Abstract
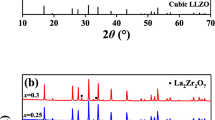
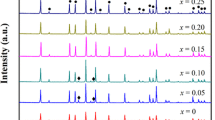
The Ba, Y and Al co-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO) was prepared by the solid-state reaction method. Effect of sintering on the crystallographic structure, morphology, total conductivity, relative density and contractibility rate of the prepared solid electrolyte was studied, respectively. The sintered samples were characterized by X-ray diffractometer (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) techniques, respectively. The cubic garnet phase Ba, Y and Al co-doped LLZO is obtained, and the room-temperature total conductivity of the Ba, Y and Al co-doped LLZO solid electrolyte is improved significantly by eliminating the grain boundary resistances and improving the densifications with controlling sintering temperature (T) and time (t), respectively. Sintering at 1160–1190 °C for 12 h and at 1190 °C for 6–15 h, respectively, the Ba, Y and Al co-doped LLZO solid electrolytes are cubic garnet phase. Sintering at 1180–1190 °C for 12 h and at 1190 °C for 12–18 h, respectively, SEM images of the cross section of the Ba, Y and Al co-doped LLZO solid electrolytes exhibit the distinctively flattened morphology without any noticeable grain boundaries. The total conductivity, relative density and contractibility rate of Li6.52La2.98Ba0.02Zr1.9Y0.1Al0.2O12 solid electrolyte are 2.96 × 10−4 S·cm−1, 94.19% and 18.61%, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen XL, Wang T, Lu WZ, Cao TX, Zhang CM. Synthesis of Ta and Ca doped Li7La3Zr2O12 solid-state electrolyte via simple solution method and its application in suppressing shuttle effect of Li–S battery. J Alloy Compd. 2018;744:386.
Koshikawa H, Matsuda S, Kamiya K, Miyayama M, Nakanishi S. Dynamic changes in charge-transfer resistance at Li metal/Li7La3Zr2O12 interfaces during electrochemical Li dissolution/deposition cycles. J Power Sour. 2018;376:147.
Chen XL, Cao TX, Xue MZ, Lu H, Zhang CM. Improved room temperature ionic conductivity of Ta and Ca doped Li7La3Zr2O12 via a modified solution method. Solid State Ion. 2018;314:92.
Zhao PC, Cao GP, Jin ZQ, Ming H, Zhang ST. Self-consolidation mechanism and its application in the preparation of Al-doped cubic Li7La3Zr2O12. Mater Des. 2018;139:65.
Han F, Yue J, Chen C, Zhao N, Fan X, Ma Z, Gao T, Wang F, Guo X, Wang C. Interphase engineering enabled all ceramic lithium battery. Joule. 2018;2:497.
Zhang F, Shen F, Fan ZY, Ji X, Zhao B, Sun ZT, Xuan YY, Han XG. Ultrathin Al2O3-coated reduced graphene oxide membrane for stable lithium metal anode. Rare Met. 2018;37(6):510.
Li T, Liu H, Shi P, Zhang Q. Recent progress in carbon/lithium metal composite anode for safe lithium metal batteries. Rare Met. 2018;37(6):449.
Yang XF, Han XG, Chen ZP, Zhou LH, Jiao WZ. Improving the Li-ion conductivity and air stability of cubic Li7La3Zr2O12 by the co-doping of Nb, Y on the Zr site. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2018;38:1673.
Yang XF, Han XG, Chen ZP, Zhou LH, Jiao WZ. Fabrication of Li7La3Zr2O12 fibers using bio-mass template Kapok. Mater Lett. 2018;217:271.
Ramakumar S, Deviannapoorani C, Dhivya L. Lithium garnets: synthesis, structure, Li+ conductivity, Li+ dynamics and applications. Prog Mater Sci. 2017;88:325.
Emil H, Wojciech Z, Li L. On fabrication procedures of Li-ion conducting garnets. J Solid State Chem. 2017;248:51.
Murugan R, Thangadurai V, Weppner W. A thermally conductive separator for stable Li metal anodes. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46:7778.
Kotobuki M, Song SF, Takahashi R. Improvement of Li ion conductivity of Li5La3Ta2O12 solid electrolyte by substitution of Ge for Ta. J Power Sour. 2017;349:105.
Kokal I, Somer M, Notten PHL. Sol-gel synthesis and lithium ion conductivity of Li7La3Zr2O12 with garnet-related type structure. Solid State Ion. 2011;185:42.
Peng HJ, Feng LL, Li L. Synthesis of Li5+xLa3HfxNb2−x O12 (x = 0.2–1) ceramics with cubic garnet-type structure. Mate-rials Lett. 2017;194:138.
Shao CY, Yu ZY, Liu HX. Enhanced ionic conductivity of titanium doped Li7La3Zr2O12 solid electrolyte. Electrochim Acta. 2017;225:345.
Andriyevsky B, Doll K, Jacob T. Ab initio molecular dynamics study of lithium diffusion in tetragonal Li7La3Zr2O12. Mater Chem Phys. 2017;185:210.
Rosenkiewitz N, Schuhmacher J, Bockmeyer M. Nitrogen-free sol-gel synthesis of Al-substituted cubic garnet Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO). J Power Sour. 2015;278:104.
Deviannapoorani C, Ramakumar S, Din MMU. Phase transition, lithium ion conductivity and structural stability of tin substituted lithium garnets. RSC Adv. 2016;6:94706.
Zhang Y, Cai J, Chen F, Tu R, Shen Q, Zhang XL, Zhan LM. Preparation of cubic Li7La3Zr2O12 solid electrolyte using a nano-sized core-shell structured precursor. J Alloy Compd. 2015;644:793.
Li YQ, Wang Z, Cao Y, Du M, Chen C, Cui ZH, Guo XX. W-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 ceramic electrolytes for solid state Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2015;180:37.
Allen JL, Wolfenstine J, Rangasamy E. Effect of substitution (Ta, Al, Ga) on the conductivity of Li7La3Zr2O12. J Power Sour. 2012;206:315.
Dhivya L, Karthik K, Ramakumar S. Facile synthesis of high lithium ion conductive cubic phase lithium garnets for electro-chemical energy storage devices. RSC Adv. 2015;5:96042.
Jiang Y, Zhu X, Qin S. Investigation of Mg2+, Sc3+ and Zn2+ doping effects on densification and ionic conductivity of low-temperature sintered Li7La3Zr2O12 garnets. Solid State Ion. 2017;300:73.
Peng HJ, Feng LL, Li L. Synthesis of Li5+xLa3HfxNb2xO12 (x = 0.2–1) ceramics with cubic garnet-type structure. Mater Lett. 2017;194:138.
Afyon S, Krumeich F, Rupp JLM. A shortcut to garnet-type fast Li-ion conductors for all-solid state batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2015;3:18636.
Wang D, Zhong G, Dolotko O. The synergistic effects of Al and Te on the structure and Li+-mobility of garnet-type solid electrolytes. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2:20271.
Liu XZ, Liu YZ, Chen J. Preparation and application of the LiBaLaZrREAlO solid electrolyte. China Patent. CN 2016106059169, 2016.
Rangasamy E, Wolfenstine J, Sakamoto J. Effect of substitution (Ta, Al, Ga) on the conductivity of Li7La3Zr2O12. Solid State Ion. 2012;206:315.
Rangasamy E, Wolfenstine J, Allen J. The effect of 24c-site (A) cation substitution on the tetragonal-cubic phase transition in Li7−xLa3−xAxZr2O12 garnet-based ceramic electrolyte. J Power Sour. 2013;230:261.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51572176 and 51372153), the Plateau Discipline Construction Program from Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. 0817) and the Collaborative Innovation Fund of Shanghai Institute of Technology (No. XTCX2017-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, XZ., Ding, L., Liu, YZ. et al. Room-temperature ionic conductivity of Ba, Y, Al co-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 solid electrolyte after sintering. Rare Met. 40, 2301–2306 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01526-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01526-x