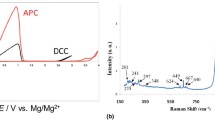
Abstract
In recent years, there has been significant growth in the demand for secondary batteries, and researchers are increasingly taking an interest in the development of next-generation battery systems. Magnesium-ion batteries (MIBs) have been recognized as the optimal alternative to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) due to their low cost, superior safety, and environment-friendliness. However, research and development on rechargeable MIBs are still underway as some serious problems need to be resolved. One of the most serious obstacles is the generation of an irreversible passivation layer on the surface of the Mg anode during cycling. In addition to exploring new electrolytes for MIBs, alternative anode materials for MIBs might be an effective solution to this issue. In this review, the composition and working principle of MIBs have been discussed. In addition, recent advances in the area of anode materials (metals and their alloys, metal oxides, and two-dimensional materials) available for MIBs and the corresponding Mg-storage mechanisms have also been summarized. Further, feasible strategies, including structural design, dimension reduction, and introduction of the second phase, have been employed to design high-performance MIB anodes.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang H, Hasa I, Passerini S. Beyond insertion for Na-ion batteries: nanostructured alloying and conversion anode materials. Adv Energy Mater. 2018;8(17):1702582.
Liang X, Chen X, Zhao H, Yang Z, Wei F, Tu H. Preparation methods of nano-Ti02 electron transport layers and properties for perovskite solar cells. Chin J Rare Met. 2019;43(2):164.
Wu Z, Yang J, Yu B, Shi B, Zhao C, Yu Z. Self-healing alginate-carboxymethyl chitosan porous scaffold as an effective binder for silicon anodes in lithium-ion batteries. Rare Met. 2019;38(9):832.
Li X, Wang J. One-dimensional and two-dimensional synergized nanostructures for high-performing energy storage and conversion. InfoMat. 2020;2(1):3.
Lin Z, Xia Q, Wang W, Li W, Chou S. Recent research progresses in ether- and ester- based electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries. InfoMat. 2019;1(3):376.
Perveen T, Siddiq M, Shahzad N, Ihsan R, Ahmad A, Shahzad MI. Prospects in anode materials for sodium ion batteries—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2020;119:109549.
Vikström H, Davidsson S, Höök M. Lithium availability and future production outlooks. Appl Energy. 2013;110:252.
Ortiz-Vitoriano N, Drewett NE, Gonzalo E, Rojo T. High performance manganese-based layered oxide cathodes: overcoming the challenges of sodium ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci. 2017;10(5):1051.
Kim H, Jeong G, Kim YU, Kim JH, Park CM, Sohn HJ. Metallic anodes for next generation secondary batteries. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42(23):9011.
Speirs J, Contestabile M, Houari Y, Gross R. The future of lithium availability for electric vehicle batteries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2014;35:183.
Kim SW, Seo DH, Ma X, Ceder G, Kang K. Electrode materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries: potential alternatives to current lithium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2012;2(7):710.
Wang F, Wu X, Li C, Zhu Y, Fu L, Wu Y, Liu X. Nanostructured positive electrode materials for post-lithium ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci. 2016;9(12):3570.
Emsley J. Nature’s Building Blocks: an AZ Guide to the Elements. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2011. 699.
Yoo HD, Shterenberg I, Gofer Y, Gershinsky G, Pour N, Aurbach D. Mg rechargeable batteries: an on-going challenge. Energy Environ Sci. 2013;6(8):2265.
Orikasa Y, Masese T, Koyama Y, Mori T, Hattori M, Yamamoto K, Okado T, Huang Z-D, Minato T, Tassel C. High energy density rechargeable magnesium battery using earth-abundant and non-toxic elements. Sci Rep. 2014;4:5622.
Rashad M, Asif M, Wang Y, He Z, Ahmed I. Recent advances in electrolytes and cathode materials for magnesium and hybrid-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2020;25:342.
Zhang Z, Dong S, Cui Z, Du A, Li G, Cui G. Rechargeable magnesium batteries using conversion-type cathodes: a perspective and minireview. Small Methods. 2018;2(10):2366.
Bucur CB. Challenges of a Rechargeable Magnesium Battery: a Guide to the Viability of this Post Lithium-ion Battery. Cham: Springer; 2018. 11.
Matsui M. Study on electrochemically deposited Mg metal. J Power Sources. 2011;196(16):7048.
Kuang C, Zeng W, Li Y. A review of electrode for rechargeable magnesium ion batteries. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2019;19(1):12.
Aurbach D, Lu Z, Schechter A, Gofer Y, Gizbar H, Turgeman R, Cohen Y, Moshkovich M, Levi E. Prototype systems for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Nature. 2000;407(6805):724.
Levi E, Levi MD, Chasid O, Aurbach D. A review on the problems of the solid state ions diffusion in cathodes for rechargeable Mg batteries. J Electroceramics. 2009;22(1):13.
Shterenberg I, Salama M, Gofer Y, Levi E, Aurbach D. The challenge of developing rechargeable magnesium batteries. MRS Bull. 2014;39(5):453.
Liu B, Luo T, Mu G, Wang X, Chen D, Shen G. Rechargeable Mg-ion batteries based on WSe2 nanowire cathodes. ACS Nano. 2013;7(9):8051.
Choi SH, Kim JS, Woo SG, Cho W, Choi SY, Choi J, Lee KT, Park MS, Kim YJ. Role of Cu in Mo6S8 and Cu mixture cathodes for magnesium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(12):7016.
Ichitsubo T, Yagi S, Nakamura R, Ichikawa Y, Okamoto S, Sugimura K, Kawaguchi T, Kitada A, Oishi M, Doi T. A new aspect of Chevrel compounds as positive electrodes for magnesium batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2(36):14858.
Huie MM, Bock DC, Takeuchi ES, Marschilok AC, Takeuchi KJ. Cathode materials for magnesium and magnesium-ion based batteries. Coord Chem Rev. 2015;287:15.
Kim RH, Kim JS, Kim HJ, Chang WS, Han DW, Lee SS, Doo SG. Highly reduced VOx nanotube cathode materials with ultra-high capacity for magnesium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2(48):20636.
Levi E, Gofer Y, Aurbach D. On the way to rechargeable Mg batteries: the challenge of new cathode materials. Chem Mater. 2010;22(3):860.
Saha P, Datta MK, Velikokhatnyi OI, Manivannan A, Alman D, Kumta PN. Rechargeable magnesium battery: current status and key challenges for the future. Prog Mater Sci. 2014;66:1.
Bucur CB, Gregory T, Oliver AG, Muldoon G. Confession of a magnesium battery. J Phys Chem Lett. 2015;6(18):3578.
Lu Z, Schechter A, Moshkovich M, Aurbach D. On the electrochemical behavior of magnesium electrodes in polar aprotic electrolyte solutions. J Electroanal Chem. 1999;466(2):203.
Deivanayagam R, Ingram BJ, Shahbazian-Yassar R. Progress in development of electrolytes for magnesium batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2019;21:136.
Muldoon J, Bucur CB, Oliver AG, Sugimoto T, Matsui M, Kim HS, Allred GD, Zajicek J, Kotani Y. Electrolyte roadblocks to a magnesium rechargeable battery. Energy Environ Sci. 2012;5(3):5941.
Zhang Z, Cui Z, Qiao L, Guan J, Xu H, Wang X, Hu P, Du H, Li S, Zhou X. Novel design concepts of efficient Mg-ion electrolytes toward high-performance magnesium–selenium and magnesium–sulfur batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2017;7(11):1602055.
Mohtadi R, Matsui M, Arthur TS, Hwang SJ. Magnesium borohydride: from hydrogen storage to magnesium battery. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2012;51(39):9780.
Ha SY, Lee YW, Woo SW, Koo B, Kim JS, Cho J, Lee KT, Choi NS. Magnesium (II) bis (trifluoromethane sulfonyl) imide-based electrolytes with wide electrochemical windows for rechargeable magnesium batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(6):4063.
Song J, Sahadeo E, Noked M, Lee SB. Mapping the challenges of magnesium battery. J Phys Chem Lett. 2016;7(9):1736.
Niu J, Yin K, Gao H, Song M, Ma W, Peng Z, Zhang Z. Composition- and size-modulated porous bismuth-tin biphase alloys as anodes for advanced magnesium ion batteries. Nanoscale. 2019;11(32):15279.
Arthur TS, Singh N, Matsui M. Electrodeposited Bi, Sb and Bi1-xSbx alloys as anodes for Mg-ion batteries. Electrochem Commun. 2012;16(1):103.
Murgia F, Stievano L, Monconduit L, Berthelot R. Insight into the electrochemical behavior of micrometric Bi and Mg3Bi2 as high performance negative electrodes for Mg batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2015;3(32):16478.
Liu Z, Lee J, Xiang G, Glass HF, Keyzer EN, Dutton SE, Grey CP. Insights into the electrochemical performances of Bi anodes for Mg ion batteries using 25Mg solid state NMR spectroscopy. Chem Commun. 2017;53(4):743.
Malik R, Burch D, Bazant M, Ceder G. Particle size dependence of the ionic diffusivity. Nano Lett. 2010;10(10):4123.
Bruce PG, Scrosati B, Tarascon JM. Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47(16):2930.
Poizot P, Laruelle S, Grugeon S, Dupont L, Tarascon J. Nano-sized transition-metal oxides as negative-electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Nature. 2000;407(6803):496.
Luo J, Maggard PA. Hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic activities of SrTiO3-coated Fe2O3 and BiFeO3. Adv Mater. 2006;18(4):514.
Amine K, Belharouak I, Chen Z, Tran T, Yumoto H, Ota N, Myung ST, Sun YK. Nanostructured anode material for high-power battery system in electric vehicles. Adv Mater. 2010;22(28):3052.
Cao Y, Xiao L, Wang W, Choi D, Nie Z, Yu J, Saraf LV, Yang Z, Liu Z. Reversible sodium ion insertion in single crystalline manganese oxide nanowires with long cycle life. Adv Mater. 2011;23(28):3155.
Darwiche A, Toiron M, Sougrati MT, Fraisse B, Stievano L, Monconduit L. Performance and mechanism of FeSb2 as negative electrode for Na-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2015;280:588.
Usui H, Yoshioka S, Wasada K, Shimizu M, Sakaguchi H. Nb-doped rutile TiO2: a potential anode material for Na-ion battery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(12):6567.
González JR, Alcántara R, Nacimiento F, Ortiz GF, Tirado JL. Microstructure of the epitaxial film of anatase nanotubes obtained at high voltage and the mechanism of its electrochemical reaction with sodium. CrystEngComm. 2014;16(21):4602.
Shao Y, Gu M, Li X, Nie Z, Zuo P, Li G, Liu T, Xiao J, Cheng Y, Wang C. Highly reversible Mg insertion in nanostructured Bi for Mg ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2014;14(1):255.
Kravchyk KV, Piveteau L, Caputo R, He M, Stadie NP, Bodnarchuk MI, Lechner RT, Kovalenko MV. Colloidal bismuth nanocrystals as a model anode material for rechargeable Mg-ion batteries: atomistic and mesoscale insights. ACS Nano. 2018;12(8):8297.
Tan YH, Yao WT, Zhang T, Ma T, Lu LL, Zhou F, Yao HB, Yu SH. High voltage magnesium-ion battery enabled by nanocluster Mg3Bi2 alloy anode in noncorrosive electrolyte. ACS Nano. 2018;12(6):5856.
Penki TR, Valurouthu G, Shivakumara S, Sethuraman VA, Munichandraiah N. In situ synthesis of bismuth (Bi)/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanocomposites as high-capacity anode materials for a Mg-ion battery. New J Chem. 2018;42(8):5996.
Jung SC, Han YK. Fast magnesium ion transport in the Bi/Mg3Bi2 two-phase electrode. J Phys Chem C. 2018;122(31):17643.
Hattori M, Yamamoto K, Matsui M, Nakanishi K, Mandai T, Choudhary A, Tateyama Y, Sodeyama K, Uchiyama T, Orikasa Y, Tamenori Y, Takeguchi T, Kanamura K, Uchimoto Y. Role of coordination structure of magnesium ions on charge and discharge behavior of magnesium alloy electrode. J Phys Chem C. 2018;122(44):25204.
Lee J, Monserrat B, Seymour ID, Liu Z, Dutton SE, Grey CP. An ab initio investigation on the electronic structure, defect energetics, and magnesium kinetics in Mg3Bi2. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6(35):16983.
Singh N, Arthur TS, Ling C, Matsui M, Mizuno F. A high energy-density tin anode for rechargeable magnesium-ion batteries. Chem Commun (Camb). 2013;49(2):149.
Malyi OI, Tan TL, Manzhos S. In search of high performance anode materials for Mg batteries: computational studies of Mg in Ge, Si, and Sn. J Power Sources. 2013;233:341.
Nguyen DT, Song SW. Magnesium stannide as a high-capacity anode for magnesium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2017;368:11.
Yaghoobnejad Asl H, Fu J, Kumar H, Welborn SS, Shenoy VB, Detsi E. In situ dealloying of bulk Mg2Sn in Mg-ion half cell as an effective route to nanostructured Sn for high performance Mg-ion battery anodes. Chem Mater. 2018;30(5):1815.
Rahman MM, Wang JZ, Hassan MF, Wexler D, Liu HK. Amorphous carbon coated high grain boundary density dual phase Li4Ti5O12–TiO2: a nanocomposite anode material for Li-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2011;1(2):212.
Wu Q, Xu J, Yang X, Lu F, He S, Yang J, Fan HJ, Wu M. Ultrathin anatase TiO2 nanosheets embedded with TiO2–B nanodomains for lithium-ion storage: capacity enhancement by phase boundaries. Adv Energy Mater. 2015;5(7):1401756.
Chu C, Yang J, Zhang Q, Wang N, Niu F, Xu X, Yang J, Fan W, Qian Y. Biphase-interface enhanced sodium storage and accelerated charge transfer: flower-like anatase/bronze TiO2/C as an advanced anode material for Na-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(50):43648.
Beaulieu LY, Larcher D, Dunlap RA, Dahn JR. Reaction of Li with grain-boundary atoms in nanostructured compounds. J Electrochem Soc. 2000;147(9):3206.
Parent LR, Cheng Y, Sushko PV, Shao Y, Liu J, Wang C-M, Browning ND. Realizing the full potential of insertion anodes for Mg-ion batteries through the nanostructuring of Sn. Nano Lett. 2015;15(2):1177.
Cheng Y, Shao Y, Parent LR, Sushko ML, Li G, Sushko PV, Browning ND, Wang C, Liu J. Interface promoted reversible Mg insertion in nanostructured tin–antimony alloys. Adv Mater. 2015;27(42):6598.
Niu J, Gao H, Ma W, Luo F, Yin K, Peng Z, Zhang Z. Dual phase enhanced superior electrochemical performance of nanoporous bismuth-tin alloy anodes for magnesium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2018;14:351.
Giang Thi Huong N, Dan-Thien N, Song SW. Unveiling the roles of formation process in improving cycling performance of magnesium stannide composite anode for magnesium-ion batteries. Adv Mater Interfaces. 2018;5(22):1801039.
Periyapperuma K, Tran TT, Purcell MI, Obrovac MN. The reversible magnesiation of Pb. Electrochim Acta. 2015;165:162.
Murgia F, Monconduit L, Stievano L, Berthelot R. Electrochemical magnesiation of the intermetallic InBi through conversion-alloying mechanism. Electrochim Acta. 2016;209:730.
Murgia F, Laurencin D, Weldekidan ET, Stievano L, Monconduit L, Doublet ML, Berthelot R. Electrochemical Mg alloying properties along the Sb1−xBix solid solution. Electrochim Acta. 2018;259:276.
Blondeau L, Foy E, Khodja H, Gauthier M. Unexpected behavior of the InSb alloy in Mg-ion batteries: unlocking the reversibility of Sb. J Phys Chem C. 2018;123(2):1120.
Murgia F, Weldekidan ET, Stievano L, Monconduit L, Berthelot R. First investigation of indium-based electrode in Mg battery. Electrochem Commun. 2015;60:56.
Fu S, Ni J, Xu Y, Zhang Q, Li L. Hydrogenation driven conductive Na2Ti3O7 nanoarrays as robust binder-free anodes for sodium-ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2016;16(7):4544.
Chen C, Xu H, Zhou T, Guo Z, Chen L, Yan M, Mai L, Hu P, Cheng S, Huang Y. Integrated intercalation-based and interfacial sodium storage in graphene-wrapped porous Li4Ti5O0 nanofibers composite aerogel. Adv Energy Mater. 2016;6(13):1600322.
Subramanian V, Karki A, Gnanasekar K, Eddy FP, Rambabu B. Nanocrystalline TiO2 (anatase) for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2006;159(1):186.
Wu N, Lyu YC, Xiao RJ, Yu X, Yin YX, Yang XQ, Li H, Gu L, Guo YG. A highly reversible, low-strain Mg-ion insertion anode material for rechargeable Mg-ion batteries. NPG Asia Mater. 2014;6(8):e120.
Wu N, Yin YX, Guo YG. Size-dependent electrochemical magnesium storage performance of spinel lithium titanate. Chem Asian J. 2014;9(8):2099.
Chen C, Wang J, Zhao Q, Wang Y, Chen J. Layered Na2Ti3O7/MgNaTi3O7/Mg0.5NaTi3O7 nanoribbons as high-performance anode of rechargeable Mg-ion batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2016;1(6):1165.
Luo L, Zhen Y, Lu Y, Zhou K, Huang J, Huang Z, Mathur S, Hong Z. Structural evolution from layered Na2Ti3O7 to Na2Ti6O13 nanowires enabling a highly reversible anode for Mg-ion batteries. Nanoscale. 2020;12(1):230.
Li H, Liu X, Zhai T, Li D, Zhou H. Li3VO4: a promising insertion anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2013;3(4):428.
Liang Z, Lin Z, Zhao Y, Dong Y, Kuang Q, Lin X, Liu X, Yan D. New understanding of Li3VO4/C as potential anode for Li-ion batteries: preparation, structure characterization and lithium insertion mechanism. J Power Sources. 2015;274:345.
Zeng J, Yang Y, Li C, Li J, Huang J, Wang J, Zhao J. Li3VO4: an insertion anode material for magnesium ion batteries with high specific capacity. Electrochim Acta. 2017;247:265.
Wu M, Liao J, Yu L, Lv R, Li P, Sun W, Tan R, Duan X, Zhang L, Li F, Kim J, Shin KH, Seok PH, Zhang W, Guo Z, Wang H, Tang Y, Gorgolis G, Galiotis C, Ma J. 2020 Roadmap on carbon materials for energy storage and conversion. Chem Asian J. 2020;15(7):995.
Sun Y, Wu Q, Shi G. Graphene based new energy materials. Energy Environ Sci. 2011;4(4):1113.
Bonaccorso F, Colombo L, Yu G, Stoller M, Tozzini V, Ferrari AC, Ruoff RS, Pellegrini V. Graphene, related two-dimensional crystals, and hybrid systems for energy conversion and storage. Science 2015;347(6217): UNSP 1246501.
Anasori B, Lukatskaya MR, Gogotsi Y. 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage. Nat Rev Mater. 2017;2(2):16098.
Tan C, Cao X, Wu XJ, He Q, Yang J, Zhang X, Chen J, Zhao W, Han S, Nam GH, Sindoro M, Zhang H. Recent advances in ultrathin two-dimensional nanomaterials. Chem Rev. 2017;117(9):6225.
Datta D, Li J, Koratkar N, Shenoy VB. Enhanced lithiation in defective graphene. Carbon. 2014;80:305.
Er D, Detsi E, Kumar H, Shenoy VB. Defective graphene and graphene allotropes as high-capacity anode materials for Mg ion batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2016;1(3):638.
Shomali E, Abdolhosseini Sarsari I, Tabatabaei F, Mosaferi M, Seriani N. Graphyne as the anode material of magnesium-ion batteries: ab initio study. Comput Mater Sci. 2019;163:315.
Ma C, Shao X, Cao D. Nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets as anode materials for lithium ion batteries: a first-principles study. J Mater Chem. 2012;22(18):8911.
Zhang J, Liu G, Hu H, Wu L, Wang Q, Xin X, Li S, Lu P. Graphene-like carbon-nitrogen materials as anode materials for Li-ion and mg-ion batteries. Appl Surf Sci. 2019;487:1026.
Zhang S, Guo S, Chen Z, Wang Y, Gao H, Gomez-Herrero J, Ares P, Zamora F, Zhu Z, Zeng H. Recent progress in 2D group-VA semiconductors: from theory to experiment. Chem Soc Rev. 2018;47(3):982.
Jin W, Wang Z, Fu YQ. Monolayer black phosphorus as potential anode materials for Mg-ion batteries. J Mater Sci. 2016;51(15):7355.
Sibari A, Marjaoui A, Lakhal M, Kerrami Z, Kara A, Benaissa M, Ennaoui A, Hamedoun M, Benyoussef A, Mounkachi O. Phosphorene as a promising anode material for (Li/Na/Mg)-ion batteries: a first-principle study. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2018;180:253.
Han X, Liu C, Sun J, Sendek AD, Yang W. Density functional theory calculations for evaluation of phosphorene as a potential anode material for magnesium batteries. RSC Adv. 2018;8(13):7196.
Benzidi H, Lakhal M, Garara M, Abdellaoui M, Benyoussef A, El Kenz A, Mounkachi O. Arsenene monolayer as an outstanding anode material for (Li/Na/Mg)-ion batteries: density functional theory. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2019;21(36):19951.
Ye XJ, Zhu GL, Liu J, Liu CS, Yan XH. Monolayer, bilayer, and heterostructure arsenene as potential anode materials for magnesium-ion batteries: a first-principles study. J Phys Chem C. 2019;123(25):15777.
Wei XL, Zhang H, Guo GC, Li XB, Lau WM, Liu LM. Modulating the atomic and electronic structures through alloying and heterostructure of single-layer MoS2. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2(7):2101.
Vakili-Nezhaad GR, Gujarathi AM, Al Rawahi N, Mohammadi M. Performance of WS2 monolayers as a new family of anode materials for metal-ion (Mg, Al and Ca) batteries. Mater Chem Phys. 2019;230:114.
Shafique A, Shin YH. Strain engineering of phonon thermal transport properties in monolayer 2H-MoTe2. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017;19(47):32072.
Lu AY, Zhu H, Xiao J, Chuu CP, Han Y, Chiu MH, Cheng CC, Yang CW, Wei KH, Yang Y, Wang Y, Sokaras D, Nordlund D, Yang P, Muller DA, Chou MY, Zhang X, Li LJ. Janus monolayers of transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat Nanotechnol. 2017;12(8):744.
Chen W, Qu Y, Yao L, Hou X, Shi X, Pan H. Electronic, magnetic, catalytic, and electrochemical properties of two-dimensional Janus transition metal chalcogenides. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6(17):8021.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Graduate Research and Innovation Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. CYS19034), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2019CDJGFCL001), and the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. KJZD-K201800101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Q., Zeng, W., Liu, SL. et al. Recent developments on anode materials for magnesium-ion batteries: a review. Rare Met. 40, 290–308 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01493-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01493-3