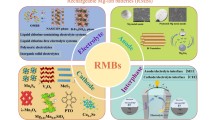
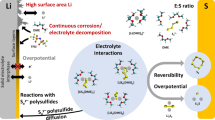
Abstract
Rechargeable magnesium (Mg) battery has been considered as a promising candidate for future battery generations because of its potential high-energy density, its safety features and low cost. The challenges lying ahead for the realization of Mg battery in general are to develop proper electrolytes fulfilling a multitude of requirements and to discover cathode materials enabling high-energy Mg batteries. The combination of Mg anode with a sulfur cathode is one of the promising electrochemical couples due to its advantages of safety, low costs, and a high theoretical energy density of over 3200 Wh/L. However, the research on magnesium-sulfur (Mg-S) battery is just at its beginning and the development of suitable electrolytes has been the key challenge for further improvement, and, thus, in the focus of recent research. In this review, we highlight the recent progress achieved in Mg electrolytes and Mg-S batteries and discuss the major technical issues, which must be resolved for the improvement of Mg-S batteries.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Manthiram: Materials challenges and opportunities of lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2, 176 (2011).
N.S. Choi, Z. Chen, S.A. Freunberger, Y.K. Sun, K. Amine, G. Yushin, L.F. Nazar, J. Cho, and P.G. Bruce: Challenges facing lithium batteries and electrical double-layer capacitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 9994 (2012).
H.D. Yoo, E. Markevich, G. Salitra, D. Sharon, and D. Aurbach: On the challenge of developing advanced technologies for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Mater. Today 17, 110 (2014).
C. Hamilton: Cobalt set to shine in metals markets in 2017. https://www.ft.com/content/e8ce859a-ff59-11e6-8d8e-a5e3738f9ae4.
T.D. Gregory, R.J. Hoffman, and R.C. Winterton: Applications to energy storage nonaqueous electrochemistry of magnesium. J. Electrochem. Soc. 137, 775 (1990).
D. Aurbach, Y. Cohen, and M. Meshkovich: The study of reversible magnesium deposition by in situ scanning tunneling microscopy. Solid State Lett. 4, A113 (2001).
M. Jöckle and A. Groß: Microscopic properties of lithium, sodium, and magnesium battery anode materials related to possible dendrite growth. J. Chem. Phys. 141, 174710 (2014).
H.D. Yoo, I. Shterenberg, Y. Gofer, G. Gershinsky, N. Pour, and D. Aurbach: Mg rechargeable batteries: an on-going challenge. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 2265 (2013).
P. Saha, M.K. Datta, O.I. Velikokhatnyi, A. Manivannan, D. Alman, and P.N. Kumta: Rechargeable magnesium battery: current status and key challenges for the future. Prog. Mater. Sci. 66, 1 (2014).
R. Mohtadi and F. Mizuno: Magnesium batteries: current state of the art, issues and future perspectives. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 5, 1291 (2014).
M.M. Huie, D.C. Bock, E.S. Takeuchi, A.C. Marschilok, and K.J. Takeuchi: Cathode materials for magnesium and magnesium-ion based batteries. Coord. Chem. Rev. 287, 15 (2015).
J. Muldoon, C.B. Bucur, and T. Gregory: Quest for nonaqueous multivalent secondary batteries: magnesium and beyond. Chem. Rev. 114, 11683 (2014).
C.B. Bucur, T. Gregory, A.G. Oliver, and J. Muldoon: Confession of a magnesium battery. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6, 3578 (2015).
J. Song, E. Sahadeo, M. Noked, and S.B. Lee: Mapping the challenges of magnesium battery. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 1736 (2016).
P. Canepa, G. Sai Gautam, D.C. Hannah, R. Malik, M. Liu, K.G. Gallagher, K.A. Persson, and G. Ceder: Odyssey of multivalent cathode materials: open questions and future challenges. Chem. Rev. 117, 4287 (2017).
A. Manthiram, Y. Fu, S. Chung, C. Zu, and Y. Su: Rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries. Chem. Rev. 114, 11751 (2014).
Z.W. Seh, Y. Sun, Q. Zhang, and Y. Cui: Designing high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 5605 (2016).
J. Muldoon, C.B. Bucur, A.G. Oliver, T. Sugimoto, M. Matsui, H.S. Kim, G.D. Allred, J. Zajicek, and Y. Kotani: Electrolyte roadblocks to a magnesium rechargeable battery. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 5941 (2012).
O. Tutusaus and R. Mohtadi: Paving the way towards highly stable and practical electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium batteries. ChemElectroChem 2, 51 (2015).
E.M. Erickson, E. Markevich, G. Salitra, D. Sharon, D. Hirshberg, E. de la Llave, I. Shterenberg, A. Rozenman, and A. Frimer: Review-development of advanced rechargeable batteries: a continuous challenge in the choice of suitable electrolyte solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 162, A2424 (2015).
Z. Lu, A. Schechter, M. Moshkovich, and D. Aurbach: On the electrochemical behavior of magnesium electrodes in polar aprotic electrolyte solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 466, 203 (1999).
D. Aurbach, G.S. Suresh, E. Levi, A. Mitelman, O. Mizrahi, O. Chusid, and M. Brunelli: Progress in rechargeable magnesium battery technology. Adv. Mater. 19, 4260 (2007).
Y. Vestfried, O. Chusid, Y. Goffer, P. Aped, and D. Aurbach: Structural analysis of electrolyte solutions comprising magnesium-aluminate chloro-organic complexes by Raman spectroscopy. Organometallics 26, 3130 (2007).
N. Pour, Y. Gofer, D.T. Major, and D. Aurbach: Structural analysis of electrolyte solutions for rechargeable Mg batteries by stereoscopic means and DFT calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 6270 (2011).
Y. Guo, F. Zhang, J. Yang, F. Wang, Y.N. Li, and S. Hirano: Boron-based electrolyte solutions with wide electrochemical windows for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 9100 (2012).
E.G. Nelson, S.I. Brody, J.W. Kampf, and B.M. Bartlett: A magnesium tetraphenylaluminate battery electrolyte exhibits a wide electrochemical potential window and reduces stainless steel corrosion. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 18194 (2014).
C. Liebenow, Z. Yang, and P. Lobitz: The electrodeposition of magnesium using solutions of organomagnesium halides, amidomagnesium halides and magnesium organoborates. Electrochem. Commun. 2, 641 (2000).
H.S. Kim, T.S. Arthur, G.D. Allred, J. Zajicek, J.G. Newman, A.E. Rodnyansky, A.G. Oliver, W.C. Boggess, and J. Muldoon: Structure and compatibility of a magnesium electrolyte with a sulphur cathode. Nat. Commun. 2, 427 (2011).
Z. Zhao-Karger, X. Zhao, O. Fuhr, and M. Fichtner: Bisamide based non-nucleophilic electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium batteries. RSC Adv. 3, 16330 (2013).
W. Seidel: Synthese von mesitylaluminium-verbindungen. Z. anorg. Allg. Chem. 524, 101 (1985).
C.B. Minella, P. Gao, Z. Zhao-Karger, X. Mu, T. Diemant, M. Pfeifer, V.S.K. Chakravadhanula, R.J. Behm, and M. Fichtner: Interlayer-expanded vanadium oxychloride as an electrode material for magnesium-based batteries. ChemElectroChem 4, 738 (2017).
Z. Zhao-Karger, X. Zhao, D. Wang, T. Diemant, R.J. Behm, and M. Fichtner: Performance improvement of magnesium sulfur batteries with modified non-nucleophilic electrolytes. Adv. Energy Mater. 5, 1 (2015).
T. Gao, M. Noked, A.J. Pearse, E. Gillette, X. Fan, Y. Zhu, C. Luo, L. Suo, and M.A. Schroeder: Enhancing the reversibility of Mg/S battery chemistry through Li+ mediation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 12388 (2015).
B.P. Vinayan, Z. Zhao-Karger, T. Diemant, V.S.K. Chakravadhanula, N.I. Schwarzburger, M.A. Cambaz, R.J. Behm, C. Kübel, and M. Fichtner: Performance study of magnesium-sulfur battery using a graphene based sulfur composite cathode electrode and a non-nucleophilic Mg electrolyte. Nanoscale 8, 3296 (2016).
X. Yu and A. Manthiram: Performance enhancement and mechanistic studies of magnesium-sulfur cells with an advanced cathode structure. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 431 (2016).
Z. Zhao-Karger, X.M. Lin, C. Bonatto Minella, D. Wang, T. Diemant, R.J. Behm, and M. Fichtner: Selenium and selenium-sulfur cathode materials for high-energy rechargeable magnesium batteries. J. Power Sources 323, 213 (2016).
H. Tian, T. Gao, X. Li, X. Wang, C. Luo, X. Fan, C. Yang, L. Suo, and Z. Ma: High power rechargeable magnesium/iodine battery chemistry. Nat. Commun. 8, 14083 (2017).
F. Wang, Y. Guo, J. Yang, Y. Nuli, and S. Hirano: A novel electrolyte system without a Grignard reagent for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Chem. Commun. 48, 10763 (2012).
E.G. Nelson, J.W. Kampf, and B.M. Bartlett: Enhanced oxidative stability of non-Grignard magnesium electrolytes through ligand modification. Chem. Commun. 50, 5193 (2014).
A.J. Crowe and B.M. Bartlett: Influence of steric bulk on the oxidative stability of phenolate-based magnesium-ion battery electrolytes. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 368 (2016).
A.J. Crowe, K.K. Stringham, and B.M. Bartlett: Fluorinated alkoxide-based magnesium-ion battery electrolytes that demonstrate Li-ion-battery-like high anodic stability and solution conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 23060 (2016).
J.T. Herb, C. Nist-Lund, J. Schwartz, and C.B. Arnold: Structural effects of magnesium dialkoxides as precursors for magnesium-ion electrolytes. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 4, A49 (2015).
J.T. Herb, C.A. Nist-Lund, and C.B. Arnold: A fluorinated dialkoxide-based magnesium-ion electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 17, 7801 (2017).
S. He, K.V. Nielson, J. Luo, and T.L. Liu: Recent advances on MgCl2 based electrolytes for rechargeable Mg batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 8, 184 (2016).
Z. Rappoport and I. Marek, The Chemistry of Organomagnesium Compounds (John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester, West Sussex, 2008).
Y. Viestfrid, M.D. Levi, Y. Gofer, and D. Aurbach: Microelectrode studies of reversible Mg deposition in THF solutions containing complexes of alkylaluminum chlorides and dialkylmagnesium. J. Electroanal. Chem. 576, 183 (2005).
R.E. Doe, R. Han, J. Hwang, A.J. Gmitter, I. Shterenberg, H.D. Yoo, N. Pour, and D. Aurbach: Novel, electrolyte solutions comprising fully inorganic salts with high anodic stability for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Chem. Commun. 50, 243 (2014).
C.J. Barile, E.C. Barile, K.R. Zavadil, R.G. Nuzzo, and A.A. Gewirth: Electrolytic conditioning of a magnesium aluminum chloride complex for reversible magnesium deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 27623 (2014).
C.J. Barile, R.G. Nuzzo, and A.A. Gewirth: Exploring salt and solvent effects in chloride-based electrolytes for magnesium electrodeposition and dissolution. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 13524 (2015).
K.A. See, K.W. Chapman, L. Zhu, K.M. Wiaderek, O.J. Borkiewicz, C.J. Barile, P.J. Chupas, and A.A. Gewirth: The interplay of Al and Mg speciation in advanced Mg battery electrolyte solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 328 (2016).
I. Shterenberg, M. Salama, Y. Gofer, E. Levi, and D. Aurbach: The challenge of developing rechargeable magnesium batteries. MRS Bull. 39, 453 (2014).
S. He, J. Luo, and T.L. Liu: MgCl2/AlCl3 electrolytes for reversible Mg deposition/stripping: electrochemical conditioning or not? J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 12718 (2017).
W. Li, S. Cheng, J. Wang, Y. Qiu, Z. Zheng, H. Lin, S. Nanda, Q. Ma, and Y. Xu: Synthesis, crystal structure, and electrochemical properties of a simple magnesium electrolyte for magnesium/sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 6406 (2016).
J. Luo, S. He, and T.L. Liu: Tertiary Mg/MgCl2/AlCl3 inorganic Mg2+ electrolytes with unprecedented electrochemical performance for reversible Mg deposition. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 1197 (2017).
M.-C. Lin, M. Gong, B. Lu, Y. Wu, D.-Y. Wang, M. Guan, M. Angell, C. Chen, and H. Dai: An ultrafast rechargeable aluminium-ion battery. Nature 520, 324 (2015).
T. Liu, Y. Shao, G. Li, M. Gu, J. Hu, S. Xu, Z. Nie, X. Chen, and C. Wang: A facile approach using MgCl2 to formulate high performance Mg2+ electrolytes for rechargeable Mg batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 3430 (2014).
Z. Zhao-Karger, J.E. Mueller, X. Zhao, O. Fuhr, T. Jacob, and M. Fichtner: Novel transmetalation reaction for electrolyte synthesis for rechargeable magnesium batteries. RSC Adv. 4, 26924 (2014).
E.D. Robert, H.L. George, E.J. Robert, and H. Jaehee: High voltage rechargeable magnesium batteries having a non-aqueous electrolyte. US Pat. Appl. Publ. US 2013/0252112 A1 (2014).
I. Shterenberga, M. Salamaa, H.D. Yoob, Y. Gofera, J.-B. Parkc, Y.-K. Sunc, and D. Aurbach: Evaluation of (CF3SO2)2N- (TFSI) based electrolyte solutions for Mg batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 162, A7118 (2015).
N. Sa, B. Pan, A. Saha-Shah, A.A. Hubaud, J.T. Vaughey, L.A. Baker, C. Liao, and A.K. Burrell: Role of chloride for a simple, non-grignard Mg electrolyte in ether-based solvents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 16002 (2016).
C. Liao, N. Sa, B. Key, A.K. Burrell, L. Cheng, L.A. Curtiss, J.T. Vaughey, J.-J. Woo, and L. Hu: The unexpected discovery of the Mg(HMDS)2/MgCl2 complex as a magnesium electrolyte for rechargeable magnesium batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 6082 (2015).
B. Pan, J. Huang, M. He, S.M. Brombosz, J.T. Vaughey, L. Zhang, A.K. Burrell, Z. Zhang, and C. Liao: The role of MgCl2 as a Lewis base in ROMgCl-MgCl2 electrolytes for magnesium-ion batteries. ChemSusChem 9, 595 (2016).
S.J. Kang, S.C. Lim, H. Kim, J.W. Heo, S. Hwang, M. Jang, D. Yang, S.T. Hong, and H. Lee: Non-grignard and Lewis acid-free sulfone electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Chem. Mater. 29, 3174 (2017).
S. Yagi, A. Tanaka, Y. Ichikawa, T. Ichitsubo, and E. Matsubara: Electrochemical stability of magnesium battery current collectors in a Grignard reagent-based electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 160, C83 (2013).
C. Wall, Z. Zhao-Karger, and M. Fichtner: Corrosion resistance of current collector materials in Bisamide based electrolyte for magnesium batteries. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 4, C8 (2014).
R. Mohtadi, M. Matsui, T.S. Arthur, and S.J. Hwang: Magnesium borohydride: from hydrogen storage to magnesium battery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 9780 (2012).
M. Kar, Z. Ma, L.M. Azofra, K. Chen, M. Forsyth, and D.R. MacFarlane: Ionic liquid electrolytes for reversible magnesium electrochemistry. Chem. Commun. 52, 4033 (2016).
T. Watkins, A. Kumar, and D.A. Buttry: Designer ionic liquids for reversible electrochemical deposition/dissolution of magnesium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 641 (2016).
J. Muldoon, C.B. Bucur, A.G. Oliver, J. Zajicek, G.D. Allred, and W.C. Boggess: Corrosion of magnesium electrolytes: chlorides-the culprit. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 482 (2013).
S.Y. Ha, Y.W. Lee, S.W. Woo, B. Koo, J.S. Kim, J. Cho, K.T. Lee, and N.S. Choi: Magnesium(II) bis(trifluoromethane sulfonyl) imide-based electrolytes with wide electrochemical windows for rechargeable magnesium batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 4063 (2014).
Z. Ma, M. Kar, C. Xiao, M. Forsyth, and D.R. MacFarlane: Electrochemical cycling of Mg in Mg[TFSI]2/tetraglyme electrolytes. Electrochem. Commun. 78, 29 (2017).
O. Tutusaus, R. Mohtadi, T.S. Arthur, F. Mizuno, E.G. Nelson, and Y.V. Sevryugina: An efficient halogen-free electrolyte for use in rechargeable magnesium batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 7900 (2015).
O. Tutusaus, R. Mohtadi, N. Singh, T.S. Arthur, and F. Mizuno: Study of electrochemical phenomena observed at the Mg metal/electrolyte interface. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 224 (2016).
S.G. McArthur, L. Geng, J. Guo, and V. Lavallo: Cation reduction and comproportionation as novel strategies to produce high voltage, halide free, carborane based electrolytes for rechargeable Mg batteries. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2, 1101 (2015).
S. McArthur, R. Jay, L. Geng, J. Guo, and V. Lavallo: Below the 12-vertex: 10-vertex carborane anions as non-corrosive, halide free, electrolytes for rechargeable Mg batteries. Chem. Commun. 53, 4453 (2017).
E.N. Keyzer, H.F.J. Glass, Z. Liu, P.M. Bayley, S.E. Dutton, C.P. Grey, and D.S. Wright: Mg(PF6)2-based electrolyte systems: understanding electrolyte-electrode interactions for the development of Mg-ion batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 8682 (2016).
R. Schwarz, M. Pejic, P. Fischer, M. Marinaro, L. Jörissen, and M. Wachtler: Magnesocene-based electrolytes: a new class of electrolytes for magnesium batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 14958 (2016).
J.T. Herb, C.A. Nist-Lund, and C.B. Arnold: A fluorinated alkoxyaluminate electrolyte for magnesium-ion batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 1227 (2016).
Z. Zhang, Z. Cui, L. Qiao, J. Guan, H. Xu, X. Wang, P. Hu, H. Du, and S. Li: Novel design concepts of efficient Mg-ion electrolytes toward high-performance magnesium-selenium and magnesium-sulfur batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1602055 (2017).
I. Krossing and I. Raabe: Noncoordinating anions-fact or fiction? A survey of likely candidates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 2066 (2004).
Z. Zhao-Karger, E.G. Bardaji, O. Fuhr, and M. Fichtner: New class of non-corrosive, highly efficient electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 10815 (2017).
J.M. Lalancette, A. Freche, J.R. Brindle, and M. Laliberte: Reductions of functional groups with sulfurated borohydrides. Application to steroidal ketones. Synthesis 10, 526 (1972).
K. Itaoka, I.T. Kim, K. Yamabuki, N. Yoshimoto, and H. Tsutsumi: Room temperature rechargeable magnesium batteries with sulfur-containing composite cathodes prepared from elemental sulfur and bis(alkenyl) compound having a cyclic or linear ether unit. J. Power Sources 297, 323 (2015).
Acknowledgment
This study is supported by the “MagS” project (grant no. 03XP0032A) from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) of Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhirong, ZK., Maximilian, F. Magnesium-sulfur battery: its beginning and recent progress. MRS Communications 7, 770–784 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.101
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.101