Abstract
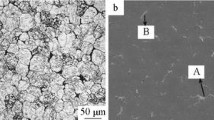
In this study, the fine-grained Mg–Li alloy was prepared by friction stir processing (FSP). The microstructure and mechanical properties of the friction-stir-processed (FSPed) Mg–Li alloy were investigated. The result showed that FSP resulted in the grain refinement, and the average grain size of the β-Li phase was about 7.5 μm. Besides the α-Mg and β-Li phases, a small amount of Li3Mg7, Li2MgAl and AlLi phases were obtained. Compared with the base metal (BM), the weakening of the crystallographic texture occurred in the FSPed material, and the c-axis of the α-phase and the <001> crystallographic orientation of the β-phase were tilted about 45° with respect to the transverse direction (TD). The average microhardness (HV 67.8) of the stir zone was higher than that of the BM (HV 61.5). The yield strength (YS) and the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of the FSPed material were higher than those of the BM, while the elongation slightly reduced. Grain refinement had more significant effect on strength improvement compared with the texture variation for the FSPed material. The fracture surfaces of the BM and FSPed materials showed dimple characteristics.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiu X, Yang Q, Guan K, Bu F, Cao ZY, Liu YB, Meng J. Microstructures and tensile properties of Mg–Zn–(Gd)–Zr alloys extruded at various temperatures. Rare Met. 2017;36(12):962.
Li D, Xue HS, Yang G, Zhang DF. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–6Zn–0.5Y magnesium alloy prepared with ultrasonic treatment. Rare Met. 2017;36(8):622.
Wang Y, Choo H. Influence of texture on Hall–Petch relationships in an Mg alloy. Acta Mater. 2014;81:83.
Li X, Li ZL, Duan BY, Li YM, Xu YL. Microstructure and texture of dimensional asymmetric spray deposited magnesium alloy containing Gd by extruding-rolling. Rare Met. 2018;37(10):1024.
Yang CW. Effect of friction stir processing on the microstructural evolution and tensile behaviors of an α/β dual-phase Mg–Li–Al–Zn alloy. Mater Trans. 2014;55(2):371.
Chen HC, Hung FY, Lui TS, Chen LH, Huang JW. Effects of friction stir process and stabilizing heat treatment on the tensile and punch-shear properties of Mg–9Li–2Al–1Zn magnesium alloy. Mater Trans. 2013;54(4):505.
Wang J, Zhang Q, Qin JY. Structural transition region of liquid Mg–Li alloys. Comput Mater Sci. 2016;117:259.
Kim WJ, Hong SI, Kim YS, Min SH, Jeong HT, Lee JD. Texture development and its effect on mechanical properties of an AZ61 Mg alloy fabricated by equal channel angular pressing. Acta Mater. 2014;51(11):3293.
Lin JB, Ren WJ, Wang QD, Ma LF, Chen YJ. Influence of grain size and texture on the yield strength of Mg alloys processed by severe plastic deformation. Adv Mater Sci Eng. 2014;2014(1):1.
Anne G, Ramesh MR, Nayaka HS, Arya SB. Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn/Al multilayered composite developed by accumulative roll bonding. Perspect Sci. 2016;8(C):104.
Srinivasarao B, Zhilyaev AP, Urrutia IG, Prado MTP. Stabilization of metastable phases in Mg–Li alloys by high-pressure torsion. Scr Mater. 2013;68(8):583.
Mishra RS, Ma ZY. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater Sci Eng R. 2005;50(1):1.
Khorrami MS, Kazeminezhad M, Miyashita Y, Kokabi AH. Improvement in the mechanical properties of Al/SiC nanocomposites fabricated by severe plastic deformation and friction stir processing. Int J Min Met Mater. 2017;24(3):297.
Akinlabi ET, Mahamood RM, Akinlabi SA, Ogunmuyiwa E. Microstructure and wear behavior of AA6061/SiC surface composite fabricated via friction stir processing with different pins and passes. Rare Met. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0691-x.
Cartigueyen S, Mahadevan K. Influence of rotational speed on the formation of friction stir processed zone in pure copper at low-heat input conditions. J Manuf Process. 2015;18:124.
Xie GM, Cui HB, Luo ZA, Misra RDK, Wang GD. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of the stir zone during friction stir processing a lean duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A. 2017;704:311.
Xue G, Zhang Z, Wang W, Hai MN, Jia SW, Wang KS. Superplasticity of fine-grained AZ31/magnesium alloy prepared by friction stir processing. Rare Met Mater Eng. 2016;45(7):1855.
Valle JAD, Rey P, Gesto D, Verdera D, Jiménez JA, Ruano OA. Mechanical properties of ultra-fine grained AZ91 magnesium alloy processed by friction stir processing. Mater Sci Eng A. 2015;628(2):198.
Xu N, Bao YF. Enhanced mechanical properties of tungsten inert gas welded AZ31 magnesium alloy joint using two-pass friction stir processing with rapid cooling. Mater Sci Eng A. 2016;655:292.
Yang Q, Feng AH, Xiao BL, Ma ZY. Influence of texture on superplastic behavior of friction stir processed ZK60 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;556(9):671.
Jamili AM, Hanzaki AZ, Abedi HR, Minárik P, Soltani R. The microstructure, texture, and room temperature mechanical properties of friction stir processed Mg–Y–Nd alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2017;690:244.
Yuan W, Mishra RS, Carlson B, Mishra RK, Verma R, Kubic R. Effect of texture on the mechanical behavior of ultrafine grained magnesium alloy. Scr Mater. 2011;64(6):580.
Liu FC, Tan MJ, Liao J, Ma ZY, Meng Q, Nakata K. Microstructural evolution and superplastic behavior in friction stir processed Mg–Li–Al–Zn alloy. J Mater Sci. 2013;48(24):8539.
Wu SK, Li YH, Chien KT, Chien C, Yang CS. X-ray diffraction studies on cold-rolled/solid-solution treated α + β Mg–10.2Li–1.2Al–0.4Zn alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2013;563:234.
Mironov S, Zhang Y, Sato YS, Kokawa H. Development of grain structure in β-phase field during friction stir welding of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Scr Mater. 2008;59(1):27.
Yu ZZ, Choo H, Feng ZL, Vogel SC. Influence of thermo-mechanical parameters on texture and tensile behavior of friction stir processed Mg alloy. Scr Mater. 2010;63(11):1112.
Vargas M, Lathabai S, Uggowitzer PJ, Qi Y, Orlov D, Estrin Y. Microstructure, crystallographic texture and mechanical behaviour of friction stir processed Mg–Zn–Ca–Zr alloy ZKX50. Mater Sci Eng A. 2017;685:253.
Wang YN, Chang CI, Lee CJ, Lin HK, Huang JC. Texture and weak grain size dependence in friction stir processed Mg–Al–Zn alloy. Scr Mater. 2006;55(7):637.
Yuan W, Mishra RS, Carlson B, Verma R, Mishra RK. Material flow and microstructural evolution during friction stir spot welding of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;543(5):200.
Srinivasu R, Rao AS, Reddy GM, Rao KS. Friction stir surfacing of cast A356 aluminium–silicon alloy with boron carbide and molybdenum disulphide powders. Def Technol. 2015;11(2):140.
Luo C, Li X, Song D, Zhou N, Li Y, Qi W. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of friction stir welded dissimilar joints of Mg–Zn–Gd and Mg–Al–Zn alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2016;664:103.
Zeng Y, Jiang B, Yang QR, Quan GF, He JJ, Jiang ZT, Pan FS. Effect of Li content on microstructure, texture and mechanical behaviors of the as-extruded Mg–Li sheets. Mater Sci Eng A. 2017;700:59.
Karami M, Mahmudi R. Work hardening behavior of the extruded and equal-channel angularly pressed Mg–Li–Zn alloys under tensile and shear deformation modes. Mater Sci Eng A. 2014;607:512.
Kumar N, Mishra RS, Dahotre NB, Brennan RE, Doherty KJ, Cho KC. Effect of friction stir processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser-processed Mg–4Y–3Nd alloy. Mater Des. 2016;110:663.
Chao HY, Sun HF, Wang ED. Working hardening behaviors of severely cold deformed and fine-grained AZ31Mg alloys at room temperature. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2011;21:s235.
Xue P, Wang BB, Chen FF, Wang WG, Xiao BL, Ma ZY. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir processed Cu with an ideal ultrafine-grained structure. Mater Charact. 2016;121:187.
Wu HJ, Wang TZ, Wu RZ, Hou LG, Zhang JH, Li XL, Zhang ML. Effects of annealing process on the interface of alternate α/β Mg–Li composite sheets prepared by accumulative roll bonding. J Mater Process Technol. 2018;254:265.
Liu T, Zhang W, Wu SD, Jiang CB, Li SX, Xu YB. Mechanical properties of a two-phase alloy Mg–8%Li–1%Al processed by equal channel angular pressing. Mater Sci Eng A. 2003;360(1–2):345.
Wei GB, Mahmoodkhani Y, Peng XD, Hadadzadeh A, Xu TC, Liu JW, Xie WD, Wells MA. Microstructure evolution and simulation study of a duplex Mg–Li alloy during double change channel angular pressing. Mater Des. 2016;90:266.
Dong HW, Wang LM, Liu K, Wang LD, Jiang B, Pan FS. Microstructure and deformation behaviors of two Mg–Li dual-phase alloys with an increasing tensile speed. Mater Des. 2016;90:157.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51574192, 51404180, 51274161 and U1360105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Che, QY., Wang, KS., Wang, W. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of magnesium–lithium alloy prepared by friction stir processing. Rare Met. 40, 2552–2559 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01217-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01217-2