Abstract
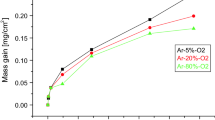
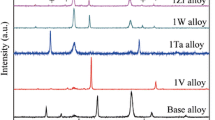
The oxidation behavior of a novel multi-element alloyed Ti2AlNb-based alloy (Ti–22Al–25Nb–1Mo–1V–1Zr–0.2Si) was studied in the temperature range of 650–850 °C. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with an energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) were used to identify the phase constituents and microstructure of the scales formed on the specimens after oxidation at different temperatures. Isothermal oxidation tests show that the oxidation rate of the alloyed Ti2AlNb-based alloy is obviously reduced at all temperatures, and the mass gains are very low for this alloy in comparison with those of Ti–22Al–25Nb alloy. The alloying elements Mo, V, Zr and Si have an obvious affect on the oxidation products of the alloys. The improved oxidation resistance for the alloy is ascribed to the introduction of Mo, V, Zr and Si elements, which are beneficial to the selective oxidation of Al to form protective oxides while are disadvantage of the formation of poor oxidation resistance oxides such as AlNbO4.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang GQ, Yuan MN, Li SX, Hou HL, Qu HT, Zhao B. Fabrication and interface reaction of SiC fiber reinforced Ti/Ti2AlNb laminated composite. Chin J Rare Met. 2017;41(10):1093.
Liang YF, Xu XJ, Lin JP. Advances in phase relationship for high Nb-containing TiAl alloys. Rare Met. 2016;35(1):15.
Hou ZY, Li YS, Mei HJ, Hu K, Chen G. Lamellar morphology of directional solidified Ti–45Al–6Nb–xW alloys. Rare Met. 2016;35(1):1.
Dey SR, Roy S, Suwas S, Fundenberger JJ, Ray RK. Annealing response of the intermetallic alloy Ti–22Al–25Nb. Intermetallics. 2010;18(6):1122.
Gogia AK, Nandy TK, Banerjee D, Carisey T, Strudel JL, Franchet JM. Microstructure and mechanical properties of orthorhombic alloys in the Ti–Al–Nb system. Intermetallics. 1998;6(7–8):741.
Boehlert CJ, Majumdar BS, Seetharaman V, Miracle DB. Part I. The microstructural evolution in Ti–Al–Nb O + Bcc orthorhombic alloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 1999;30A(9):2305.
Xue C, Zeng WD, Xu B, Liang XB, Zhang JW, Li SQ. B2 grain growth and particle pinning effect of Ti–22Al–25Nb orthorhombic intermetallic alloy during heating process. Intermetallics. 2012;29(10):41.
Wang W, Zeng WD, Xue C, Liang XB, Zhang JW. Microstructure control and mechanical properties from isothermal forging and heat treatment of Ti–22Al–25Nb (at.%) orthorhombic alloy. Intermetallics. 2015;56(4):79.
Zhu HP, Qu SJ, Qi GY, Shen J. High temperature oxidation behavior of as-rolled Ti2AlNb-based alloy. Chin J Rare Met. 2016;42(2):104.
Peng JH, Mao Y, Li SQ, Sun XF. Microstructure controlling by heat treatment and complex processing for Ti2AlNb based alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2001;299(1):75.
Wang W, Zeng WD, Xue C, Liang XB, Zhang JW. Designed bimodal size lamellar O microstructures in Ti2AlNb based alloy: microstructural evolution, tensile and creep properties. Mater Sci Eng A. 2014;618:288.
Wang GF, Yang JL, Jiao XY. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–22Al–25Nb alloy fabricated by elemental powder metallurgy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2016;654:69.
Germann L, Banerjee D, Guédou JY, Strudel JL. Effect of composition on the mechanical properties of newly developed Ti2AlNb-based titanium aluminide. Intermetallics. 2005;13(9):920.
Lin P, He ZB, Yuan SJ, Shen J. Tensile deformation behavior of Ti–22Al–25Nb alloy at elevated temperatures. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;556(11):617.
Mao Y, Li SQ, Zhang JW, Peng JH, Zou DX, Zhong ZY. Microstructure and tensile properties of orthorhombic Ti–Al–Nb–Ta alloys. Intermetallics. 2000;8(5–6):659.
Peng JH, Li SQ, Mao Y, Sun XF. Phase transformation and microstructures in Ti–Al–Nb–Ta system. Mater Lett. 2002;53(1–2):57.
Tang F, Nakazawa S, Hagiwara M. The effect of quaternary additions on the microstructures and mechanical properties of orthorhombic Ti2AlNb-based alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2002;329–331(6):492.
Yang SJ, Nam SW, Hagiwara M. Phase identification and effect of W on the microstructure and micro-hardness of Ti2AlNb-based intermetallic alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2003;350(1):280.
Chen YY, Si YF, Kong FT, Liu ZG, Li JW. Effects of yttrium on microstructures and properties of Ti–17Al–27Nb alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2006;16(2):316.
Chen YY, Xiao SL, Wang ZT, Kong FT, Xu LJ. The effect of yttrium addition on the oxidation resistance of Ti2AlNb based alloy. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed. 2009;25(S1):5.
Zhang TB, Huang G, Hu R, Li JS. Microstructural stability of long term aging treated Ti–22Al–26Nb–1Zr orthorhombic titanium aluminide. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2015;25(8):2549.
Mao Y, Hagiwara M, Emura S. Creep behavior and tensile properties of Mo- and Fe-added orthorhombic Ti–22Al–11Nb–2Mo–1Fe alloy. Scripta Mater. 2007;57(3):261.
Depka T, Somsen C, Eggeler G, Mukherji D, Rösler J, Krüger M, Saage H, Heilmaier M. Microstructures of Co–Re–Cr, Mo–Si and Mo–Si–B high-temperature alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2009;510–511(10):337.
Shen Y, Ding XF, Wang FG, Tan Y, Yang JM. High temperature oxidation behavior of Ti–Al–Nb ternary alloys. J Mater Sci. 2004;39(21):6583.
Leyens C, Gedanitz H. Long-term oxidation of orthorhombic alloy Ti–22Al–25Nb in air between 650 and 800 °C. Scripta Mater. 1999;41(8):901.
Zheng DY, Xiong YM, Zhu SL, Li MS, Wang FH. Oxidation and hot corrosion behavior of Ti2AlNb-based alloy with and without enamel coating at 800 °C. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2006;16(s3):s2050.
Wang YH, Liu ZG, Ouyang JH, Wang YM, Zhou Y. Influence of electrolyte compositions on structure and high-temperature oxidation resistance of microarc oxidation coatings formed on Ti2AlNb alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2015;647:431.
Zhang XJ, Zhao SY, Gao CX, Wang L, Wang SJ, Zhang Y. Oxidation behavior of Ti–22Al–26Nb alloy at high temperatures. Rare Metal Mater Eng. 2009;38(12):2183.
Dang W, Li JS, Zhang TB, Kou HC. Oxidation behavior of Zr-containing Ti2AlNb-based alloy at 800 °C. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2015;25(3):783.
Dang W, Li JS, Zhang TB, Kou HC. High-temperature oxidation behavior of Ti–22Al–27(Nb, Zr) alloys. Rare Met Mater Eng. 2015;44(2):0261.
Zhu HP, Qu SJ, Qi GY, Shen J. High temperature oxidation behavior of as-rolled Ti2AlNb-based alloy. Chin J Rare Met. 2016;40(2):104.
Leyens C. Oxidation of orthorhombic titanium aluminide Ti–22Al–25Nb in air between 650 and 1000 °C. J Mater Eng Perform. 2001;10(2):225.
Małecka J. Investigation of the oxidation behavior of orthorhombic Ti2AlNb alloy. J Mater Eng Perform. 2015;24(5):1834.
Leyens C. Environmental effects on orthorhombic alloy Ti–22Al–25Nb in air between 650 and 1000 °C. Oxid Met. 2000;54(1/2):475.
Roy TK, Balasubramaniam R, Ghosh A. High-temperature oxidation of Ti3Al-based titanium aluminides in oxygen. Metall Mater Trans A. 1996;27(12):3993.
Ramachandran M, Reddy RG. Effect of Nb and Mo on the oxidation rates of Ti–Al intermetallics. High Temp Mater Process. 2008;27(4):235.
Shida Y, Anada H. Role of W, Mo, Nb and Si on oxidation of TiAl in air at high temperatures. Mater Trans. 1994;35(9):623.
Chen G, Sun Z, Zhou X. Oxidation of intermetallic alloys in Ti–Al–Nb ternary system. Corrosion. 1992;48(11):939.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51601146) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2017M613234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, YS., Hu, R., Luo, WZ. et al. Oxidation behavior of a novel multi-element alloyed Ti2AlNb-based alloy in temperature range of 650–850 °C. Rare Met. 37, 838–845 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1101-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1101-3