Abstract
Rare metals play an important role in development of superalloys. Over the last two decades, the application of the rare metals in superalloys has achieved progress significantly. They present multi-beneficial effects for strengthening the matrix and the γ′ phase, increasing the lattice misfit, cleaning the grain boundary, improving the carbides and eutectics, refining the grain, stabilizing the oxidation film, etc., so that the elevated temperature rupture life and elevated temperature oxidation resistance are improved significantly, leading to a broad application in the superalloys. In order to meet the higher demand for better superalloys in the future, more intensive research is necessary on the effects of the rare metals on the superalloy, and especially on the combination effect of various rare metals and mutual influence among them. Utilization of the computational materials science and combinatorial high throughput experiment will be of importance in application of rare metals in superalloys.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthod P, Michon S, Di Martino J, Mathieu S, Noël S, Podor R, Rapin C. Thermodynamic calculations for studying high temperature oxidation of superalloys. Calphad. 2003;27(3):279.
Berthod P, Aranda L, Vébert C, Michon S. Experimental and thermodynamic study of the high temperature microstructure of tantalum containing nickel-based alloys. Calphad. 2004;28(2):1596.
Wang YQ, Wei YH, Yang NS. Influence of lanthanum on stress rupture property of Ni–20Cr–20Co–18W superalloy. J Iron Steel Res. 1985;5:69.
Chen SF, Ma HP, Ju Q, Zhao GP. Effect of rare earth element lanthanum on oxidation behavior of GH230 at 1000 °C in air. J Iron Steel Res. 2009;21(11):45.
Lin QY. Segregation and action of lanthanum in NiCrCoW alloy. J Chin Rare Earth Soc. 1998;16(2):158.
Zeng BS, Wu SQ, Zhang SL. Role and distribution of La in Co-base superalloy GH188. J Chin Rare Earth Soc. 1986;4:45.
Pan XL, Yu HY, Tu GF, Sun WR, Hu ZQ. Effect of rare earth metals on solidification behaviour in nickel based superalloy. Mater Sci Technol. 2012;28:560.
Chen SF, Ma HP, Ju Q, Zhao GP. Effect of lanthanum content on the microstructure and property of GH230 alloy. China Metall. 2009;19(10):13.
Meng ZB, Zeng BS, Wang ZG. Study on lanthanide precipitate type and magnesium segregation to gra in boundary in cobalt-base superalloy GH188. J Iron Steel Res. 1999;11(3):30.
Guo JT, Zhou LZ, Yuan C, Hou JS, Qin XZ. Microstructure and properties of several originally invented and unique superalloys in China. Chin J Nonferrous Met. 2011;21(2):237.
Zheng L, Xiao CB, Zhang GQ, Yuan H, Han B. Tang Dingzhong, Investigation of the master alloy cleanliness of high Cr content cast Ni-base superalloy K4648. J Mater Eng. 2012;3:1.
Li XB. Effect of cerium on solidification segregation of sulfur in nickel-based C-4 alloy. Foundry Technol. 2003;24:434.
Anliker DM, Newkirk JB. The effects of cerium on the microstructure of INCO 901 superalloy. Metall Trans A. 1976;7A:1711.
Cui C, Han G, Sun X. Effect of Ce addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of a Ni–Co-based superalloy. Adv Mater Res. 2012;415–417:2062.
Yangshan S, Zhengjun Y, Zhonghua Z, Haibo H. Mechanical properties of Fe3Al-based alloys with cerium addition. Scr Metall Mater. 1995;33(5):811.
Guo JT, Ren WL, Zhou JY. Effect of rare earth elements on intermetallics (aluminides). Mater Eng. 2002;1:36.
Li H, Guo JT, Sun C, Wang SH, Tan MH. Effect of yttrium and cerium on compression properties of Ni3Al-based alloy. J Chin Rare Earth Soc. 1991;9(3):243.
Li FM, Qian XY, Li JG, Wang LA, Zhao J. Application and development trend of rare earth in aviation industry. Mater Eng. 1998;6:10.
Zhang GY, Tan GN, Zhang H, Li HQ. Effect of different content of Ce on oxidation resistance of NiAl–28Cr–5.5Mo–0.5H alloy. Chin J Rare Met. 2009;33(3):333.
Zhang SZ, Guo JT, Ren WL, Zhou WL. Effects of rare earth elements on high temperature oxidation resistance of NiAl/CrMo(Hf) alloy. J Chin Soc Corros Prot. 2005;25(12):110.
Shi ST, Huang YW, Han Y. Influence of rare earth metals Y, Ce and La on the high temperature sulfidation of Fe–25Cr–40Ni superalloy. Key Eng Mater. 1991;20–28(2):1617.
Fox AG, Tabbernor MA. The bonding charge density of β′NiAl. Acta Metall Mater. 1991;39(4):669.
Whittenberger JD, Raj SV, Locci I, Salem J. Elevated temperature strength and room-temperature toughness of directionally solidified Ni–33Al–33Cr–1Mo. Metall Mater Trans A. 2002;33(5):1385.
Johnson DR, Chen XF, Oliver BF, Noebe RD, Whittenberger JD. Processing and mechanical properties of in situ composites from the NiAlCr and the NiAl (Cr, Mo) eutectic systems. Intermetallics. 1995;3(2):99.
Kumar KS, Mannan SK, Viswanadham RK. Fracture toughness of NiAl and NiAl-based composites. Acta Metall Mater. 1992;40(6):1201.
Cui CY, Guo JT, Qi YH, Ye HQ. High temperature embrittlement of NiAl alloy induced by hot isostatic pressing (HIPing) and aging. Scr Mater. 2001;44(10):2437.
Guo JT, Sheng LY, Tian YX, Zhou LZ, Ye HQ. Effect of Ho on the microstructure and compressive properties of NiAl-based eutectic alloy. Mater Lett. 2008;62(23):3910.
Li H, Guo J, Huai K, Ye H. Microstructure characterization and room temperature deformation of a rapidly solidified NiAl-based eutectic alloy containing trace Dy. J Cryst Growth. 2006;290(1):258.
Sheng LY, Guo JT, Tian YX, Zhou LZ, Ye HQ. Microstructure and mechanical properties of rapidly solidified NiAl–Cr (Mo) eutectic alloy doped with trace Dy. J Alloy Compd. 2009;475(1–2):730.
Xie Y, Guo JT, Liang YC, Zhou LZ, Ye HQ. Modification of NiAl–Cr(Mo)–0.15Hf alloy by Sc addition. Intermetallics. 2009;17(6):400.
Sun B, Che X, Yang G, Zhou Y, Lin D. The ductility of La-doped rapidly solidified NiAl. Scr Metall Mater. 1995;33(7):1145.
Yang JM, Jeng SM, Bain K, Amato RA. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of in situ directional solidified NiAl/Cr (Mo) eutectic composite. Acta Mater. 1997;45(1):295.
Weili R, Jianting G, Jiyang Z. Influences of yttrium on microstructure and mechanical properties of NiAl–28Cr–5.5Mo–0.5Hf alloy. J Rare Earths. 2002;20(4):295.
Ren WL, Guo JT, Li GS, Zhou JY. Effect of Nd on microstructure and mechanical properties of NiAl-based intermetallic alloy. Mater Lett. 2003;57(8):1374.
Ren WL, Guo JT, Li GS, Zhou JY. The role of Nd solid-solution and grain-boundary segregation in binary NiAl intermetallic compound. J Mater Sci Technol. 2004;20:163.
Liang YC, Guo JT, Zhou LZ, Xie Y, Hu ZQ. Effect of Gd on the microstructures and properties of NiAl intermetallics. Aci Metall Sin. 2008;44:535.
Han YF, Xiao CB. Effect of yttrium and silicon on microstructure and properties of Ni3AI base alloy IC6. Aci Metall Sin. 1998;34(11):1153.
Wang RM, Li CZ, Yan MG. Micro-mechanism study on the properties affects in a low expansion superalloy GH907 with addition of rare elements. Mater Eng. 2001;7:25.
Zhou PJ, Yu JJ, Sun XF, Guan HR, He XM, Hu ZQ. Influence of Y on stress rupture property of a Ni-based superalloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;551:236.
Peng ZJ, Li ZJ, Hou JS, Man YL, Guo JT, Zhou LZ. Effect of yttrium and cerium on microstructure and mechanical properties of revert nickel-base superalloy K444 with low hafnium content. J Chin Rare Earth Soc. 2009;27(6):822.
Wang RM, Song YG, Han YF. Effect of rare earth on the microstructures and properties of a low expansion superalloy. J Alloy Compd. 2000;311(1):60.
Guo JT, Huai KW, Gao Q, Ren WL, Li GS. Effects of rare earth elements on the microstructure and mechanical properties of NiAl-based eutectic alloy. Intermetallics. 2007;15(5–6):727.
Xiao CB, Han YF. Effect of silicon on microstructure and stress rupture properties at 1100 °C of yttrium modified Ni–Al–Mo–B alloy IC6. J Mater Sci. 2001;36(4):1027.
Zhou PJ, Yu JJ, Sun XF, Guan HR, Hu ZQ. Role of yttrium in the microstructure and mechanical properties of a boron-modified nickel-based superalloy. Scr Mater. 2007;57:643.
Ren WL. Microstructure and mechanical properties of NiAl-based eutectic alloys and alloying behavior of rare earths. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology; 2002, 1.
Zhou YJ, Zhang GY, Wang ZY, Yang Z. Study on influence of rare earth elements on properties of Ni-base superalloys through electron theory. Rare Metal Mater Eng. 2007;36(12):2160.
Yu P, Wang YQ. Oxidation behavior of K38G superalloy with 0.1 mass% yttrium at 1000 °C in air. Corros Sci Prot Technol. 2007;19(3):189.
Xiao CB, Han YF. Effect of yttrium on the microstructure and high temperature oxidation resistance of Ni3Al base alloyIC6. J Mater Eng. 1998;6:22.
Wang SH, Guo JT, Li H, Sun C, Tan MH, Lai WH. On the YNi5 phase and its effect upon properties of Ni3Al alloy. Metall Sin. 1991;27(6):A433.
Yu P, Wang YQ, Wang W. Effect of reactive element yttrium on oxidation behavior of K38G superalloy at 800 °C in air. Corros Sci Prot Technol. 2006;18(3):183.
Xiao CB, Han YF. Interface behavior of sulfur and yttrium in the yttrium modified Ni3Al-base alloy IC6 during high temperature oxidation process. J Chin Rare Earths Soc. 1999;17(4):377.
Erickson GL. The development and application of CMSX-10. Superalloys. 1996;1996:35.
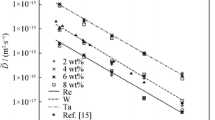
Li JR, Tang DZ, Chen RZ. Effect of rhenium (Re) in single crystal superalloys. J Mater Eng. 1997;8:3.
Sha W, Cerezo A, Smith G. Phase chemistry and precipitation reactions in maraging steels: part III. model alloys. Metall Trans A. 1997;16:1985.
Erickson GL. The development of CMSX-10, a third generation SX casting superalloy. In: Proceedings of the second pacific rim international conference on advanced materials and processing (PRCIM-2). Kyongju, 1995, 22.
Fullagar KPL, Harris K, Erickson GL, Broomfield RW, Hulands M, Sikkenga SL. Aero engine test experience with CMSX-4 alloy single crystal turbine blades. J Eng Gas Turbines Power. 1996;118(2):380.
Darolia RDF, Lahrman RD. Field, formation of topologically close packed phases in nickel-base single crystal superalloys. In: The Sixth International Symposium on Superalloys–Superalloys 1988. Pennsylvania: Champion, 1988. 255.
Walston W, Schaeffer J, Murphy W. A new type of microstructural instability in superalloys-SRZ. In: The Eighth International Symposium on Superalloys–Superalloys 1996. Pennsylvania: Champion, 1996. 9.
Pollock TM, Murphy WH, Goldman EH, Uram DL, Tu JS. Grain defect formation during directional solidification of nickel base single crystals. In: The Seventh International Symposium on Superalloys–Superalloys 1992. Pennsylvania: Champion, 1992. 125.
Sato A, Harada H, Yokokawa T, Murakumo T, Koizumi Y, Kobayashi T, Imai H. The effects of ruthenium on the phase stability of fourth generation Ni-base single crystal superalloys. Scr Mater. 2006;54:1679.
Yeh AC, Tin S. Effects of Ru on the high-temperature phase stability of Ni-base single-crystal superalloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 2006;37(9):2621.
Sato A, Harada H, Yokokawa T, Murakumo T, Koizumi Y, Kobayashi T, Imai H. The effects of ruthenium on the phase stability of fourth generation Ni-base single crystal superalloys. Scr Mater. 2006;54(9):1679.
Hobbs RA, Zhang L, Rae CMF, Tin S. The effect of ruthenium on the intermediate to high temperature creep response of high refractory content single crystal nickel-base superalloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008;489(1–2):65.
Feng Q, Nandy TK, Pollock TM. Observation of a Ru-rich Heusler phase in a multicomponent Ni-base superalloy. Scr Mater. 2004;50(6):849.
Yeh AC, Tin S. Effects of Ru and Re additions on the high temperature flow stresses of Ni-base single crystal superalloys. Scr Mater. 2005;52(6):519.
Caldwell EC, Fela FJG, Fuchs E. Segregation of elements in high refractory content single crystal ni-based superalloy. In: The 10th International Symposium on Superalloys–Superalloys 2004. Pennsylvania: Champion, 2004. 811.
Hobbs RA, Tin S, Rae CMF, Hinton BRW, Aitken HCJ. Solidification characteristic of advanced Ni-base single crystal superalloys. In: The 10th International Symposium on Superalloys–Superalloys 2004. Pennsylvania: Champion, 2004, 819.
Kearsey, R.M., J.C. Beddoes, K.M. Jaansalu, W.T. Thompson, A. P., The effects of Re, W and Ru on microsegregation behaviour in single crystal superalloy systems. In: The 10th International Symposium on Superalloys -Superalloys 2004, Champion, Pennsylvania, 2004: 801.
Koizumi, Y., T. Kobayashi, J. Zhang, T. Yokokawa, H. Harada, Y. Aoki, A. M. Development of a Next-Generation Ni-base Single Crystal Superalloy. In: Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress. Tokyo. 2003. 1.
Zhang JX, Murakumo T, Koizumi Y, Kobayashi T, Harada H, Masaki S Jr. Interfacial dislocation networks strengthening a fourth-generation single-crystal TMS-138 superalloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2002;33(12):3741.
Carroll LJ, Feng Q, Mansfield JF, Pollock TM. High refractory, low misfit ru-containing single-crystal superalloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 2006;37(10):2927.
Ofori AP, Rossouw CJ, Humphreys CJ. Determining the site occupancy of Ru in the L12 phase of a Ni-base superalloy using ALCHEMI. Acta Mater. 2005;53(1):97.
Carroll LJ, Feng Q, Mansfield JF, Pollock TM. Elemental partitioning in Ru-containing nickel-base single crystal superalloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2007;457(1–2):292.
Reed RC, Yeh AC, Tin S, Babu SS, Miller MK. Identification of the partitioning characteristics of ruthenium in single crystal superalloys using atom probe tomography. Scr Mater. 2004;51:327.
Zhu QX, Guan H. Effect of niobium on creep property of nickel- based alloy. Phys Exam Test. 2005;23(3):33.
Li HF, Liu ZL, Xiang LX, Zhou LC. Effects of niobium on strengthening of GH871 superalloy. Ordnance Mater Sci Eng. 1998;21(4):21.
Chen GS, Wu BH, Zhou LC, Li YQ. Effect of Nb on strengthening of Fe-base superalloy at medium high temperature. Acta Metall Sin. 1992;28(9):385.
Shi YJ, Du YL, Chen G. Progress in research on high niobium containing TiAl-based alloy. Chin J Rare Met. 2007;31(6):834.
Zhang WJ, Deevi SC, Chen GL. On the origin of superior high strength of Ti–45Al–10Nb alloys. Intermetallics. 2002;10(5):403.
Paul JDH, Appel F, Wagner R. The compression behaviour of niobium alloyed γ-titanium alumindies. Acta Mater. 1998;46(4):1075.
Zhang W, Liu Y, Huang JS, Liu B, He YH. Research progress and prospects for refractory TiAl alloy with high Nb content. Rare Met Lett. 2007;26(8):1.
Zheng YR. The effect of Hf in cast superalloy solidification. Acta Metall Sin. 1986;22:A119.
Zheng YR. Influence of Hf on weld cracking for cast nickel base superalloys. Trans China Weld Inst. 1988;9:162.
Wang LB, Chen RZ, Wang YP. Influence of Hf content of on segregation behavior and mechanical properties of directionally solidified superalloy DZ22. Aeronaut Mater. 1989;9(2):1.
Zheng YR, Cai YL, Ruan ZC, Ma SW. Investigation of effect mechanism of Hf and Zr in high temperature materials. J Aeronaut Mater. 2006;26(3):25.
Zhen BL, Zhang SJ. The phase composition and the rules of the phase precipitation in Hf-bearing nickel base superalloys. J Iron Steel Res. 1981;1:65.
Larson JM, Volin TE, Larson FG. Effect of hafnium on powder metallurgy astrology. In: Braun JD, Arrowsmith HW, McCall JL, editors. Microstructural science. New York: American Elsevier Pub; 1977. 209.
Miner R. Effects of C and Hf concentration on phase relations and microstructure of a wrought powder-metallurgy superalloy. Metall Trans A. 1977;8(2):259.
Han SB, Zhang YW. Research overview on the effect of Hafnium on PM superalloy. Powder Metall Ind. 2009;19(5):48.
Johna R, Tadeub C, Davidc F, Josephd L, Anthony B. Effect of processing and composition on the structure and properties of P/M EP741NP type alloys. Chin J Aeronaut. 2007;20:97.
Voice W, Hardy M, Rugg D. Powder prospects ‘set for takeoff’ as production methods change. Met Powder Rep. 2005;60(4):8.
Radavich J, Carneiro T, Furrer D, Lemsky J, Banik A. The effect of hafnium, noibium and heat treatment on advanced powder metallurgy superalloys. In: proceedings of the eleventh international symposium on advanced superalloys. Shanghai, 2007, 114.
Zheng L, Gu CQ, Zhang GQ. Effect of Ta addition on microstructure of cast nickel base superalloys containing low level of Cr and high level of W. Rare Metal Mater Eng. 2005;34:194.
Sun YJ, Kang JG, Kong SK. Effect of Al, Ti and Ta on microstructure and properties of Ni-based single crystal superalloy. Spec Cast Nonferrous Alloys. 2008;28:660.
Zheng L. Formation and transformation of α phase in Ta-containing low Cr and high W content cast Ni-base superalloy. Chin J Nonferrous Met. 2005;15:1566.
Wu K, Liu GQ, Hu BF, Wu H, Zhang YW, Tao Y, Liu JT. Carbides in a new type Hf-Ta-containing nickle-based superalloy powder. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing. 2010;32:1464.
Zheng L, Gu CQ, Yu BZ, She L, Tang DZ. High-temperature oxidation behavior of low Cr and high W content cast Ni-base superalloy and effect of Ta alloying. J Aeronaut Mater. 2005;25:1.
Zhang J. Effect of Ti and Ta on hot cracking susceptibility of directionally solidified Ni-based superalloy IN792. Scr Mater. 2003;48:677.
Zheng L. Formation of eutectic (γ′ + α) and α transformation in Ta-bearing high W content cast Ni-base superalloys. Scr Mater. 2005;53(8):943.
Amouyal Yaron, Mao Zugang, Seidman DN. Effects of tantalum on the partitioning of tungsten between the γ′ and γ phase in nickel-based superalloys: linking experimental and computational approaches. Acta Mater. 2010;58:5898.
Gschneidner K, Ji M, Wang C, Ho K, Russell A, Mudryk Y, Becker A, Larson J. Influence of the electronic structure on the ductile behavior of B2 CsCl-type AB intermetallics. Acta Mater. 2009;57(19):5876.
Zhang Z, Russell AM, Biner SB, Gschneidner KA Jr, Lo CCH. Fracture toughness of polycrystalline YCu, DyCu, and YAg. Intermetallics. 2005;13(5):559.
Cao GH, Shechtman D, Wu DM, Becker AT, Chumbley LS, Lograsso TA, Russell AM, Gschneidner KA Jr. Determination of slip systems and their relation to the high ductility and fracture toughness of the B2 DyCu intermetallic compound. Acta Mater. 2007;55(11):3765.
Cao GH, Yu Z. Dislocations in the ductile B2 YAg intermetallic compound. J Alloy Compd. 2009;488(1):44.
Cao GH, Yu Z, Russell AM. The deformation behavior of DyCu ductile intermetallic compound under compression. Mater Sci Eng A. 2011;528(24):7173.
Acknowledgments
The supports from State Basic Research Development Program of China (No. 2010BC100404) and Shanghai Science and Technology Committee are acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, KD., Ren, ZM. & Li, CJ. Progress in application of rare metals in superalloys. Rare Met. 33, 111–126 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0256-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0256-9