PL) emission spectra of Tb3+-doped samples show 5D4 → 7FJ (J = 3–6) transitions under 254 nm-excitation. The dominant peak at 544 nm for 5D4 → 7F5 transition is responsible for the emission of green light on ultraviolet–visible excitation in both the Tb3+-doped host matrixes. Owing to advantageous properties like intense PL and high crystallinity, these nanophosphors could possess potential applications in the mercury free lighting sources and optoelectronic devices.
Graphic abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin YC, Bettinelli M, Karlsson M. Unraveling the mechanisms of thermal quenching of luminescence in Ce3+-doped garnet phosphors. Chem Mater. 2019;31(11):3851.
Singh D, Tanwar V, Simantilke A, Mari B, Kadyan PS, Singh I. Rapid synthesis and enhancement of down conversion emission properties of green SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Ln3+ (Ln3+ = Dy/Dy, Nd) nanophosphors. J Electron Mater. 2016;45(6):2718.
Shen B, Wu F, Zhang Y, Xia H, Chen B, Hu J. Multicolour emission from thermally stable Tb3+/Eu3+ co-doped CaLa4Si3O13 phosphors for single-component w-LEDs application. J Alloys Compd. 2019;809:151836.
Singh D, Tanwar V, Simantilke A, Mari B, Kadyan PS, Singh I. Rapid synthesis and enhancement in down conversion emission properties of BaAl2O4:Eu2+, RE3+ (RE3+ = Y, Pr) nanophosphors. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2016;27(3):2260.
He L, Song Z, Jia X, Xia Z, Liu Q. Consequence of optimal bonding on disordered structure and improved luminescence properties in T-Phase (Ba, Ca)2SiO4:Eu2+ phosphor. Inorg Chem. 2018;57(7):4146.
Kadyan S, Singh D. Synthesis, structure and photoluminescent characterization of MYAl3O7:Eu3+ (M = Ca, Sr, Mg and Ba) red emitting materials for display applications. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2018;29(20):17277.
Cheng J, Zhang J, Lu J, Bian X, Zhang H, Shen Z, Ni X, Ma P, Shi J. Color-tunable Ca4La6(SiO4)4(PO4)2O2:Ce3+, Tb3+ phosphor: luminescence and energy transfer properties. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2019;30(21):19609.
Li X, Zhang Y, Geng D, Lian J, Zhang G, Hou Z, Lin J. CaGdAlO4:Tb3+/Eu3+ as promising phosphors for full-color field emission displays. J Mater Chem C. 2014;2(46):9924.
Liu H, Hao Y, Wanga H, Zhao J, Huang P, Xu B. Luminescent properties of R+ doped Sr2SiO4:Eu3+(R+ = Li+, Na+ and K+) red-emitting phosphors for white LEDs. J Lumin. 2011;131(11):2422.
Sheoran S, Singh V, Singh S, Kadyan S, Singh J, Singh D. Down-conversion characteristics of Eu3+ doped M2Y2Si2O9 (M = Ba, Ca, Mg and Sr) nanomaterials for innovative solar panels. Proc Nat Sci Mater. 2019;29(4):457.
Singh D, Sheoran S, Tanwar V, Bhagwan S. Optical characteristics of Eu(III) doped MSiO3 (M = Mg, Ca, Sr and Ba) nanomaterials for white light emitting applications. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2017;28(4):3243.
Ricci PC, Carbonaro CM, Corpino R, Cannas C, Salis M. Optical and structural characterization of terbium-doped Y2SiO5 phosphor particles. J Phys Chem C. 2011;115(33):16630.
Hirai T, Kondo Y. Preparation of Y2SiO5:Ln3+ (Ln = Eu, Tb, Sm) and Gd9.33(SiO4)6O2:Ln3+ (Ln = Eu, Tb) phosphor fine particles using an emulsion liquid membrane system. J Phys Chem C. 2007;111(1):168.
Zhang X, Zhou L, Pang Q, Shi J, Gong M. Tunable luminescence and Ce3+ → Tb3+ → Eu3+ energy transfer of broadband-excited and narrow line red emitting Y2SiO5:Ce3+, Tb3+, Eu3+ phosphor. J Phys Chem C. 2014;118(14):7591.
Chen Y, Liu B, Shi C, Kirm M, True M, Vielhauer S, Zimmerer G. Luminescent properties of Gd2SiO5 powder doped with Eu3+ under VUV–UV excitation. J Phys Condens Matter. 2005;17(7):1217.
Kolk EVD, Dorenbos P, Eijk CWEV. 5d electron delocalization of Ce3+ and Pr3+ in Y2SiO5 and Lu2SiO5. Phys Rev B. 2005;71(16):1165120.
Dramicanin MD, Jokanovic V, Viana B, Fidancev EA, Mitric M, Andric Z. Luminescence and structural properties of Gd2SiO5:Eu3+ nanophosphors synthesized from the hydrothermal obtained silica sol. J Alloys Compd. 2006;424(1–2):213.
Cates EL, Cho M, Kim JH. Converting visible light into UVC: microbial inactivation by Pr3+-activated upconversion materials. Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45(8):3680.
Zulfiqar U, Subhani T, Husain SW. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles from sodium silicate under alkaline conditions. J Sol Gel Sci Technol. 2016;77(3):753.
Ha MG, Han KR, Jeong JS, Bae JS, Jeong ED, Hong KS. Characterization and optical properties of Y2SiO5:Eu3+ phosphors prepared by using the reverse micelle and the sol–gel processes. J Korean Phys Soc. 2012;61(6):858.
Lin C, Kong D, Liu X, Wang H, Yu M, Lin J. Monodisperse and core–shell-structured SiO2@YBO3:Eu3+ spherical particles: synthesis and characterization. Inorg Chem. 2007;46(7):2674.
Rahman IA, Padavettan V. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles by sol–gel: size-dependent properties, surface modification, and applications in silica–polymer nanocomposites—a review. J Nanomater. 2012;2012:1.
Varma A, Mukasyan AS, Rogachev AS, Manukyan KV. Solution combustion synthesis of nanoscale materials. Chem Rev. 2016;116(23):14493.
Cannas C, Musinu A, Piccaluga G, Deidda C, Serra F, Bazzoni M, Enzo S. Advances in the structure and microstructure determination of yttrium silicates using the Rietveld method. J Solid State Chem. 2005;178(5):1526.
Ghosh P, Sadhu S, Patra A. Preparation and photoluminescence properties of Y2SiO5:Eu3+ nanocrystals. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2006;8(28):3342.
Yokota H, Yoshida M, Ishibashi H, Yano T, Yamamoto H, Kikkawa S. Cathodoluminescence of Ce-doped Gd2SiO5 and Gd9.33(SiO4)6O2 phosphor under continuous electron irradiation. J Alloys Compd. 2011;509(3):800.
Parganiha Y, Kaur J, Dubey N, Dubey V, Shrivastava R, Dhoble SJ, Swart HC. Luminescence and structural properties of Gd2SiO5:Eu3+ phosphors synthesized from the modified solid state method. Ceram Int. 2017;43(12):9084.
Shen SQ, Maa Q, Xu ZB, Xie JJ, Shi Y, Wang J, Ai F. Fabrication, structure and luminescence properties of polycrystalline Tb3+-doped Lu2SiO5 films by Pechini sol–gel method. Appl Surf Sci. 2011;258(5):1768.
Sahu IP, Bisen DP, Brahme N, Tamrakar RK. Photoluminescence properties of europium doped di-strontium magnesium di-silicate phosphor by solid state reaction method. J Radiat Res Appl Sci. 2015;8(1):104.
Gou Z, Chang J, Zhai W. Preparation and characterization of novel bioactive dicalcium silicate ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2005;25(9):1507.
Kadyan S, Singh S, Simantilleke A, Mari B, Singh D. Rapid-gel combustion synthesis, structure and luminescence investigations of trivalent europium doped MGdAlO4 (M = Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+) nanophosphors. Optik. 2020;200:163450.
Xia G, Zhou S, Zhang J, Wang S, Xu J. Solution combustion synthesis, structure and luminescence of Y3Al5O12:Tb3+ phosphors. J Alloys Compd. 2006;421(1–2):294.
Raja A, Annadurai G, Daniel DJ, Ramasamy P. Synthesis, optical and thermal properties of novel Tb3+ doped RbCaF3 fluoroperovskite phosphors. J Alloys Compd. 2016;683:654.
Zhao D, Ma FX, Fan YC, Zhang L, Zhang RJ, Duan PG. PbLnB7O13 (Ln = Tb or Eu): a new type of layered polyborate with multi-colour light emission properties. Dalton Trans. 2017;46(26):8673.
Sun L, Devakumar B, Liang J, Wang S, Sun Q, Huang X. Highly efficient Ce3+ → Tb3+ energy transfer induced bright narrowband green emissions from garnet-type Ca2YZr2(AlO4)3:Ce3+, Tb3+ phosphors for white LEDs with high color rendering index. J Mater Chem C. 2019;7(34):10471.
Mansuy C, Dujardin C, Mahiou R, Nedelec JM. Characterization and scintillation properties of sol–gel derived Lu2SiO5:Ln3+ (Ln = Ce, Eu and Tb) powders. Opt Mater. 2009;31(9):1334.
Guo H, Devakumar B, Li B, Huang X. Novel Na3Sc2(PO4)3:Ce3+, Tb3+ phosphors for white LEDs: Tunable blue-green color emission, high quantum efficiency and external thermal stability. Dyes Pigments. 2018;151(4):81.
Huang X, Li B, Guo H. Synthesis, photoluminescence, cathodoluminescence, and thermal properties of novel Tb3+-doped BiOCl green-emitting phosphors. J Alloys Compd. 2017;695:2773.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) from CSIR, New Delhi, India (No. 09/382(0194)/2017-EMR-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Singh, D. Structural and optical properties of green emitting Y2SiO5:Tb3+ and Gd2SiO5:Tb3+ nanoparticles for modern lighting applications. Rare Met. 40, 3289–3298 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01585-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01585-0