Abstract
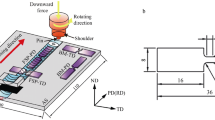
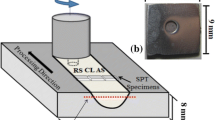
Mg-3.99Y-3.81Nd-0.53Zr (WE43) casting alloy was subjected to single-pass friction stir processing (FSP) at a constant processing speed of 60 mm·min−1 and various rotation speeds of 400, 800, 1200, and 1500 r·min−1, and microstructures and mechanical properties of the experimental materials were investigated. FSP results in the generation of fine-grained microstructure, and fundamental breakage and dissolution of the coarse second phases. With the rotation speeds increasing, the average grain size of the FSP specimen in the stir zone first decreases and then increases, and the finest microstructure (~2 μm) was prepared at the rotation speed of 800 r·min−1. Owing to the finer and more uniform microstructure, the mechanical properties of WE43 alloy after FSP are significantly improved. The variation tendency of the tensile properties is consistent with the change of the grain size. The maximum tensile strength, elongation, and average microhardness of the FSP WE43 alloy obtained at 800 r·min−1 are 290 MPa, 17.2 %, and HV 92.9, respectively. The fracture morphology shows that small dimples can be observed on the FSP specimens, while the as-cast alloy fails through cleavage fracture.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi WY, Ma Y. Microstructure of ZM6 magnesium alloy with different Nd content. Rare Met. 2013;32(3):234.
Xu DK, Liu L, Xu YB, Han EH. The effect of precipitates on the mechanical properties of ZK60-Y alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2006;420(1):322.
Mohri T, Mabuchi M, Saito N, Nakamura M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a Mg-4Y-3RE alloy processed by thermo-mechanical treatment. Mater Sci Eng A. 1998;257(2):294.
Panigrahi SK, Yuan W, Mishra RS, DeLorme R, Davis B, Howell RA, Cho K. A study on the combined effect of forging and aging in Mg-Y-RE alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2011;530:28.
Ryspaev T, Trojanová Z, Padalka O, Wesling V. Microstructure of superplastic QE22 and EZ33 magnesium alloys. Mater Lett. 2008;62(24):4041.
Mishra RS, Ma ZY. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater Sci Eng R. 2005;50(1):1.
Yang SY, Zhong HR, Tao YS, Yang Y. Microstructure and properties of friction stir welded joints of magnesium rare earth alloy. Chin J Rare Met. 2013;37(1):37.
Yang Q, Feng AH, Xiao BL, Ma ZY. Influence of texture on superplastic behavior of friction stir processed ZK60 magnesium alloy. Mat Sci Eng A. 2012;556:671.
Feng AH, Ma ZY. Microstructural evolution of cast Mg-Al-Zn during friction stir processing and subsequent aging. Acta Mater. 2009;57(14):4248.
Tsujikawa M, Chung SW, Tanaka M, Takigawa Y, Oki S, Higashi K. High-strengthening of Mg-5.5 mass % Y-4.3 mass % Zn cast alloy by friction stir processing. Mater Trans. 2005;46(12):3081.
Freeney TA, Mishra RS. Effect of friction stir processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of a cast-magnesium–rare earth alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2010;41(1):73.
Xiao BL, Yang Q, Yang J, Wang WG, Xie GM, Ma ZY. Enhanced mechanical properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr casting via friction stir processing. Alloys Compd. 2011;509(6):2879.
Yang Q, Xiao BL, Ma ZY. Influence of process parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction-stir-processed Mg-Gd-Y-Zr casting. Metall Mater Trans A. 2012;43(6):2094.
Ping DH, Hono K, Nie JF. Atom probe characterization of plate-like precipitates in a Mg-RE-Zn-Zr casting alloy. Scr Mater. 2003;48(8):1017.
Zhang HJ, Liu HJ, Yu L. Microstructure and mechanical properties as a function of rotation speed in underwater friction stir welded aluminum alloy joints. Mater Des. 2011;32(8):4402.
Chen ZW, Pasang T, Qi Y. Shear flow and formation of nugget zone during friction stir welding of aluminum alloy 5083-O. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008;474(1):312.
Chang CI, Lee CJ, Huang JC. Relationship between grain size and Zener-Holloman parameter during friction stir processing in AZ31 Mg alloys. Scr Mater. 2004;51(6):509.
Feng AH, Xiao BL, Ma ZY, Chen RS. Effect of friction stir processing procedures on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Al-Zn casting. Metall Mater Trans A. 2009;40(10):2447.
Laser T, Hartig C. Nu¨rnberg MR, Letzig D, Bormann R. The influence of calcium and cerium mischmetal on the microstructural evolution of Mg-3Al-1Zn during extrusion and resulting mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2008;56(12):2791.
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2012ZZ0051)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhang, DT., Chai, F. et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of WE43 magnesium alloy prepared by friction stir processing. Rare Met. 39, 1267–1272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0306-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0306-3